Trichloressigsure Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
FARBLOSE UND HYGROSKOPISCHE KRISTALLE MIT STECHENDEM GERUCH.
CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Zersetzung beim Erhitzen unter Bildung giftiger und ?tzender Rauche mit Chlorwasserstoff und Chloroform. Starke S?ure in w?ssriger L?sung. Reagiert sehr heftig mit Basen. ?tzend gegenüber vielen Metallen.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV: 1 ppm (als TWA); Krebskategorie A3 (best?tigte krebserzeugende Wirkung beim Tier mit unbekannter Bedeutung für den Menschen); (ACGIH 2005).
MAK: IIb (nicht festgelegt, aber Informationen vorhanden) (DFG 2005).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation der D?mpfe und durch Verschlucken.
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Beim Verdampfen bei 20°C tritt langsam eine gesundheitssch?dliche Kontamination der Luft ein.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Die Substanz ver?tzt die Augen, die Haut und die Atemwege. ?tzend beim Verschlucken. Inhalation des Dampfes kann zu Lungen?dem führen (s.Anm.). Die Auswirkungen treten u.U. verz?gert ein. ?rztliche Beobachtung notwendig.
LECKAGE
Verschüttetes Material in wassergefüllten Beh?ltern sammeln; falls erforderlich durch Anfeuchten Staubentwicklung verhindern. Reste vorsichtig mit Alkali wie Natriumbicarbonat oder Natriumhydroxid neutralisieren. Dann mit viel Wasser wegspülen. Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Vollschutzanzug mit umgebungsluftunabh?ngigem Atemschutzger?t.
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
R40:Verdacht auf krebserzeugende Wirkung.
R51/53:Giftig für Wasserorganismen, kann in Gew?ssern l?ngerfristig sch?dliche Wirkungen haben.
R50/53:Sehr giftig für Wasserorganismen, kann in Gew?ssern l?ngerfristig sch?dliche Wirkungen haben.
R35:Verursacht schwere Ver?tzungen.
R38:Reizt die Haut.
R11:Leichtentzündlich.
R34:Verursacht Ver?tzungen.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S36/37:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzkleidung tragen.
S61:Freisetzung in die Umwelt vermeiden. Besondere Anweisungen einholen/Sicherheitsdatenblatt zu Rate ziehen.
S60:Dieses Produkt und sein Beh?lter sind als gef?hrlicher Abfall zu entsorgen.
S45:Bei Unfall oder Unwohlsein sofort Arzt zuziehen (wenn m?glich, dieses Etikett vorzeigen).
S36/37/39:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung,Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
S24/25:Berührung mit den Augen und der Haut vermeiden.
Aussehen Eigenschaften
C2HCl3O2; Trichloretansäure, TCA. Farblose schwach sauer und stechend riechende Kristalle. Leicht wasserlöslich und hygroskopisch.
Gefahren für Mensch und Umwelt
Verursacht schwere Verätzungen. Eiweißfällend, daher bei Augenkontakt große Erblindungsgefahr.
Zu vermeidende Stoffe sind Alkalihydroxide, starke Oxidationsmittel, Sulfoxide und Kupfer.
Bei Temperaturen oberhalb 200鳦 setzt Zersetzung in Chlorwasserstoff, Kohlendioxid, Kohlenmonoxid und Phosgen ein.
LD50 (oral,Ratte) 3320 mg/kg
Nicht ins Abwasser gelangen lassen, pH-Verschiebung!
Schutzma?nahmen und Verhaltensregeln
Lagerung unter +30鳦.
Schutzhandschuhe als kurzzeitiger Staubschutz
Verhalten im Gefahrfall
Persönliche Maßnahmen: Substanzkontakt vermeiden.
Maßnahmen zum Umweltschutz: Nicht in die Kanalisation gelangen lassen. Auch in Verdünnung noch ätzend.
Reinigungsverfahren: Trocken aufnehmen. Der Entsorgung zuführen. Nachreinigen.
Kohlendioxid, Wasser. Löschmittel auf Umgebung abstimmen. Entweichende Dämpfe mit Wasser niederschlagen.
Nicht brennbar. Im Brandfall Entstehung gefährlicher Dämpfe (Chlorwasserstoff, Kohlenmonoxid, Phosgen) möglich.
Erste Hilfe
Nach Hautkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser abwaschen. Abtupfen mit Polyethylenglycol 400.
Nach Augenkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser bei geöffnetem Lidspalt mindestens 10 Minuten ausspülen. Sofort Augenarzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Einatmen: Frischluft. Arzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Verschlucken: Viel Wasser trinken lassen. Erbrechen vermeiden (Perforationsgefahr). Sofort Arzt hinzuziehen. Bei Atemstillstand Atemspende oder Gerätebeatmung.
Nach Kleidungskontakt: Kontaminierte Kleidung sofort entfernen.
Ersthelfer: siehe gesonderten Anschlag
Sachgerechte Entsorgung
Vorsichtig mit Hydrogencarbonat- oder Natriumhydroxidlösung neutralisieren, in wäßrige neutrale Lösemittelabfälle.
