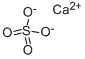Calciumsulfat
|
|
Calciumsulfat Eigenschaften
- Schmelzpunkt:
- 1450 °C
- Dichte
- 2.960
- Brechungsindex
- 1.575
- storage temp.
- Store at RT.
- L?slichkeit
- 2g/l
- Aggregatzustand
- Powder
- Wichte
- 2.96
- Farbe
- White
- Geruch (Odor)
- wh. to sl. yel.-wh. powd. or crystals, odorless, tasteless
- Wasserl?slichkeit
- Soluble in water.
- Sensitive
- Moisture Sensitive
- Merck
- 14,1706
- Expositionsgrenzwerte
- ACGIH: TWA 10 mg/m3
OSHA: TWA 15 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3
NIOSH: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3
- Stabilit?t:
- Stable. Incompatible with aluminium, strong acids.
- LogP
- -1.031 (est)
- CAS Datenbank
- 7778-18-9(CAS DataBase Reference)
- EPA chemische Informationen
- Calcium sulfate (7778-18-9)
Sicherheit
- Risiko- und Sicherheitserkl?rung
- Gefahreninformationscode (GHS)
| Kennzeichnung gef?hrlicher | T,N,Xi | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| R-S?tze: | 49-42/43-51/53-36/37-68-60-50/53 | ||
| S-S?tze: | 53-22-36/37-45-60-24/25-36-26-61 | ||
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG 3 | ||
| OEB | B | ||
| OEL | TWA: 10 mg/m3 (total) | ||
| WGK Germany | 1 | ||
| RTECS-Nr. | WS6920000 | ||
| F | 3 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| HazardClass | 9 | ||
| HS Code | 28332980 | ||
| Giftige Stoffe Daten | 7778-18-9(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Bildanzeige (GHS) |
 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alarmwort | Achtung | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gefahrenhinweise |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheit |
|
Calciumsulfat Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
WEISSES HYGROSKOPISCHES PULVER ODER KRISTALLINES PULVER.ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV: (als Gesamtstaub, kein Asbest und <1 % kristallinen Quarz enthaltend) 10 mg/m?(als TWA); (ACGIH 2005).MAK: 1.5 mg/m?(Alveoleng?ngige Fraktion); 4 mg/m?(Einatembare Fraktion); (DFG 2006).
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Eine bel?stigende Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann beim Dispergieren schnell erreicht werden.WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION:Reizt m?glicherweise mechanisch. Verschlucken kann Magen-Darm-Blockade verursachen
WIRKUNGEN NACH WIEDERHOLTER ODER LANGZEITEXPOSITION
Risiko der Lungensch?digung bei wiederholter oder l?ngerer Exposition gegenüber Staubpartikeln, wenn kristalliner Quarz vorhanden ist.LECKAGE
Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Atemschutzger?t, P1-Filter für inerte Partikel. Verschüttetes Material in Beh?ltern sammeln; falls erforderlich durch Anfeuchten Staubentwicklung verhindern. Reste mit viel Wasser wegspülen.R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R49:Kann Krebs erzeugen beim Einatmen.R42/43:Sensibilisierung durch Einatmen und Hautkontakt m?glich.
R51/53:Giftig für Wasserorganismen, kann in Gew?ssern l?ngerfristig sch?dliche Wirkungen haben.
R36/37:Reizt die Augen und die Atmungsorgane.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S53:Exposition vermeiden - vor Gebrauch besondere Anweisungen einholen.S22:Staub nicht einatmen.
S36/37:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzkleidung tragen.
S45:Bei Unfall oder Unwohlsein sofort Arzt zuziehen (wenn m?glich, dieses Etikett vorzeigen).
S60:Dieses Produkt und sein Beh?lter sind als gef?hrlicher Abfall zu entsorgen.
S24/25:Berührung mit den Augen und der Haut vermeiden.
S36:DE: Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung tragen.
