Stickstoff
|
|
Stickstoff Eigenschaften
- Schmelzpunkt:
- −210 °C(lit.)
- Siedepunkt:
- −196 °C(lit.)
- Dichte
- 1.2506
- Dampfdichte
- 0.97 (vs air)
- L?slichkeit
- At 20 °C and at a pressure of 101 kPa, 1 volume dissolves in about 62 volumes of water and about 10 volumes of ethanol (96 per cent).
- Aggregatzustand
- colorless gas
- Farbe
- colorless
- Geruch (Odor)
- odorless, tasteless
- Wasserl?slichkeit
- slightly soluble H2O; insoluble alcohol [HAW93]
- Merck
- 13,6634
- Dielectric constant
- 1.0(20℃)
- CAS Datenbank
- 7727-37-9(CAS DataBase Reference)
- NIST chemische Informationen
- Nitrogen(7727-37-9)
- EPA chemische Informationen
- Nitrogen (7727-37-9)
Sicherheit
- Risiko- und Sicherheitserkl?rung
- Gefahreninformationscode (GHS)
| S-S?tze: | 38 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RIDADR | UN 1066 2.2 | ||
| WGK Germany | - | ||
| RTECS-Nr. | QW9700000 | ||
| F | 4.5-31 | ||
| DOT Classification | 2.2 (Nonflammable gas) | ||
| HazardClass | 2.2 | ||
| Giftige Stoffe Daten | 7727-37-9(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Bildanzeige (GHS) |

|
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alarmwort | Warnung | ||||||||||||||
| Gefahrenhinweise |
|
||||||||||||||
| Sicherheit |
|
Stickstoff Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
GERUCHLOSE FARBLOSE TIEFKALTE FLüSSIGKEIT.ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
GERUCHLOSES FARBLOSES KOMPRIMIERTES GAS.PHYSIKALISCHE GEFAHREN
Das Gas vermischt sich leicht mit Luft.PHYSIKALISCHE GEFAHREN
Das Gas ist im kalten Zustand schwerer als Luft. Es kann sich in tiefer gelegenen Bereichen sammeln und den Luftsauerstoff verdr?ngen.ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV: Erstickungsgefahr durch Sauerstoffverdr?ngung. (ACGIH 2005).MAK nicht festgelegt (DFG 2005).
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV: Erstickungsgefahr durch Sauerstoffverdr?ngung. (ACGIH 2005).MAK nicht festgelegt (DFG 2005).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation.AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation.INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Beim Entweichen aus dem Beh?lter verdampft die Flüssigkeit sehr schnell, wobei die Luft verdr?ngt wird. Ernste Erstickungsgefahr in geschlossenen R?umen. (S. Anm.)INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Beim Entweichen aus dem Beh?lter kann das Gas die Luft verdr?ngen. Erstickungsgefahr in geschlossenen R?umen. (S. Anm.)WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION:Die Flüssigkeit kann Erfrierungen hervorrufen.
LECKAGE
Belüftung. Wasserstrahl NIEMALS auf die Flüssigkeit richten. Chemikalienschutzanzug mit umgebungsluftunabh?ngigem Atemschutzger?t.LECKAGE
Belüftung. Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Umgebungsluftunabh?ngiges Atemschutzger?t.S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S38:Bei unzureichender Belüftung Atemschutzger?t anlegen.Beschreibung
Nitrogen makes up the major portion of the atmosphere (78.08 percent by volume, 75.5 percent by weight). It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, nontoxic, almost totally inert gas, and is colorless as a liquid. Nitrogen is nonflammable, will not support combustion, and is not life supporting. It combines with some of the more active metals such as lithium and magnesium to form nitrides, and at high temperatures it will also combine with hydrogen, oxygen, and other elements. It is used as an inert protection against atmospheric contamination in many nonwelding applications. Nitrogen is only slightly soluble in water and most other liquids, and is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. As a liquid at cryogenic temperatures it is nonmagnetic. It is shipped as a nonliquefied gas at pressures of 2000 psig (13 790 kPa) or above, and also as a cryogenic fluid at pressures and temperatures below 200 psig (1380 kPa) and -261°F (-163°C).Chemische Eigenschaften
