Hydroxylammoniumchlorid Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
FARBLOSE HYGROSKOPISCHE KRISTALLE.
CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Langsame Zersetzung bei Kontakt mit Feuchtigkeit. Beim Erhitzen bilden sich giftige Rauche. Schwache S?ure in w?ssriger L?sung.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV nicht festgelegt (ACGIH 2005).
MAK: (Hydroxylamin und Salze) Sensibilisierung der Haut; (DFG 2005).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation des Aerosols, über die Haut und durch Verschlucken.
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Verdampfung bei 20°C vernachl?ssigbar; eine gesundheitssch?dliche Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann jedoch beim Dispergieren schnell erreicht werden.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Die Substanz reizt die Augen, die Haut und die Atemwege. M?glich sind Auswirkungen auf die roten Blutk?rperchen mit nachfolgender Meth?moglobinbildung. ?rztliche Beobachtung notwendig.
WIRKUNGEN NACH WIEDERHOLTER ODER LANGZEITEXPOSITION
Wiederholter oder andauernder Kontakt kann zu Hautsensibilisierung führen.
LECKAGE
NICHT in die Kanalisation spülen. Verschüttetes Material in Beh?ltern sammeln; falls erforderlich durch Anfeuchten Staubentwicklung verhindern. Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Atemschutzger?t, P2-Filter für sch?dliche Partikel.
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Verschlucken.
R36/38:Reizt die Augen und die Haut.
R43:Sensibilisierung durch Hautkontakt m?glich.
R48/22:Gesundheitssch?dlich: Gefahr ernster Gesundheitssch?den bei l?ngerer Exposition durch Verschlucken.
R50:Sehr giftig für Wasserorganismen.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S22:Staub nicht einatmen.
S24:Berührung mit der Haut vermeiden.
S37:Geeignete Schutzhandschuhe tragen.
S61:Freisetzung in die Umwelt vermeiden. Besondere Anweisungen einholen/Sicherheitsdatenblatt zu Rate ziehen.
Aussehen Eigenschaften
H4ClNO; Hydroxylaminhydrochlorid. Farblose, schwach nach Chlor riechende Kristalle.
Gefahren für Mensch und Umwelt
Gesundheitsschädlich beim Verschlucken. Es kann zu Magen-Darm-Störungen kommen. Reizt die Augen und die Haut. Sensibilisierung durch Hautkontakt möglich. Bei Resorption kann es zur Methämoglobinbildung kommen.
Mit Oxidationsmitteln heftige Reaktionen möglich. Bildet mit alkalischen Stoffen in der Hitze Hydroxylamin. Ausserdem explosionsartige Zerstzung möglich.
Substanz ist brennbar und kann im Brandfall nitrose Gase, Stickoxide, Chlorwasserstoff und Chlor freisetzten.
Schutzma?nahmen und Verhaltensregeln
Schutzhandschuhe als kurzzeitiger Staubschutz.
Verhalten im Gefahrfall
Trocken aufnehmen, der Entsorgung zuführen, nachreinigen.
Wasser, Kohlendioxid, Schaum, Pulver.
Erste Hilfe
Nach Hautkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser abwaschen.
Nach Augenkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser bei geöffnetem Lidspalt mindestens 10 Minuten ausspülen. Augenarzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Einatmen: Frischluft
Nach Verschlucken: Viel Wasser trinken lassen, Erbrechen auslösen, Arzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Kleidungskontakt: Kontaminierte Kleidung entfernen.
Ersthelfer: siehe gesonderten Anschlag
Sachgerechte Entsorgung
Laborchemikalienabfälle.
Beschreibung
Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is a reducing agent that is routinely used for the deacetylation of SATA to form free sulfhydryls (Figure 1), for cleavage of protein cross‐linkers that contain carbonyl groups (i.e. EGS) and for mutagenesis of plasmid DNA.
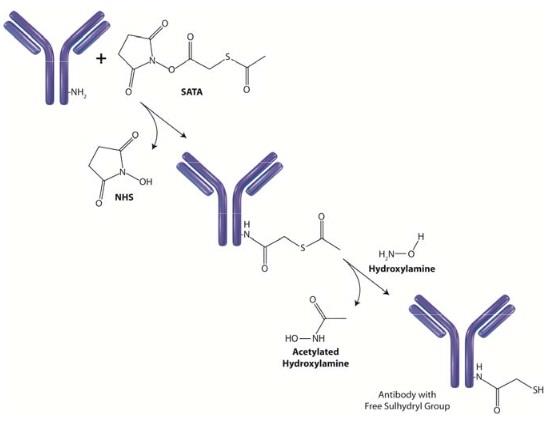
Hydroxylamine converts aldehydes and ketones (carbonyls) to their oxime derivative in weak bases, therefore cross‐linkers and other compounds with carbonyl groups are cleavable with Hydroxylamine hydrochloride.
SATA and SATP are modification reagents that add a sulfhydryl group to primary amines on biomolecules. The initial modification results in the addition of an acetyl‐protected sulfur enabling storage of the biomolecule. To generate a free sulfhydryl the biomolecule is treated with hydroxylamine to remove the protecting acetyl group (see figure).
EGS and sulfo‐EGS are homobifunctional, succinimidyl ester, amine reactive crosslinkers that are resistant to cleavage by denaturants used in SDS‐PAGE conditions, but may be cleaved with hydroxylamine.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride(NH2OH.HCl) is an inorganic compound that is the hydrochloric acid salt of hydroxylamine. It is highly hygroscopic and decomposes when exposed to dampness above 151℃. This compound is primarily used as a reducing agent and imaging agent and is instrumental in the preparation of oximes in organic synthesis. It can convert aldehydes and ketones to oximes and acid chlorides to hydroxamic acids. However, This product is highly toxic and irritating to the skin.
