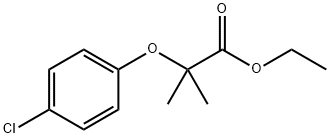
Clofibrat
|
|
Clofibrat Eigenschaften
- Schmelzpunkt:
- <25 °C
- Siedepunkt:
- 154 °C
- Dichte
- 1.14 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
- Brechungsindex
- n
20/D 1.503
- Flammpunkt:
- 113 °C
- storage temp.
- 2-8°C
- L?slichkeit
- Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO.
- Aggregatzustand
- liquid
- Farbe
- clear, colorless
- Wasserl?slichkeit
- 97.08mg/L(room temperature)
- Merck
- 14,2377
- BRN
- 1913459
- CAS Datenbank
- 637-07-0(CAS DataBase Reference)
- IARC
- 3 (Vol. Sup 7, 66) 1996
- NIST chemische Informationen
- Clofibrate(637-07-0)
- EPA chemische Informationen
- Clofibrate (637-07-0)
Sicherheit
- Risiko- und Sicherheitserkl?rung
- Gefahreninformationscode (GHS)
| Kennzeichnung gef?hrlicher | Xn,N | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| R-S?tze: | 22-37/38-41-51/53-40 | ||
| S-S?tze: | 26-36/37/39-61-45-36/37 | ||
| RIDADR | UN 3082 9/PG 3 | ||
| WGK Germany | 3 | ||
| RTECS-Nr. | UE9480000 | ||
| HazardClass | 9 | ||
| HS Code | 29189900 | ||
| Giftige Stoffe Daten | 637-07-0(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| Toxizit?t | LD50 in mice, rats (g/kg): 1.28, 1.65 orally (Metz) |
| Bildanzeige (GHS) |
 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alarmwort | Achtung | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gefahrenhinweise |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheit |
|
Clofibrat Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Verschlucken.R37/38:Reizt die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
R41:Gefahr ernster Augensch?den.
R51/53:Giftig für Wasserorganismen, kann in Gew?ssern l?ngerfristig sch?dliche Wirkungen haben.
R40:Verdacht auf krebserzeugende Wirkung.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.S36/37/39:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung,Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
S61:Freisetzung in die Umwelt vermeiden. Besondere Anweisungen einholen/Sicherheitsdatenblatt zu Rate ziehen.
S45:Bei Unfall oder Unwohlsein sofort Arzt zuziehen (wenn m?glich, dieses Etikett vorzeigen).
S36/37:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzkleidung tragen.
Beschreibung
Researchers in France observed in 1953 that structures derived from dehydrocholic acid, phenylethyl acetic acid, and certain other disubstituted acetic acids exhibited hypocholesterolemic properties in rats and humans. Several years later, Thorp and Waring discovered clof ibrate as an effective compound for lowering lipids in animal models, with minimal toxicity. Its mode of action was initially attributed to seasonal variations in adrenal and thyroid function, and the administration of androsterone was found to potentiate the hypocholesterolemic effect of this compound. Subsequently, several clinical trials were performed which showed that clofibrate decreases lipid levels in hypercholesterolemic patients, mainly as the result of a reduction in the very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), and less in the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) fraction, and that the coadministration of androsterone was not necessary for its hypolipidemic effect. Despite reported hepatomegaly in rats following long-term treatment with clofibrate, this drug was approved in the United States in 1967 for the treatment of hyperlipidemias.Clofibrate can be chemically synthesized by the condensation of phenol with ethyl 2-chloro-2-methylpropionate in the presence of a dehydrochlorinating agent, followed by chlorination and purification. It can also be synthesized by the condensation of p-chlorophenol with acetone and chloroform followed by esterifying the resultant acid to give clofibrate.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Clear Colorless OilVerwenden
Clofibrate is a lipid-lowering agent (antilipidemic) used for controlling high cholesterol (anticholesteremic) and triacylglyceride levels in the blood. It increases lipoprotein lipase activity to promote the conversion of VLDL to LDL, thereby reducing VLDL levels. It is indicated only in subjects with increased concentrations of VLDL and intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL) who have failed to respond adequately to gemfibrozil or nicotinic acid. Clofibrate is of limited utility for patients with either familial hypercholesterolemia or polygenic hypercholesterolemia, as comparatively more effective drugs are available for lowering the concentration of LDL in these patients.Clofibrate has no effect on hyperchylomicronemia, nor does it affect concentrations of high-density lipoproteins (HDL). Thus, clofibrate appears to have specific efficacy only in patients with familial type-III hyperlipoproteinemia. There is no substantial evidence proving efficacy of clofibrate in preventing deaths from coronary artery disease. Clofibrate has been used to prevent or control polydipsia, polyuria, and dehydration in a limited number of patients with mild to moderate neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus. A 5-year multicenter study reported failure of clofibrate in reducing or preventing mortality in cardiovascular disorders, which has provided a setback for the prophylactic use of this drug.
