Carboxymethyl cellulose
|
|
Carboxymethyl cellulose Eigenschaften
- Dichte
- 1.050 g/cm3(Temp: 15-18 °C)
- storage temp.
- 2-8°C
- L?slichkeit
- Practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol. It swells with water to form a suspension and becomes viscid in 1 M sodium hydroxide.
- Aggregatzustand
- preswollen, microgranular
- Farbe
- White to off-white
- Geruch (Odor)
- odorless
- Stabilit?t:
- Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
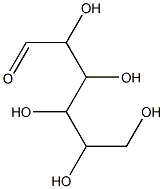
- InChI
- InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-3(9)5(11)6(12)4(10)2-8/h1,3-6,8-12H,2H2
- InChIKey
- GZCGUPFRVQAUEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- SMILES
- C(=O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)CO
- LogP
- -3.17
- CAS Datenbank
- 9000-11-7(CAS DataBase Reference)
- EPA chemische Informationen
- Cellulose, carboxymethyl ether (9000-11-7)
Sicherheit
| WGK Germany | 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RTECS-Nr. | FJ5700000 | ||
| HS Code | 3912310000 | ||
| Toxizit?t | LD50 unreported in mammal (species unspecified): 13340mg/kg |
Carboxymethyl cellulose Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
Chemische Eigenschaften
Cellulose is a natural substance normally present in most diets because it is the major structural carbohydrate of green plants. Cellulose is essentially a linear polymer of glucopyranose units connected by α-1,4-glucoside links. In nature, cellulose is present in plant cell walls as fibers. The molecular weight of the isolated cellulose is approximately 50,000 daltons. The principal sources of cellulose for food-related purposes are cotton linters and wood pulp.Chemical processing converts cellulose into forms or derivatives suitable for incorporation into food products or for use in food packaging materials. For food use, the optimum degree of substitution of a carboxymethyl-residue on each anhydroglucopyranose unit on cellulose is 0.95. By preliminary mild acid hydrolysis, the degree of polymerization (i.e., molecular size) of the cellulose may be reduced before carboxymethylation. Control of the degree of substitution and the degree of polymerization during processing results in production of a wide variety of derivatives that differ in such physical properties as gelling, temperature, viscosity and dispersibility in water. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is used as a thickening agent and stabilizer in foods. Because carboxymethyl cellulose is spontaneously converted to sodium salt in alkaline solution, it is probable that any distinction between carboxymethyl cellulose and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose in foodstuffs is artificial.*
Verwenden
carboxymethyl cellulose (cellulose gum) is a thickener. used in cosmetic formulations when a reactant is not required or desired. often used in bath preparations, beauty masks, hand creams, and shampoos. It is considered a non-comedogenic raw material.synthetische
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is produced by treating wood pulp or cotton linters with alkali and monochloroacetic acid. It occurs as a white- or cream-colored powder or granules.Industrielle Verwendung
Carboxymethyl cellulose is manufactured with molecular weights ranging from 50,000 to 800,000. Several modifications are of interest to flotation because they display good depressing properties for highly floatable magnesium-bearing minerals. These include sodium salts of phenolphthalein ether cellulose and ethanesulfo cellulose.Carcinogenicity
Sarcomas were produced at the site of repeated subcutaneous injection of aqueous solutions of carboxymethylcellulose. It should be noted, however, that massive doses were given and therefore there must have been considerable local trauma.Carboxymethyl cellulose Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
Carboxymethyl cellulose Anbieter Lieferant Produzent Hersteller Vertrieb H?ndler.
Global( 288)Lieferanten
| Firmenname | Telefon | Land | Produktkatalog | Edge Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd | +8613343047651 |
admin@zlchemi.com | China | 3692 | 58 |
| Hebei Kingfiner Technology Development Co.Ltd | +86-15532196582 +86-15373005021 |
lisa@kingfinertech.com | China | 3007 | 58 |
| Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12831 | 58 |
| Hebei Yanxi Chemical Co., Ltd. | +8617531153977 |
allison@yan-xi.com | China | 5856 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 |
sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5889 | 58 |
| Hebei Fengjia New Material Co., Ltd | +86-0311-87836622 +86-17333973358 |
sales06@hbduling.cn | China | 8051 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Haibo Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +undefined18602966907 |
qinhe02@xaltbio.com | China | 997 | 58 |
| Shandong Juchuang Chemical Co., LTD | +undefined15030412209 |
admin@juchuangchem.com | China | 298 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21634 | 55 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418679 +8618949832763 |
info@tnjchem.com | China | 2986 | 55 |
9000-11-7()Verwandte Suche:
Ethylbenzol
CELLULOSE ACETATE
DIETHYLAMINOETHYL CELLULOSE
Cellulose
CELLULOSE
Ethyl cellulose
Carboxymethyl cellulose
Xanthan Gummi
Ethylisocyanacetat
N-Butylisocyanid
1,1,3,3-Tetramethylbutylisocyanat
(Ethylenbis(nitrilomethylidyn)-2,2'-diphenolato)cobalt(II)
(p-Toluolsulfonyl)methylisocyanid
Dichloro(ethylendiamin)platin
CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE CALCIUM (1.5 G) (AS)
Kupfer(II)-4-oxopent-2-en-2-olat
2-Methylpropylisocyanid
Diethylether
- CM 32-CELLULOSE
- CM 52-CELLULOSE
- CELLULOSE, CARBOXYMETHYL ETHER
- Cellulose CM
- CARBOXYMETHYL CELLULOSE ETHER
- CM CELLULOSE CATION EXCHANGER FAST FLOW FIBROUS FOR
- E466
- CM-Cellulose,Carboxymethyl cellulose
- Carmellose (500 mg)
- CarboxyMethyl cellulose 32
- CarboxyMethyl cellulose 52
- Carboxymethyl ether cellusose
- Carboxymethyl cellulose
- CM-Cellulose 23
- CM-Cellulose 22
- CM-Cellulose 32
- CM-Cellulose 52
- CAMTEMPO(TM)
- SELECTACEL(R) CM, STANDARD
- 7h
- 7h(carbohydrate)
- almelose
- apergel
- apeyel
- carbose
- carboxymethylatedcellulosepulp
- cellulosecarboxymethylate
- celluloseglycolicacid
- cellulosegum7h
- cmc-4lf
- cmcellulosecationexchangerfastflowfibrousf
- colloresine
- glycocelta
- glycolicacidcelluloseether
- thylose
- Carboxyl Methyl Cellulose
- cm cellulose fibrous form
- cm cellulose microgranular form 25-60 microns
- CM CELLULOSE MICROGRANULAR FORMPRESWOLLE N
- Cmc (Sodium Carboxy Methyl Cellulose) Food
- Carboxy Methylated Cellulose
- CMC(GEJ)
- Cmc (Sodium Carboxy Methyl Cellulose) Industrial Grade
- Carmellose CRS
- 9000/11/7 0:00:00
- Carboxymethyl cellulose USP/EP/BP
- CM Cellulose CM-52
- CM Cellulose CM-32
- Carmellose (1096611)
- CM CELLULOSE
- 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal
- CMC
- kmts
- Carmellose
- croscarmellose
- acetic acid,2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal
- pentahydroxyhexanal
- NS-300