Nitrogen occurs naturally as approximately 78% v/v of the atmosphere. It is a nonreactive, noncombustible, colorless, tasteless, and odorless gas. It is often used under refrigeration as a cryogenic liquid. The boiling point is -195.8 °C and -320 °F. Nitrogen is not combustible. Nitrogen can combine with oxygen at high temperatures to form oxides and may form ammonia in contact with hydrogen at elevated temperatures. Cyanides can form if nitrogen is heated with carbon in presence of alkalies or barium oxide. If nitrogen comes in contact with ozone, nitrogen can oxidize explosively.It is usually handled as a compressed gas, stored in metal cylinders.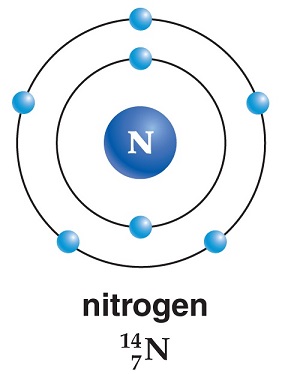
Physikalische Eigenschaften
In its natural gaseous state, nitrogen is a relatively inert diatomic molecule (N2) that iscolorless, odorless, and tasteless, yet it is responsible for hundreds of active compounds. Itmakes up about 78% of the air we breathe. We are constantly taking it into our lungs withno stimulation or sensation; therefore, we really do not detect its presence. When liquefied, itis still colorless and odorless and resembles water in density. The melting point of nitrogen is–209.86°C, its boiling point is –195.8°C, and its density as a gas is 0.0012506 g/cm3.Isotopes
There are 19 isotopes of nitrogen, two of which are stable. The stable ones andtheir proportion to the natural abundance of nitrogen on Earth follow: N-14 = 99.634%and N-15 = 0.366%. The other 17 isotopes are radioactive and man-made in nuclearreactors and have half-lives ranging from a few nanoseconds to 9.965 minutes.Origin of Name
From the two Greek words nitron and genes, which together stand for “soda or saltpeter forming.”Occurrence
Nitrogen is the 30th most abundant element on Earth. There is an almost unlimited sourceof nitrogen available to us considering that our atmosphere constitutes 4/5, or over 78%, ofthe nitrogen by volume. Over 33 million tons of nitrogen is produced each year by liquefyingair and then using fractional distillation to produce nitrogen as well as other gases in the atmosphere. During this process the air is cooled and then slowly warmed to fractionaltemperature points at which each specific gas in the air will “boil” off. (Note: Oxygen, argon,carbon dioxide, and nitrogen all have specific boiling points and these gases can be used tocollect the specific gas during the fractionation process.) When the temperature –reaches–195.8°C, the nitrogen is boiled off and collected.There is a balance of nitrogen with other gases in the atmosphere that is maintained bywhat is called the nitrogen cycle. This cycle includes several processes, including nitrogen fixationof bacteria in the soil by legumes (bean and pea plants). Lightning produces nitrogen, asdo industrial waste gases and the decomposition products of organic material (i.e., organicproteins and amino acids in plants and animals contain nitrogen). In time, these sourcesreplace the nitrogen in the atmosphere to complete the cycle.
Ammonia (NH3) is the first binary molecule discovered in outer space of our galaxy, theMilky Way. It may also be the main compound that forms the rings of the planet Saturn.
Charakteristisch
There are approximately 4,000 trillion tons of gas in the atmosphere, and nitrogen makesup about 78% of these gases. It is slightly soluble in water and alcohol. It is noncombustibleand is considered an asphyxiant gas (i.e., breathing pure nitrogen will deprive the body ofoxygen).Although nitrogen is considered an inert element, it forms some compounds that are veryactive. Of the diatomic molecules, such as CO2 , it is difficult to separate the two atoms innitrogen’s molecules because of their strong binding energy. This is the reason that, along withcarbon dioxide, nitrogen gas is stable. However, once separated, the individual atoms of nitrogen(N) become very reactive and do combine with hundreds of other elements.
Nitrogen can be liquefied easily, making it useful in many applications wherein sustainedcooling is needed. At high temperatures, nitrogen reacts with many metals to form nitrides.