Physikalische Eigenschaften
It is a colorless monoclinic crystal that is hygroscopic and decomposes slowly in moist air. It has a density of 1.67 g/cm3 at a temperature of 17°C and melts at 151°C with decomposition. It is highly soluble in water, with a solubility of 84g/100g at 20°C, and is also soluble in lower alcohols and glycols. A 0.1 molar solution of this substance has a pH of 3.4.
Charakteristisch
Features of Hydroxylamine hydrochloride:
Quench amine-labeling or crosslinking reactions (e.g., with NHS esters)
Expose protected sulfhydryl groups on SATA-modified molecules
Cleave carbonyl-containing crosslinkers such as EGS and Sulfo-EGS
Verwenden
Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is a monomoamine oxidase inhibitor. It is used to prepare oximes and hydroxmic acids in organic synthesis. It acts as a copolymerization inhibitor. It can be used to remove bromine and polybromide from a solution during extraction of lignin from lignocellulosic biomass. It is key starting material for the preparation of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. It plays a vital role in rubber and plastic industries as an antioxidant, a vulcanization accelerator and a radical scavenger. It is also used as a color stabilizer and emulsion additive in color films.
Definition
ChEBI: Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is an organic molecular entity. It is a colorless inorganic compound (HONH2) used in organic synthesis and as a reducing agent, due to its ability to donate nitric oxide.
synthetische
Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is prepared by electrolytic reduction of ammonium chloride. Or by the action of nitromethane with hydrochloric acid and water to obtain hydroxylamine hydrochloride.
Biotechnological Applications
Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is a strong reducing agent that is useful in biochemical crosslinking applications, including the deacetylation of SATA and chemical cleavage of EGS and Sulfo-EGS. Hydroxylamine converts carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones) to their oxime derivatives in the presence of a weak base. Therefore, crosslinkers and other compounds that contain a carbonyl within their structure are cleavable with hydroxylamine?HCl.
MAN0011201_HydroxylamineHCl_UG.pdf
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Hydroxylamine hydrochloride appears as colorless or off-white crystalline solid. pH (0.1 molar aqueous solution) 3.4. pH (0.2 molar aqueous solution) 3.2. (NTP, 1992)
Air & Water Reaktionen
Hygroscopic. Sensitive to prolonged exposure to air. Water soluble. Reacts slowly with water.
Reaktivit?t anzeigen
A powerful reducing agent. Reacts with bases and oxidizing agents.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, strong irritant to tissue.
Brandgefahr
Flash point data for Hydroxylamine hydrochloride are not available; however, Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is probably combustible.
Kontakt-Allergie
Hydroxylamine and its salts are used in various
branches of industry, as reducing agents in color film
developers or as reagents in laboratories.
l?uterung methode
Crystallise the salt from aqueous75% ethanol or boiling methanol, and dry it under vacuum over CaSO4 or P2O5. It has also been dissolved in a minimum of water and saturated with HCl; after three such crystallisations, it is dried under a vacuum over CaCl2 and NaOH. Its solubility at 20o is 85% in H2O, 6% in EtOH and 12% in MeOH. [Hurd Inorg Synth I 87 1939, Semon in Org Synth Coll Vol I 318 1941.]
Hydroxylammoniumchlorid Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
2-CHLOROBENZALOXIME
Pyrazole-1,3-dimethyl-5-phenoxy-4-carboxaldehyde oxime
Methyl 3-amino-4-methylthiophene-2-carboxylate
4-(METHYLTHIO)BENZYLAMINE
4-AMINO-1,2,5-OXADIAZOLE-3-CARBONITRILE
2-Pyridylamid oxime
5-AMINOISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID ETHYL ESTER
Ethyl-5-methylisoxazol-3-carboxylat
5 A-CHLORO-6 B,19-EPOXY-3 B -HYDROXY-5 A-ANDROSTAN-17-ONE
4-Pyridylamidoxime
5-Chloro-3,6-dihydroxy-5-androstan-17-one 3-acetate
Ethyl-3-(2,6-dichlorphenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-carboxylat
3,4,5-Trimethoxybenzylamin
Epiandrosterone acetate
3-(2,6-Dichlorphenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-carboxylsure
Butanonoxim
5-METHYL-4-ISOXAZOLESULFONYL CHLORIDE
NEMONAPRIDE
5-Methyl-3-phenylisoxazole
2,6-Dicyano-4-Nitroaniline
Diphenylethandiondioxim
Heptaminol
3-(2-Chlorphenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-carbonylchlorid
6-Bromoisatin
4-Aminotetrahydropyran hydrochloride
5-Methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-carbonylchlorid
3-METHYLTHIOPHENE-2-CARBONITRILE
(2,6-DIMETHYLPHENOXY)ACETOXIME
3-(2-Chlorphenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-carboxylsure
3-METHYL-5-PHENYLISOXAZOLE
Adrafinil
3-PYRIDYLAMIDOXIME
Ethyl-5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-carboxylat
Benzamidoxim
Veratronitril
Heptanaloxim
17-Ethinylandrost-5-ene-3,17-diol
N-Hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt
3-METHYL-5-PHENYL-4-ISOXAZOLECARBOXYLIC ACID
2-AMINO-5,6-DICHLOROBENZOIC ACID