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
Beschreibung
Calcium sulfate and its hydrates are important industrial compounds that have been used throughout history. Calcium sulfate is obtained naturally from mined gypsum rock, but it also exists in mineral form. Gypsum forms in beds as sedimentary rock when calcium sulfate, which is a natural component of seawater, is deposited as shallow marine water bodies evaporate. Gypsum is a transparent, soft, white mineral and is the most common sulfate mineral.Chemische Eigenschaften
Calcium sulfate forms white to clear crystals. It is commonly encountered in the anhydrous form or as the dihydrate.Physikalische Eigenschaften
Anhydrous calcium sulfate is a crystalline substance; orthorhombic; the color may vary as white, gray, blue or brick-red; occurs as insoluble anhydrite or porous soluble anhydrite; density 2.96 g/cm3; hardness 3.5 Mohs; insoluble anhydrite is practically insoluble in water (0.21% at 20°C); soluble anhydrite readily absorbs moisture and is soluble in water.Hemihydrate is a white fine powder; sparingly soluble in water (3g/L at 25°C); combines with water, setting to a hard mass.
Dihydrate may occur as lumps or powder; density 2.32 g/cm3; partially loses water on heating at 100°C; slightly soluble in water (2.4 g/L at 25°C); KSP =2.4x10-5; almost insoluble in organic solvents.
History
Gypsum’s use dates back to prehistoric times. Archeological evidence shows that it was mined from caves and used to paint ancient gravestones. The earliest evidence of its use as a building material dates from 6000 b.c.e. in the southwest Asian areas of ancient Anatolia and Syria. Egyptians used gypsum and plaster in their buildings and monuments, with both found in the Great Pyramids built around 3700 b.c.e. Calcium sulfate has been used for more than 2,000 years in China to produce tofu. The word gypsum comes from the Greek word for chalk, gypsos. The Greek natural philosopher Theophrastus (371–286 b.c.e.) referred to gypsum in his writings. Gypsum was extensively used in Roman times and throughout the Middle Ages.In the 1700s, Paris was a leading plaster center, with most of its buildings made using plaster. After the fire of London in 1666 destroyed 80% of the city, the king of France ordered all wooden houses in France to be covered with plaster as protection against fire. The hemihydrate form got the name plaster of Paris from the extensive gypsum deposits quarried in the Montmartre district of Paris. In 1765 and 1766, Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794) presented papers to the French Academy of Science on gypsum that explained the setting of plaster. Lavoisier determined that gypsum is a hydrated salt and that set plaster occurs when the hemihydrate form rehydrates back to gypsum.
Verwenden
The largest use of calcium sulfate is in the construction industry, which accounts for more than 90% of its production.Gypsum has hundreds of other applications outside the construction industry. It can be used agriculturally for several purposes: to supply calcium and sulfur to soils, to balance pH, and to condition soil. Food grade calcium sulfate is used as a calcium supplement in enriched foods such as flour, cereals, and baked goods. It is used as a gelling and firming agent with canned vegetables. Calcium sulfate is the most common tofu coagulant. The positively charged calcium ion in calcium sulfate attracts the negatively charged groups in protein molecules, causing thermally denatured proteins to coagulate. Anhydrous calcium sulfate is used as a filler to whiten food and consumer products such as frostings, ice creams, paper, paints, and toothpaste. Powdered gypsum can be used as a chalk for marking athletic fields and other large areas.Definition
anhydrite: An important rockforminganhydrous mineral form ofcalcium sulphate, CaSO4. It is chemicallysimilar to gypsum but isharder and heavier and crystallizes inthe rhombic form (gypsum is monoclinic).Under natural conditions anhydriteslowly hydrates to formgypsum. It occurs chiefly in whiteand greyish granular masses and isoften found in the caprock of certainsalt domes. It is used as a raw materialin the chemical industry and inthe manufacture of cement and fertilizers.Vorbereitung Methode
Anhydrous calcium sulfate occurs naturally as the mineral anhydrite. The naturally occurring rock gypsum may be crushed and ground for use as the dihydrate or calcined at 1508℃ to produce the hemihydrate. A purer variety of calcium sulfate may also be obtained chemically by reacting calcium carbonate with sulfuric acid or by precipitation from calcium chloride and a soluble sulfate.Allgemeine Beschreibung
Odorless, white powder or colorless, crystalline solid. Crystals sometimes have a blue, gray or reddish tinge or can be brick red. Density: 2.96 g cm-3.Reaktivit?t anzeigen
CALCIUM SULFATE is non-combustible. Decomposes to give toxic oxides of sulfur, but only at very high temperature (>1500°C). Generally of low reactivity but may act as an oxidizing agent: incompatible with diazomethane, aluminum, and phosphorus. Certain forms of CALCIUM SULFATE react with water; others do not. INSOLUBLE ANHYDRITE or dead-burned gypsum is made by the dehydration of CALCIUM SULFATE dihydrate (gypsum) at high (> 600°C) temperature. At room temperature, insoluble anhydrite dissolves very slowly to the extent of 0.24 g per 100 g of water and does not absorb moisture from the air. SOLUBLE ANHYDRITE, which is obtained by heating CALCIUM SULFATE dihydrate at a temperature below 300°C, has a high affinity for water and is used as a desiccant. Soluble anhydrite absorbs water to form CALCIUM SULFATE hemihydrate (Plaster of Paris).Health Hazard
Calcium sulfate is considered to be a nuisance dust.There have been no reports of adverse effects in humans exposed to calcium sulfate. Excessive concentrations would be expected to cause reduced visibility and skin and upper respiratory tract irritation.1 One report on gypsum miners attributed adverse effects to respirable quartz rather than calcium sulfate.
