| Identification | More | [Name]
L-Homocystine | [CAS]
626-72-2 | [Synonyms]
(H-HCY-OH)2
(H-HOCYS-OH)2
(H-HOMOCYS-OH)2
H-L-HOCYSTINE
L-4,4'-DITHIO-BIS(2-AMINOBUTANOIC ACID)
L-4,4'-Dithiobis(2-aminobutyric acid)
L-HOMOCYSTINE | [EINECS(EC#)]
210-962-5 | [Molecular Formula]
C8H16N2O4S2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00020391 | [Molecular Weight]
268.35 | [MOL File]
626-72-2.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
281-284 °C (dec.)(lit.) | [alpha ]
77 º (c=1% in 1N HCl) | [Boiling point ]
507.6±50.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.443±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
Store at 0-5°C | [solubility ]
H2O : 5 mg/mL (18.63 mM; ultrasonic and adjust pH to 3 with H2O)DMSO : 1 mg/mL (3.73 mM; ultrasonic and adjust pH to 5 with HCl) | [form ]
Powder | [pka]
1.90±0.10(Predicted) | [color ]
Off-white to light yellow | [BRN ]
1728583 | [InChIKey]
ZTVZLYBCZNMWCF-WDSKDSINSA-N | [CAS DataBase Reference]
626-72-2(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
626-72-2(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Safety Statements ]
S22:Do not breathe dust .
S24/25:Avoid contact with skin and eyes . | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [HS Code ]
29309090 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
L-homocysteine is an aliphatic amino acid with the molecular formula (C8H16N2O4S2). It is a white powder with an acidic taste and is easily soluble in water. It has limited solubility in ethanol. L-homocysteine has a sulfhydryl group on its side chain, which allows it to form disulfide bonds with other L-homocysteine residues in proteins. This feature contributes to the stable three-dimensional structure of proteins. As a result, L-homocysteine finds extensive applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, feed, and cosmetics. | [Uses]
Increased levels lead to hyperhomocysteinemia; a cardiovascular risk factor in prediction of coronary heart disease as well as being associated with congenital birth defects, pregnancy complications and cancer. | [Definition]
ChEBI: L,L-homocystine is a homocystine in which both chiral centres have L configuration. It is functionally related to a L-homocysteine. It is a tautomer of a L,L-homocystine zwitterion. | [Biological Activity]
L-Homocystine is the oxidized member of the L-homocysteine:L-homocystine pair. Homocysteine/homocystine is derived from methionine. Homocysteine is a pro-thrombotic factorvasodilation impairing agentpro-inflammatory factor and endoplasmatic reticulum-stress inducer used to study cardiovascular disease mechanisms. | [Synthesis]
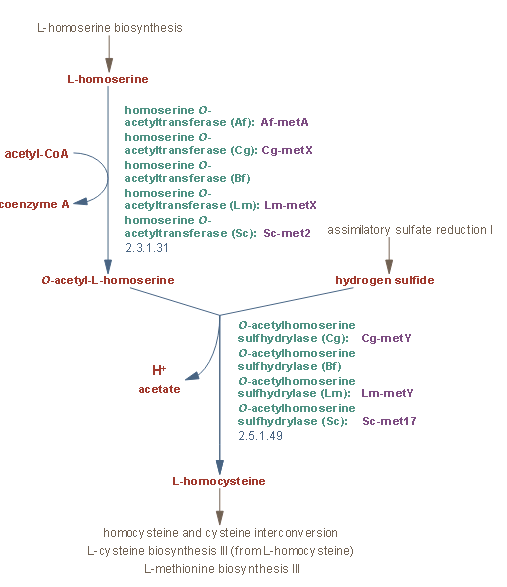
L-homoserine(626-72-2) is biosynthesized from L-aspartate, which is synthesized from oxaloacetate, a TCA cycle intermediate. Homoserine is activated through esterification to form the O-acetyl ester by the enzyme homoserine O-acetyltransferase. In certain organisms, including the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and certain bacteria, hydrogen sulfide reacts with O-acetyl-L-homoserine, replacing the acetyl group and forming L-homocysteine.
 | [Purification Methods]
The acid (3g) is dissolved in freshly boiled H2O (30mL) under N2, cooled under N2 (all operations should be under N2), absolute EtOH (100mL) is added, the acid is filtered off, and a second crop is obtained by diluting the filtrate to 500mL with absolute EtOH, kept overnight in a refrigerator, filtered, washed with EtOH and dried in a vacuum. The D(R,R)-form has similar properties but is –ve in M HCl and +ve in H2O. [du Vigneaud & Patterson J Biol Chem 109 101 1935, du Vigneaud & Brown Biochemical Preparations 5 93, 95 1975, Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 2667-2670 1961, Beilstein 4 III 1643, 4 IV 3199, Koegel et al. J Am Chem Soc 77 5708 1955.] |
|
|