Beschreibung
Trichloroacetic acid, also known as TCA or 76-03-9, is a colorless or white orthorhombic crystal with strong deliquescence and a slight, special irritant smell. It is highly corrosive. TCA's aqueous solution is strongly acidic, with a pH of 1.2 for a 0.1 mol solution. Concentrations of TCA at or below 30% cannot be stored for long periods due to decomposition into chloroform, hydrogen chloride, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide. Dilute alkali leads to hydrolysis into chloroform and carbon dioxide. Concentrated alkali results in the formation of formic acid. TCA is a highly toxic substance with an oral LD50 of 3320mg/kg.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Trichloroacetic acid, a colorless crystalline solid, is commonly utilized in liquid solutions. It has the ability to absorb moisture from the surrounding air and become syrupy. When dissolved in water, the process releases heat. However, this potent acid is corrosive to both metals and tissue.
Verwenden
Protein precipitation reagentTrichloroacetic acid is used as a precipitating agent in biochemistry for precipitation of proteins, DNA and RNA. It is an active ingredient used in cosmetic treatments like chemical peels, tattoo removal and the treatment of warts including genital warts. It is also used to determine protein concentration and as a decalcifier and fixative in microscopy.
Definition
ChEBI: Trichloroacetic acid is a monocarboxylic acid that is acetic acid in which all three methyl hydrogens are substituted by chlorine. It has a role as a metabolite, a carcinogenic agent and a mouse metabolite. It is a monocarboxylic acid and an organochlorine compound. It is functionally related to an acetic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a trichloroacetate.
Application
Trichloroacetic acid(76-03-9) can be used as pharmaceutical raw materials, herbicides (potassium trichloroacetate and sodium trichloroacetate, etc.), textile dyeing auxiliaries, metal surface treatment agent and acid chloride, anhydride, amide, polyester, organometallic salt, water salicylaldehyde, chlorocarboxylic acid and the raw materials of other organic synthesis.
In addition, in medicine, it can also be used as etherifying agents and keratolytics, bile pigment reagents and protein precipitation reagents. In the field of biochemistry, it can be used for separation analysis of biological phosphate compounds and reagents for determination of fluoride and lipid as well as microscopic fixative, decalcification, chromatography reagents.
The product is warts agent and astringent in pharmaceutical field, mainly used as biochemical drug extractant for the extraction of many highly efficient drugs such as adenosine triphosphate, cytochrome C and placental polysaccharides.
In addition, trichloroacetic acid, together with alkaline phenol, can be used for salicylaldehyde compound synthesis by ReimerTiemann reaction. It can also react with monoolefine compounds for synthesizing chlorocarboxylic acid [CCl3 (CH2CH2) nCOOH].
Reaktionen
Trichloroacetic acid is a strong organic acid with a dissociation constant K = 3 × 10-2. It has lively chemical properties. Its sodium salt is easily subject to decarboxylation into chloroform. It will be reduced to alcohol upon coming across LiAlH4. It can have halogen replacement reaction with KBr:
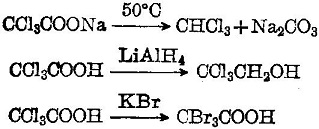
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) is derived from Trichloroethylene (TCE) metabolism. It is used as an acid decalcifying agent. TCA is used as a fixative for nuclear staining and protein precipitation.
Reaktivit?t anzeigen
Trichloroacetic acid is a strong acid; when heated, in the presence of water, decomposes forming phosgene and HCl. [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980 p. 915]. The acid was added to copper wool and rinsed down with dimethyl sulfoxide. This caused what was thought to be an extremely exothermic dehydrohalogenation reaction that melted the neck of the flask, [Chem. Eng. News, 1981, 59(28), 4].
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Brandgefahr
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Sicherheitsprofil
Poison by ingestion and
subcutaneous routes. Moderately toxic by
intraperitoneal route. Questionable
carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic
data. Experimental reproductive effects.
Mutation data reported. A corrosive irritant
to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
When heated to decomposition it emits
toxic fumes of Cland Na2O. Used as an
herbicide.
m?gliche Exposition
This haloacetic acid can be a byproduct of drinking water disinfection and may increase the risk of cancer. Trichloroacetic acid is used as medication; in organic syntheses; as a reagent for albumin detection; as an intermediate in pesticide manufacture and in the production of sodium trichloroacetate which is itself a herbicide.
Carcinogenicity
TCA was not mutagenic in bacterial
assays.The IARC has determined that there is
limited evidence for the carcinogenicity of
TCA in experimental animals and that it is not
classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans. Neutralized TCA was not clastogenic
in human lymphocytes in vitro or in the mouse
bone marrow micronucleus test.
Versand/Shipping
UN1839 (solid) & UN2564 (solution) Trichloroacetic acid, solid and Trichloroacetic acid, solution, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
l?uterung methode
Purify the acid by fractional crystallisation from its melt, then crystallise it repeatedly from dry *benzene and store it over conc H2SO4 in a vacuum desiccator. It can also be crystallised from CHCl3 or cyclohexane, and dried over P2O5 or Mg(ClO4)2 in a vacuum desiccator. Trichloroacetic acid can be fractionally distilled under reduced pressure from MgSO4. Layne, Jaffé and Zimmer [J Am Chem Soc 85 435 1963] dried trichloroacetic acid in *benzene by distilling off the *benzene-water azeotrope, then crystallised the acid from the remaining *benzene solution. Manipulations should be carried out under N2. [Toxic vapours, use a well ventilated fume cupboard.] [Beilstein 2 IV 508.]
Inkompatibilit?ten
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, silver salts, strong acids, strong bases, moisture, iron, zinc, aluminum. Corrosive to iron, steel and other metals.
Einzelnachweise
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/trichloroacetic_acid#section=Top
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trichloroacetic_acid
Trichloressigsure Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