Definition
ChEBI: The ethyl ester of clofibric acid.Weltgesundheitsorganisation (WHO)
Clofibrate, an antihyperlipidaemic agent, was introduced in 1967 and was subsequently extensively studied in the primary and secondary prevention of ischaemic heart disease. Following reports, published in 1978, of increased mortality among patients receiving clofibrate in a WHO-sponsored cooperative trial concerned with the primary prevention of ischaemic heart disease, the drug was withdrawn in some countries and its approved indications were severely restricted in many others. These restrictions have become the norm for more recently developed analogues of clofibrate. (Reference: (WHODI) WHO Drug Information, 2, 6, 1979)Allgemeine Beschreibung
Clofibrate, ethyl 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropionate (Atromid-S), is a stable, colorless topale yellow liquid with a faint odor and a characteristictaste. It is soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in water.Clofibrate is prepared by a Williamson synthesis, condensingp-chlorophenol with ethyl -bromoisobutyrate, or bythe interaction of a mixture of acetone, p-chlorophenol, andchloroform in the presence of excess potassium hydroxide.The acid obtained by either of these methods is esterified togive clofibrate. Both acid and ester are active; the latter, however,is preferred for medicinal use. Clofibrate is hydrolyzedrapidly to 2-p-chlorophenoxy-2-methylpropionic acid by esterasesin vivo and, bound to serum albumin, circulates inblood. The acid has been investigated as a hypolipidemicagent. It is absorbed more slowly and to a smaller extent thanis the ester. The aluminum salt of the acid gives even lowerblood levels than p-chlorophenoxy-2-methylpropionic acid.
Hazard
Questionable carcinogen; toxic; causes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, stiffness, cramps, and muscle tenderness.Biologische Aktivit?t
PPAR agonist (EC 50 values are 50, 500 and > 100 μ M at PPAR α , PPAR γ and PPAR δ respectively). Antihyperlipoproteinemic.Mechanism of action
The three structurally related fibrates available in the United States are gemfibrozil (Lopid), fenofibrate (Tricor) and clofibrate (Atromid-S).They share common uses and toxicities. The fibrates typically lower VLDL triglyceride by 40% or more and elevate plasma HDL cholesterol by 10 to 15%. The reduction of plasma triglycerides in humans appears due to increased lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity. The fibrates activate a nuclear receptor (transcription factor) termed peroxisomal proliferation activated receptor (PPAR) that is a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. PPAR increases transcription of the LPL gene and decreases transcription of the apolipoprotein CIII gene (apo CIII). Since LPL is responsible for catabolism of VLDL triglyceride and apo CIII is an inhibitor of LPL activity, the combined consequences of these changes are increased LPL activity and enhanced removal of triglyceride from the circulation.The elevation of HDL levels by fibrates may be due to two drug actions: induced synthesis of apo-A1, the principal apoprotein of HDL, and increased assembly of new HDL particles in the circulation. Surface components of VLDL contribute to formation of HDL, as the VLDL particles are reduced in size through the action of LPL.The increased rate of catabolism of VLDL caused by the fibrates would provide more components for assembly of HDL particles.