Verwenden
In manufacture of ammonia, nitric acid, nitrates, cyanides, etc.; in manufacture of explosives; in filling high-temp thermometers, incandescent bulbs; to form an inert atm for preservation of materials, for use in dry boxes or glove bags. Liquid nitrogen in food-freezing processes; in the laboratory as a coolant. Pharmaceutic aid (air displacement).Vorbereitung Methode
Nitrogen is obtained commercially, in large quantities, by the fractional distillation of liquefied air.Definition
Nitrogen, N2, is a colorless,odorless, inert gas that comprises 80%of the earth's atmosphere. It serves as a diluent and controls natural burning and respiration rates, which would be much faster in higher concentrations of oxygen. Nitrogen is soluble in water and alcohol, but is essentially insoluble in most other liquids. It is essential to practically all forms of life and its compounds serve as foods or fertilizers. Nitrogen is used in the manufacture of ammonia and nitric acid. Nitrogen is essentially an inert gas at ambient and moderate temperatures. Therefore, it is easily handled by most metals.At elevated temperatures, nitrogen can be aggressive to metals and alloys.Allgemeine Beschreibung
A colorless odorless gas. Noncombustible and nontoxic. Makes up the major portion of the atmosphere, but will not support life by itself. Used in food processing, in purging air conditioning and refrigeration systems, and in pressurizing aircraft tires. May cause asphyxiation by displacement of air. Under prolonged exposure to fire or heat containers may rupture violently and rocket.Air & Water Reaktionen
Slightly soluble in water.Reaktivit?t anzeigen
These substances undergo no chemical reactions under any known circumstances except those under extreme conditions (liquid Nitrogen reacts violently in mixture with magnesium powder when a fuse is lit. Due to formation of magnesium nitride). Otherwise, they are nonflammable, noncombustible and nontoxic. They can asphyxiate.Hazard
Nitrogen is nontoxic, but it is an asphyxiate gas that cannot, by itself, support oxidation(combustion) or support life. If you breathe pure nitrogen for any period of time, you will die—not because the nitrogen gas is a poison, but because your body will be deprived of oxygen.Nitrogen oxides are formed under certain conditions when nitrogen combines with oxygen,thus contributing to pollution. One source is from the internal combustion engine thatproduces NO similar to lightning. Once released, it combines with more oxygen to form ,which is a very reactive polluting gas. Nitrogen dioxide NO2 is the main cause of “brown”smog over some cities and is harmful to plants, animals, and humans. To make matter worse,if there is adequate sunlight at the time of the smog, the ultraviolet light of the sun will breakdown the N and O of the NO2 to form free radicals of oxygen that are reactive, forming ozone(O3), which is itself a strong oxidizing agent that adds to pollution.
Several of the oxygen, hydrogen, and halogen compounds of nitrogen are toxic wheninhaled. A common error made in using household cleaners is to mix or use together ammoniacleaning fluids (containing nitrogen) and Clorox-type cleaning fluids (containing chlorine).The combined fumes can be deadly in any confined area. NEVER mix Clorox with ammoniatypecleaning fluids.
Health Hazard
Vapors may cause dizziness or asphyxiation without warning. Vapors from liquefied gas are initially heavier than air and spread along ground.Brandgefahr
Non-flammable gases. Containers may explode when heated. Ruptured cylinders may rocket.Industrielle Verwendung
Nitrogen is often called an inert gas, and is used for some inert atmospheres for metal treating and in lightbulbs to prevent arcing, but it is not chemically inert. It is a necessary element in animal and plant life, and is a constituent of many useful compounds. Nitrogen combines with many metals to form hard nitrides useful as wear-resistant metals. Small amounts of nitrogen in steels inhibit grain growth at high temperatures, and also increase the strength of some steels. It is also used to produce a hard surface on steels.Because of the importance of nitrogen compounds in agriculture and chemical industry, much of the industrial interest in elementary nitrogen has been in processes for converting elemental nitrogen into nitrogen compounds. The principal methods for doing this are the direct synthesis of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen, the electric arc process, which involves the direct combination ofN2 and O2 to nitric oxide, and the cyanamide process.
