Cetuximab Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
Originator
ImClone (US)
Verwenden
Treatment of EGF receptor-expressing cancers
(monoclonal antibod.
Trademarks
Erbitux
Mechanism of action
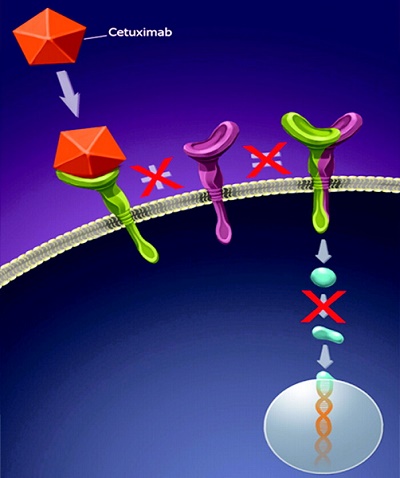
Cetuximab, a monoclonal antibody, binds to the extracellular domain of the EGFR, which is overexpressed in many human cancers, including head, neck, and colorectal types. This process prevents the EGFR from binding with its endogenous ligand, blocking the receptor-dependent transduction pathway and providing many antitumor effects involving cell-cycle arrest, induction of apoptosis, inhibition of angiogenesis, inhibition of metastasis, internalization, and downregulation of the EGFR, and enhancement of the sensitivity to radiochemotherapy[1].
Toxikologie
The majority of skin toxicities were mild to moderate, symptomatic treatments were effective in controlling them. The skin discomfort caused by cetuximab can affect the quality of life temporarily; with long term treatment, severity of skin toxicity may decrease.
Einzelnachweise
[1] W Bou-Assaly, S Mukherji. “Cetuximab (erbitux).” American Journal of Neuroradiology 31 4 (2010): 626–7.
Cetuximab Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