Clinical Use
Clofibrate is the drug of choice in the treatment of typeIII hyperlipoproteinemias and may also be useful, to a lesserextent, in types IIb and IV hyperlipoproteinemias. The drugis not effective in types I and IIa.Clofibrate can lower plasma concentrations of both triglyceridesand cholesterol, but it has a more consistent clinicaleffect on triglycerides. It also affects lipoprotein plasmalevels by enhancing removal of triglycerides from the circulationand causes reduction of VLDL by stimulatinglipoprotein lipase to increase the catabolism of this lipoproteinto LDL. Clofibrate lowers triglyceride levels in theserum much more than cholesterol levels and decreases levelsof FFAs and phospholipids. The lowering of cholesterollevels may result from more than one mechanism. Clofibrateinhibits the incorporation of acetate into the synthesis ofcholesterol, between the acetate and mevalonate step, by inhibitingsn-glyceryl-3-phosphate acyltransferase. Clofibratealso regulates cholesterol synthesis in the liver by inhibitingmicrosomal reduction of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA(HMG-CoA), catalyzed by HMG-CoA reductase. Clofibratemay lower plasma lipids by means other than impairment ofcholesterol biosynthesis, such as increasing excretionthrough the biliary tract.
Nebenwirkungen
The fibrates are generally well tolerated, with GI distress being the most likely complaint. Other adverse effects include myositis and erectile dysfunction, particularly with clofibrate. There is ongoing concern about the fibrates increasing the risk of gallstones, although the extent of risk is unclear. Because clofibrate was associated with increased mortality in early clinical trials, it should be considered as a second-line drug.Sicherheitsprofil
Poison by intravenous route.Moderately toxic by ingestion and other routes. Anexperimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductiveeffects. Reduces plasma lipid levels. Human systemiceffects by ingestion: muscle weakness, muscle spasms, andfever. QArzneimittelwechselwirkung
The fibrates potentiate the actions of the coumarin anticoagulants, such as warfarin, so care should be taken to reduce the dose of simultaneously administered anticoagulants, and plasma prothrombin should be frequently measured until the level stabilizes. As mentioned earlier, great care should be given to combining a statin with a fibrate, since this combination may increase the risk of myositis and perhaps rhabdomyolysis.Environmental Fate
Clofibrate characteristically reduces plasma triglycerides by lowering the concentration of VLDL within 2–5 days after initiation of therapy. In a majority of patients, total cholesterol and LDL concentrations in plasma fall slightly. However, some patients who exhibit a large fall in VLDL may show a paradoxical rise in LDL, resulting in minimal net effect on total cholesterol levels.The drug has several proposed antilipidemic actions, including increased triglyceride and VLDL clearance, mobilization of cholesterol from tissues, increased fecal excretion of neutral sterols, decreased hepatic lipoprotein synthesis and/or secretion, decreased free fatty acid release, and decreased triglyceride synthesis. The precise mechanisms by which clofibrate lowers serum concentrations of triglycerides and cholesterol are not known.
Stoffwechsel
The pro-drug fenofibrate undergoes rapid hydrolysis to produce fenofibric acid. This active metabolite can then be further metabolized by oxidative or conjugative pathways. Gemfibrozil is slightly different in that it does not require initial bioactivation; however, similar to fenofibric acid, it can be oxidized or conjugated. Oxidation of the aromatic methyl groups produces inactive hydroxymethyl and carboxylic acid analogues. As a drug class, fibrates and their oxidized analogues are primarily excreted as glucuronide conjugates in the urine. Oxidization requires the CYP3A4 isozyme; however, because of the ability of these compounds to be conjugated and eliminated either with or without oxidation, drug interactions with other compounds affecting the CYP3A4 system are less important here than with other drug classes.Clofibrat Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
Clofibrat Anbieter Lieferant Produzent Hersteller Vertrieb H?ndler.