Pharmazeutische Anwendungen
Calcium sulfate dihydrate is used in the formulation of tablets and capsules. In granular form it has good compaction properties and moderate disintegration properties.Calcium sulfate hemihydrate, is used in the preparation of plaster of Paris bandage, which is used for the immobilization of limbs and fractures; it should not be used in the formulation of tablets or capsules.
Anhydrous calcium sulfate is hygroscopic and is used as a desiccant. The uptake of water can cause the tablets to become very hard and to fail to disintegrate on storage. Therefore, anhydrous calcium sulfate is not recommended for the formulation of tablets, capsules, or powders for oral administration.
Therapeutically, calcium sulfate is used in dental and craniofacial surgical procedures.
Landwirtschaftliche Anwendung
Anhydrite is a naturally occurring, solid, white mineral called anhydrous calcium sulphate (CaSO4). It differs from gypsum in hardness and in hydration. It is used as a raw material in the chemical industry and in the manufacture of fertilizers and cement.Sicherheitsprofil
A nuisance dust. Reacts violently with aluminum when heated. Mixtures with diazomethane react exothermically and eventually explode. Mixtures with phosphorus ignite at high temperatures. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SO,, See also CALCIUM COMPOUNDS and SULFATES.Sicherheit(Safety)
Calcium sulfate dihydrate is used as an excipient in oral capsule and tablet formulations. At the levels at which it is used as an excipient, it is generally regarded as nontoxic. However, ingestion of a sufficiently large quantity can result in obstruction of the upper intestinal tract after absorption of moisture.Owing to the limited intestinal absorption of calcium from its salts, hypercalcemia cannot be induced even after the ingestion of massive oral doses.
Calcium salts are soluble in bronchial fluid. Pure salts do not induce pneumoconiosis.
m?gliche Exposition
Calcium sulfate is used as a pigment; in Portland cement, in tiles and plaster; in polishing powders, a filler in paints and paper coatings; in the drying of gases and liquids; a soil conditioner; in molds and surgical casts; in wallboard, and many others.Lager
Calcium sulfate is chemically stable. Anhydrous calcium sulfate is hygroscopic and may cake on storage. Store in a well-closed container in a dry place, avoiding heat.Versand/Shipping
Calcium sulfate is a “NONREGULATED MATERIAL.”Inkompatibilit?ten
In the presence of moisture, calcium salts may be incompatible with amines, amino acids, peptides, and proteins, which may form complexes. Calcium salts will interfere with the bioavailability of tetracycline antibiotics. It is also anticipated that calcium sulfate would be incompatible with indomethacin, aspirin, aspartame, ampicillin, cephalexin, and erythromycin since these materials are incompatible with other calcium salts.Calcium sulfate may react violently, at high temperatures, with phosphorus and aluminum powder; it can react violently with diazomethane.
Waste disposal
LandfillingRegulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral capsules, sustained release, tablets). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK and Europe. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.Calciumsulfat Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
Calciumsulfat Anbieter Lieferant Produzent Hersteller Vertrieb H?ndler.