Materials Uses
Gaseous nitrogen is noncorrosive and inert, and may consequently be contained in systems constructed of any common metals and designed to safely withstand the pressures involved. At the temperature of liquid nitrogen, ordinary carbon steels and most alloy steels lose their ductility and are considered unsafe for liquid nitrogen service. Satisfactory materials for use with liquid nitrogen include austenitic stainless steel (for example, types 304 and 316) and other nickel-chromium alloys, copper, Monel, brass, and aluminum.Pharmakologie
Atropine does not reactivate the phosphorylated AChE but competes with acetylcholine for binding with the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor acting as an antagonist.Sicherheitsprofil
Low toxicity. In high concentrations it is a simple as-p~h yxiant. The release of nitrogen from solution in the blood, with formation of small bubbles, is the cause of most of the symptoms and changes found in compressed air illness (caisson disease). It is a narcotic at hgh concentration and hgh pressure. Both the narcotic effects and the bends are hazards of compressed air atmospheres such as found in underwater dving. Nonflammable gas. Can react violently with lithium, neodymium, titanium under the proper condtions. See also ARGON.Sicherheit(Safety)
Nitrogen is generally regarded as a nontoxic and nonirritant material. However, it is an asphyxiant and inhalation of large quantities is therefore hazardous.m?gliche Exposition
Nitrogen is present in the air we breathe. Health effects may occur at concentrations above 80%. It has many medical and industrial uses including the quick freezing of food. The gas is used for purging, heat treating; food freezing; annealing, cooling, oil recovery; in the inert blanketing of sensitive materials and as a reactant in chemical synthesis of ammonia.Lager
Nitrogen is stable and chemically unreactive. It should be stored in tightly sealed metal cylinders in a cool, dry place.Versand/Shipping
UN1066 Nitrogen, compressed, Hazard Class:, Hazard Class: 2.2; Labels: 2.2-Nonflammable compressed gas; UN1977 Nitrogen, refrigerated liquid cryogenic liquid, Hazard Class:, Hazard Class: 2.2; Labels: 2.2- Nonflammable compressed gas. Cylinders must be transported in a secure upright position, in a well-ventilated truck. Protect cylinder and labels from physical damage. The owner of the compressed gas cylinder is the only entity allowed by federal law (49CFR) to transport and refill them. It is a violation of transportation regulations to refill compressed gas cylinders without the express written permission of the owner.Inkompatibilit?ten
Containers may explode when heated. Liquid nitrogen is very unreactive, nonflammable, noncombustible and nontoxic. Contact with water may result in vigorous or violent boiling and extremely rapid vaporization. If the water is hot, there is the possibility that a liquid “superheat” explosion may occur. Pressures may build to dangerous levels if the liquid contacts water in a closed container.Waste disposal
Return refillable compressed gas cylinders to supplier. Vent to atmosphere.Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (injections; dental preparations; nasal sprays; oral solutions; rectal gels). Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in parenteral and nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK and USA. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.Stickstoff Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
Calcium nitrate tetrahydrate
octyl phenyl polyoxyethylene (30) ether
2-Fluoropyridine-6-carboxylic acid
2-Furanboronic acid
Isopropyl(4-chlorophenyl)acetyl chloride
Emulsifier LAE-9
Irinotecan
Aluminiumnitrid
PPV
C^{8~9^} alkyl phenyl polyoxyethylene (15) ether
2-ETHOXYPHENYLBORONIC ACID
Hydrogen[4-[[4-(diethylamino)phenyl][4-[ethyl[(3-sulfonatobenzyl)amino]-o-tolyl]methylen]-3-methylcyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-yliden](ethyl)(3-sulfonatobenzyl)ammonium, Natriumsalz
Propylisocyanat
tri-isopropanlamiue polyoxypropyleal polyoxy-ethylene ether
Ethylphenylglyoxylat
3,4-Diethoxyaniline
Ferric nitrate nonahydrate
Dicyclohexylphenylphosphin
pesticide emulsifier 602^<#^>
3-Chlorothiophene-2-carboxylic acid
2-(Trifluormethoxy)phenylboronic acid
softening agent SCI-A
an improved PVA hydrogel as artificial vitreous body
transfer factor (TF)
2-Fluoro-3-pyridylboronic acid
Calciumnitrit
AE series crude oil viscosity reducer
5-Chlor-2-(4-chlorphenoxy)anilin
dacron oiling agent 99^<#^>
pare isopropyl phenol polyoxyethylene (9~10) ether
4-Cyanophenylboronic acid
Ethyl-3-thenoat
polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene monobutyl ether
Thienamycin
2-Isopropylphenylboronic acid
6-Methylpyridine-3-boronic Acid
Diethylphenylphosphin
ETHYL 2-(1-METHYL-1H-IMIDAZOL-2-YL)-2-OXOACETATE
Quinoline-5-boronic acid
Ethyl-4-hydroxy-7-trifluormethyl-3-chinolincarboxylat
Stickstoff Anbieter Lieferant Produzent Hersteller Vertrieb H?ndler.