Global( 267)Lieferanten
| Firmenname | Telefon | Land | Produktkatalog | Edge Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanjing ChemLin Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | 025-83697070 |
product@chemlin.com.cn | CHINA | 3009 | 60 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 |
sales@coreychem.com | China | 29879 | 58 |
| Chongqing Chemdad Co., Ltd | +86-023-6139-8061 +86-86-13650506873 |
sales@chemdad.com | China | 39894 | 58 |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 |
sales@conier.com | China | 49374 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-29-87569262 +86-15003564040 |
1087@dideu.com | China | 3167 | 58 |
| Neostar United (Changzhou) Industrial Co., Ltd. | +86-0519-85551759 +8613506123987 |
marketing1@neostarunited.com | China | 8840 | 58 |
| TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | +1-781-999-5354 +1-00000000000 |
marketing@targetmol.com | United States | 32161 | 58 |
| Jinan Qinmu Fine Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +8618660799346 |
sales@qinmuchem.com | China | 1009 | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418671 +8618949823763 |
sales@tnjchem.com | China | 34563 | 58 |
| AFINE CHEMICALS LIMITED | +86-0571-85134551 |
sales@afinechem.com | China | 15352 | 58 |
637-07-0(Clofibrat)Verwandte Suche:
Ethylacrylat
2-Phenoxyethylisobutyrat
Butylacrylat
gamma-(4-Chlorphenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-2-pyridin-propanamin-,(Z)-2-butendioat (1:1)
Ethylbutyrat
Tributylphosphat
Ethyl-2-methylbutyrat
Ethyl-2-brombutyrat
ISOXADIFEN-ETHYL
Ethylpropiolat
Beclobrat
Ethylcyanacetat
Ethanol
Ethyl-4-hydroxybenzoat
2-(p-Chlorphenoxy)-2-methylpropionsure
n-Butylacetat
Ethylacetat
Ethyl-2-brom-2-methylpropionat
- Androtor
- 2-(4-Chlorophenoxy)isobutyric Acid Ethyl Ester Ethyl 2-(4-Chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate
- 2-(4-Chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropionic acid ethyl ester, Ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropionate, Ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate
- 2-(P-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropionic*acid ethyl
- Phenoxyisobutyricacidethylester
- Fibrate
- Clofibrate 0.1
- Anti-PPFIA1 (N-terminal) antibody produced in rabbit
- LIP.1
- LIP1
- Clofibrate (Clofibric Acid Ethyl Ester)
- Clofibrate (1 g)
- 2-(P-CHLOROPHENOXY)-2-METHYLPROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ESTER
- 2-(4-CHLOROPHENOXY)ISOBUTYRIC ACID ETHYL ESTER
- 2-(4-CHLOROPHENOXY)-2-METHYLPROPANOIC ACID ETHYL ESTER
- 2-(4-CHLOROPHENOXY)-2-METHYLPROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ESTER
- Abitrate
- 2-(P-CHLOROPHENOXY)-2-METHYLPROPIONICACI D ETHYL ES
- CLOFIBRATE EPC(CRM STANDARD)
- CLOFIBRATE USP(CRM STANDARD)
- 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)-2-methyl-propionicaciethylester
- 2-(p-Chlorophenoxy)isobutyric acid ethyl ester
- Acetic acid, (p-chlorophenoxy)dimethyl-, ethyl ester
- alpha-(p-Chlorophenoxy)isobutyric acid, ethyl ester
- alpha-(p-chlorophenoxy)isobutyricacid,ethylester
- 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methyl-propionicaciethylester
- Athranid-Wirkstoff
- Atrolen
- Atromid
- Atromid S
- Atromida
- Atromidin
- atromids
- Atrovis
- AY 61123
- ay61123
- Azionyl
- Bioscleran
- Bresit
- Cartagyl
- chlorophenoxyisobutyricacidethylester
- Chlorphenisate
- Cinnarizin
- Citiflus
- Claripex
- Claripex CPIB
- Ethyl2-(p-chlorophenoxy)-2-mefhyl-pro-pionate
- ethyl2-(p-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropionate
- ethylalpha-(4-chlorophenoxy)-alpha-methylpropionate
- ethylalpha-(4-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate
- ethylalpha-(p-chlorophenoxy)-alpha-methylpropionate
- ethylalpha-(p-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate
- ethyl-alpha-p-chlorophenoxy-isobutyrate
- ethylchlorophenoxyisobutyrate
- ethylclofibrate
- ethylpara-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate
- Ethylp-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate
- Fibralem