6893-26-1
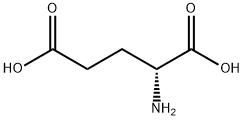 6893-26-1 結(jié)構(gòu)式
6893-26-1 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
D-麩胺酸
D-2-氨基戊二酸
D-麩氨酸
D-麩質(zhì)酸
D-谷氨酸(試劑)
D-Α-氨基戊二酸,D-Α-AMINOPENTANEDIOIC ACID
D-谷氨酸/Α-氨基戊二酸
D-谷氨酸, 99+%
NSC 77686
H-D-GLU-OH
d-glutamic
D-Glutamate
d-glutamicaci
D-Glutaminsure
D-GLUTAMIC ACID
(R)-GLUTAMIC ACID
GLUTAMIC ACID, D-
D-Glutaminic acid
(2R)-GlutaMic Acid
D-GLUCURONOLACTONE
D-(-)-GLUTAMIC ACID
D-GLUTAMIC ACID, 99+%
D-GlutaMic acid, 95+%
D-α-AMinoglutaric acid
D-2-AMINOGLUTARIC ACID
(R)-2-AMINOGLUTARIC ACID
D-GLUTAMIC ACID extrapure
(2R)-2-Aminoglutaric acid
D-ALPHA-AMINOGLUTARIC ACID
D-2-AMINOPENTANEDIOIC ACID
[R]-2-AMINOPENTANEDIOIC ACID
D(-)-GlutaMic acid, 99+% 5GR
D(-)-GlutaMic acid, 99+% 25GR
(2R)-2-aminopentanedioic acid
D-1-AMinopropane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid
(R)-1-AMINOPROPANE-1,3-DICARBOXYLIC ACID
(R)-2-Aminoglutaric acid, (R)-2-Aminopentanedioic acid, D-Glu, R-(-)-1-Aminopropane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
安全數(shù)據(jù)
知名試劑公司產(chǎn)品信息
D(-)-Glutamic acid, 99+%(6893-26-1)
D-Glutamic Acid,>98.0%(T)(6893-26-1)
| 報(bào)價(jià)日期 | 產(chǎn)品編號(hào) | 產(chǎn)品名稱 | CAS號(hào) | 包裝 | 價(jià)格 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-100805 | D-谷氨酸 D-Glutamic acid | 6893-26-1 | 500mg | 250元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-100805 | D-谷氨酸 D-Glutamic acid | 6893-26-1 | 1 g | 300元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-100805 | D-谷氨酸 D-Glutamic acid | 6893-26-1 | 5 g | 550元 |
常見(jiàn)問(wèn)題列表
|
Human Endogenous Metabolite
|
Various d-amino acids, such as D-serine, D-aspartic acid (D-Asp), and D-glutamic acid (D-Glu) are widely found in mammals including human beings and they are now thought to be the candidates of novel physiologically active substances and/or biomarkers. D-[Asp/Glu] (4 mg/mL) inhibits IgE binding (75%) to peanuts while D-Glu, D-Asp has no inhibitory effect. IgE is specific for D-[Asp/Glu] and may have the potential for removing IgE or reducing IgE binding to peanut allergens.
D-glutamic acid is currently paid attention as a modulator of neuronal transmission and hormonal secretion. It is metabolized only by D-aspartate oxidase in mammals. After intraperitoneal injection, L-glutamate is catabolized via a-ketoglutarate, whereas D-glutamate is converted to n-pyrrolidone carboxylic acid. Carbon 2 of both D- and L-glutamate is converted in the cecum to the methyl carbon of acetate. Both rat liver and kidney catalyze the conversion of D-glutamic acid to n-pyrrolidone carboxylic acid.