Global( 332)Lieferanten
| Firmenname | Telefon | Land | Produktkatalog | Edge Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12809 | 58 |
| Hebei Yanxi Chemical Co., Ltd. | +8617531153977 |
allison@yan-xi.com | China | 5854 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531151365 |
mina@chuanghaibio.com | China | 18137 | 58 |
| Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd | +8613343047651 |
admin@zlchemi.com | China | 3692 | 58 |
| Shanghai Zheyan Biotech Co., Ltd. | 18017610038 |
zheyansh@163.com | CHINA | 3619 | 58 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 |
sales@coreychem.com | China | 29858 | 58 |
| SHANDONG ZHI SHANG CHEMICAL CO.LTD | +86 18953170293 |
sales@sdzschem.com | China | 2930 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22963 | 58 |
| Shandong chuangyingchemical Co., Ltd. | 18853181302 |
sale@chuangyingchem.com | CHINA | 5906 | 58 |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 |
sales@conier.com | China | 49732 | 58 |
7778-18-9(Calciumsulfat)Verwandte Suche:
Certrichlorid
Dinatriumhydrogenorthophosphat
Kieselsure, Calciumsalz
Calciumchlorid
Trinatriumorthophosphat
Diammoniumoxalat
Natriumhydrogensulfat
Kupfersulfat
Scandiumtrichlorid
Bariumbromid
Zinnchlorid
Dinatriumtetraborat, wasserfrei
Chromtrichlorid
Lithiumiodid
Magnesiumsulfat
Kieselsure, Kaliumsalz
Magnesiumbromid
Zitronensure
- anhydrousgypsum
- anhydroussulfateoflime
- calciumsulfate(1:1)
- calciumsulfate(anhydrous)
- naturalanhydrite
- sulfatedecalcium,anhydre
- Sulfuricacid,calciumsalt(1:1)
- sulfuricacidcalcium(2+)salt(1:1)
- thiolite
- Drierite,regular(CaSO4),LabGrade
- CALCIUM SULFATE ANHYDROUS (ANHYDRIT)
- Drierite, with indicator, 4 mesh
- Drierite, with indicator, 8 mesh
- CALCIUM SULFATE, ANHYDROUS INDICATING
- CALCIUM SULFATE, -325 MESH, 99%
- DRIERITE, 10-20 MESH, WITHOUT INDICATOR
- Drierite(R)Indicating10/20Mesh
- Drierite(R)RegularGrade,8Mesh
- CalciumSulphateAnhydrousFcc
- Drierite(R)RegularGrade,10/20Mesh
- CalciumSulphateAnhydrous(Dried)
- CalciumSulphateAnhydrous
- Drierite(R)Indicating20/40Mesh
- Drierite(R)RegularGrade,Powder
- CalciumSulphateAnhydrousNf
- Calciumsulfate,anhydrous,99%min
- Calciumsulphate,anhydrous,10-20mesh
- Drierite,indicating(CaSO4),LabGrade
- CalciuM Sulfate Whistler
- CALCIUM SULFATE ANHYDROUS, GRANULAR CA.
- Drierite(R) , 10-20 Mesh
- Drierite(R) , 4 Mesh
- Drierite(R) , 6 Mesh
- Drierite(R) , 8 Mesh
- Drierite(R) , Indicating, 4 Mesh
- Drierite(R) , Regular, 20-40 Mesh
- Calcium sulfate >=99.99% trace metals basis
- Calcium sulfate Vetec(TM) reagent grade
- CALCIUM SULFATE, ANHYDROUS REAGENT
- DRIERITE 10-20 MESH
- DRIERITE 10-20 MESH, INDICATING
- DRIERITE 20-40 MESH
- DRIERITE 4 MESH
- DRIERITE 4 MESH, INDICATING
- DRIERITE 6 MESH
- DRIERITE 6 MESH, INDICATING
- DRIERITE 8 MESH
- DRIERITE 8 MESH, INDICATING
- calcium sulfate, anhydrous, puratronic
- CALCIUMSULFATE,ANHYDROUS,FCC
- CALCIUMSULFATE,ANHYDROUS,POWDER,REAGENT
- CALCIUMSULFATE,ANHYDROUS,TECH
- DRIERITEINDICATING
- DRIERITEREGULAR
- CALCIUMSULPHATEFIBER
- CALCIUMSULPHATEFIBRE
- CALCIUMSULPHATEWHISKER
- Drierite(R),with indicator,20-40 mesh