Dimethylterephthalat Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
WEISSE FLOCKEN.
PHYSIKALISCHE GEFAHREN
Staubexplosion der pulverisierten oder granulierten Substanz in Gemischen mit Luft m?glich.
CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Zersetzung beim Verbrennen unter Bildung reizender Rauche.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV nicht festgelegt (ACGIH 2005).
MAK nicht festgelegt (DFG 2005).
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Beim Verdampfen bei 20°C tritt eine gesundheitssch?dliche Kontamination der Luft nicht oder nur sehr langsam ein.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Reizt m?glicherweise mechanisch.
LECKAGE
Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Atemschutzger?t, P2-Filter für sch?dliche Partikel. NICHT in die Umwelt gelangen lassen. Verschüttetes Material in abdichtbaren Beh?ltern sammeln; falls erforderlich durch Anfeuchten Staubentwicklung verhindern. Reste sorgf?ltig sammeln. An sicheren Ort bringen.
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S24/25:Berührung mit den Augen und der Haut vermeiden.
Beschreibung
Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) is an organic compound with the formula C
6H
4(CO
2CH
3)
2. It is the diester formed from terephthalic acid and methanol. It is a white solid that melts to give a distillable colourless liquid.
Chemische Eigenschaften
The empirical formula of dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) is
C10H10O4. Its structural formula is 1,4-(COOCH3)2C6H4. At
room temperature, exists as colorless crystals. DMT is soluble in ether and
chloroform, slightly soluble in ethanol, and fairly insoluble in
water (<1 g/L at 13℃).
Verwenden
Dimethyl terephthalate is used in the production of polyesters, including polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and poly trimethylene terephthalate. It consists of benzene substituted with carboxy methyl groups (CO
2CH
3) at the 1 and 4 positions. Because DMT is volatile, it is an intermediate in some schemes for the recyclic of PET, e.g. from plastic bottles.
Hydrogenation of DMT affords the diol cyclohexanedimethanol, which is a useful monomer.
Definition
ChEBI: Dimethyl terephthalate is a diester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy groups of terephthalic acid with methanol. It is a primary ingredient widely used in the manufacture of polyesters and industrial plastics. It is a methyl ester, a diester and a phthalate ester. It derives from a terephthalic acid.
synthetische
Several processes have been developed for the preparation of dimethyl
terephthalate from p-xylene, but the most important proceeds as follows:
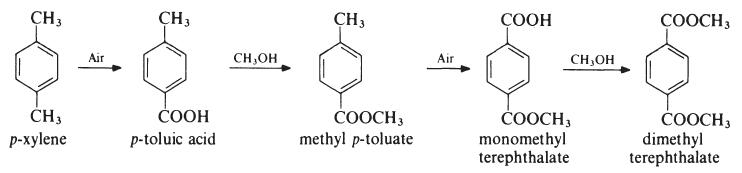
The oxidation steps are carried out in the liquid phase at about 170??C and
1.5 MPa (15 atmospheres) in the presence of a cobalt acetate or naphthenate
catalyst whilst the esterifications are conducted at about 150??C.
Dimethyl terephthalate may also be produced by esterification of terephthalic
acid.
Vorbereitung Methode
Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) has been produced in a number of ways. Conventionally and still of commercial value is the direct esterification of terephthalic acid. Alternatively, it can be prepared by alternating oxidation and methyl-esterification steps from p-xylene via methyl-p-toluate.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Dimethyl terephthalate appears as white solid or heated colorless liquid. Has no odor. Liquid solidifies in cool water. Solid and liquid sink in water. (USCG, 1999)
Air & Water Reaktionen
When mixed with air, the vapor or dust forms very hazardous and highly reactive mixtures. . Insoluble in water.
Reaktivit?t anzeigen
DIMETHYL TEREPHTHALATE is an ester. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. Can generate electrostatic charges. [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 250]. DIMETHYL TEREPHTHALATE is sensitive to heat. The molten material reacts with water due to the temperature. DIMETHYL TEREPHTHALATE is incompatible with strong oxidizers, strong acids and strong bases.
Health Hazard
Molten DMT will cause severe burns of skin on contact.
Brandgefahr
DIMETHYL TEREPHTHALATE is combustible.
Sicherheitsprofil
Moderately toxic by
intraperitoneal route. Mdly toxic by
ingestion. An eye irritant. Mutation data
reported. When heated to decomposition it
emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes
Carcinogenicity
In a study conducted by the
NCI, DMT was not considered to be carcinogenic in
rats or mice ingesting 2500 or 5000 ppm in the diet for
103 weeks.
Source
Dimethyl terephthalate is a natural product found in Hypotrachyna nepalensis, Uncaria elliptica, and other organisms with data available.
l?uterung methode
Purify it by recrystallisation from aqueous EtOH, MeOH or CCl4; or by zone melting. [Beilstein 6 H 843, 6 III 4250, 6 IV 3303.] .
Dimethylterephthalat Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
polyester-based liquid crystalling ionmer containing sulfonate group
Polyester resin paint
Methylhydrogenterephthalat
Polyethylene Terephthalate
Antistatic finishing agent
Cyclohex-1,4-ylendimethanol
3,8,15,20,27,32-Hexaoxatetracyclo[32.2.2.210,13.222,25]dotetraconta-1(3
2-Hydroxyethylmethylterephthalat
Bis(hydroxyethyl)terephthalat
(α,α,α,α',α',α'-2H6)p-Xylol
TRANS-1,4-CYCLOHEXANEDIMETHANOL