Global( 122)Lieferanten
| Firmenname | Telefon | Land | Produktkatalog | Edge Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaanxi Didu New Materials Co. Ltd | +86-89586680 +86-13289823923 |
1026@dideu.com | China | 8670 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21634 | 55 |
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28172 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22963 | 58 |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 |
sales@conier.com | China | 49374 | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418671 +8618949823763 |
sales@tnjchem.com | China | 34563 | 58 |
| XIAMEN AMITY INDUSTRY AND TRADE CO., LTD. | +8618950047208 |
ellena@amitychem.com | China | 43416 | 58 |
| Mainchem Co., Ltd. | +86-0592-6210733 |
sale@mainchem.com | China | 32343 | 55 |
| Chemwill Asia Co.,Ltd. | 86-21-51086038 |
chemwill_asia@126.com | CHINA | 23912 | 58 |
| Guangzhou Yuejia Gas Co., Ltd | 400-6377517 19876107228 |
linfeng@yigas.cn | China | 39 | 58 |
7727-37-9(Stickstoff)Verwandte Suche:
Olanzapine
Helium
Wasserstoff
Acetylen
(Z)-But-2-en
2-(2H-Benzotriazol-2-yl)-p-kresol
2,2-Dibrom-2-cyanacetamid
1,2-Dihydro-1-methyl-5H-tetrazol-5-thion
Dikaliumtetraiodomercurat
2,2'-Dimethyl-2,2'-azodipropiono-nitril
5-Chlor-2-methoxybenzoldiazoniumchlorid
Natriumazid
3,3'-Dimethoxybiphenyl-4,4'-di(diazonium)zinkchlorid
4-chlorbenzoldiazoniumhexafluorphosphat
4-(diethylamino)benzoldiazoniumtetrafluorborat
4-(Phenylcarboxamido)-2,5-dimethoxybenzoldiazoniumchlorid
4-(Phenylcarboxamido)-2-methoxy-5-methylbenzoldiazoniumchlorid
- N-trogen(enrichedair)
- NITROGEN(CRYOGENICLIQUID)
- nitrogen molecule
- NITROGEN-MOLECULE
- CUSTOM GAS MIX (CODE I-460)
- NITROGEN
- NITROGEN STANDARD
- NITROGEN STANDARD, (AS AMMONIA)
- azote,liquide
- Diatomic nitrogen
- Diazyne
- nitrogen,liquid
- nitrogen,liquified
- nitrogen,refrigeratedliquid(cryogenicliquid)
- nitrogen-14
- nitrogengas
- nitrogeno
- Nitrogen Messer(R) CANGas, 99.999%
- HYDROGEN AND NITROGEN
- HYDROGEN NITROGEN
- CAL-MAT NITROGEN
- Nitrogen solution
- Molecular nitrogen
- molecularnitrogen
- molekularerStickstoff
- molnitrogen
- nitrogen(gaseous)
- nitrogen(liqufied)
- nitrogen(non-specificname)
- nitrogen,compressed
- NITROGEN, 99.998+%
- NITROGEN, PRESSURE TIN WITH 1 L
- netrogen
- Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen Standard
- STICKSTOFF, GAS, 5.0
- Nitrogen,Total
- Nitrogen, 99.999%
- nitrogen refrigerated liquid
- Liquid nitrogen,high purity
- Nitrogen,high purity
- Nitrogen,pure
- nitrogen N2
- Nitrogen ISO 9001:2015 REACH
- NITROGEN FROM
- LN2
- Standard solution for the determination of nitrogen
- Dinitrogen
- Stickstoff
- Liquid nitrogen
- Nitrogen gas
- Fluorine nitrogen gas
- Nitrogen (Annex I, Cat. 6)
- 7727-37-9
- Compressed and Liquefied Gases
- Synthetic Reagents
- Compressed and Liquefied Gases
- Chemical Synthesis
- Electronic Chemicals







