626-72-2
中文名稱
L-高胱氨酸
英文名稱
L-Homocystine
CAS
626-72-2
EINECS 編號
210-962-5
分子式
C8H16N2O4S2
MDL 編號
MFCD00020391
分子量
268.35
MOL 文件
626-72-2.mol
更新日期
2025/05/19 16:09:05
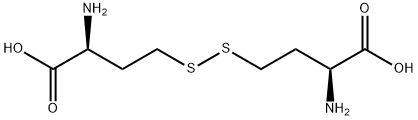 626-72-2 結(jié)構(gòu)式
626-72-2 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
中文別名
L-4,4'-二硫雙(2-氨基丁酸)L-高胱氨酸
L-4,4ˊ-二硫雙(2-氨基丁酸)
L-類胱氨酸
L-同型胱氨酸
L-4,4'-二硫雙(2-氨基丁酸)
L-高胱氨酸
英文別名
(H-HCY-OH)2(H-HOCYS-OH)2
(H-HOMOCYS-OH)2
H-L-HOCYSTINE
L-4,4'-DITHIO-BIS(2-AMINOBUTANOIC ACID)
L-4,4'-Dithiobis(2-aminobutyric acid)
L-HOMOCYSTINE
4,4’-dithiobis[2-amino-,[s-(theta,theta)]-butanoicaci
(H-Hcy-OH)?
L-homocystine cell culture tested
[S-(R*,R*)]-4,4'-dithiobis[2-aminobutyric] acid
2-amino-4-(3-amino-3-carboxy-propyl)disulfanyl-butanoic acid
H-HoCys-OH
(H-Hcys-OH) 2
L-Homocystine
H-L-HCystine
(2S,2'S)-2,2'-Diamino-(4,4'-dithiobisbutyric acid)
3,3'-(Dithiobismethylene)bisalanine
4,4'-Dithiobis[(2S)-2-aminobutanoic acid]
4,4'-Dithiobis[(S)-2-aminobutanoic acid]
所屬類別
生物化工:常見氨基酸及蛋白質(zhì)類物理化學性質(zhì)
熔點281-284 °C (dec.)(lit.)
比旋光度77 º (c=1% in 1N HCl)
沸點507.6±50.0 °C(Predicted)
密度1.443±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
儲存條件Store at 0-5°C
溶解度H2O : 5 mg/mL (18.63 mM; ultrasonic and adjust pH to 3 with H2O)DMSO : 1 mg/mL (3.73 mM; ultrasonic and adjust pH to 5 with HCl)
酸度系數(shù)(pKa)1.90±0.10(Predicted)
形態(tài)粉末
顏色Off-white to light yellow
BRN1728583
InChIKeyZTVZLYBCZNMWCF-WDSKDSINSA-N
CAS 數(shù)據(jù)庫626-72-2(CAS DataBase Reference)
EPA化學物質(zhì)信息L-Homocystine (626-72-2)
常見問題列表
用途
在食品行業(yè)中,L-高胱氨酸與五碳糖或者六碳糖類共同加熱可以產(chǎn)生肉類的香味,同時將半腕氨酸加入玉米的加工品中,可以促使玉米的香味增加10-40倍。應(yīng)用
在醫(yī)藥方面,L-高胱氨酸因為在生物體內(nèi)具有抱合作用,因此對于例如甲酸、乙酸、四氯化碳、酒精等毒物具有廣泛的解毒作用,并且可以維持角蛋白生成中巰基酶的活性。L-高胱氨酸鹽酸鹽具有能夠恢復肝功能的用途,對于血清病、銻劑及放射性藥物中毒,也有一定的治療作用。生物活性
L-Homocystine 是L-homocysteine 的一種氧化物,L-homocysteine 是一種抗血栓因子,血管舒張損害劑,促炎因子,也是研究心血管疾病發(fā)生機制的內(nèi)質(zhì)網(wǎng)應(yīng)激反應(yīng)的誘導劑。靶點
|
Human Endogenous Metabolite
|
體內(nèi)研究
A single or multiple doses of L-Homocystine administered to mice during organogenesis can aggravate the developmental disturbances caused by a single dose of VPA administered on GD 8. Whereas, VPA lowers significantly plasma FA and vitamin B12 concentrations, it has no direct impact on the homocysteine concentrations. Therefore, it is proposed that high levels of homocysteine disturb the FA, vitamin B12, and possibly methionine metabolism thus providing a favorable situation for VPA to interfere with the development of susceptible embryos.