482-27-9
中文名稱
異茴芹靈
英文名稱
ISOPIMPINELLIN
CAS
482-27-9
分子式
C13H10O5
MDL 編號
MFCD00017407
分子量
246.22
MOL 文件
482-27-9.mol
更新日期
2025/01/04 09:15:02
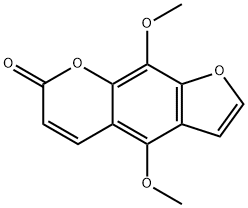 482-27-9 結構式
482-27-9 結構式
基本信息
中文別名
異茴芹靈異茴芹內酯
異虎耳草素
英文別名
4,9-DIMETHOXYPSORALEN5,9-DIMETHOXYPSORALEN
AKOS 243-24
DIMETHYLPSORALEN
ISOPIMPINELLIN
4,9-Dimethoxy-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one
4,9-Dimethoxy-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one
5,8-Dimethoxy-6,7-furanocoumarin
5,8-Dimethoxypsoralen
5,8-Dimethoxypsoralene
7H-Furo[3,2-g][1]benzopyran-7-one, 4,9-dimethoxy-
7H-Furo[3,2-g][1]benzopyran-7-one,4,9-dimethoxy-
4,9-Dimethoxy-7H-furo[3,2-g][1]benzopyran-7-one
DIMETHYLPSORALEN hplc
ISOPIMPINELLIN WITH HPLC
4,9-Dimethoxy-7H-furo[3,2-γ],[1]benzopyran-7-one
4,9-Dimethoxy-furo[3,2-γ],chromen-7-one
所屬類別
醫(yī)藥中間體:吡喃類化合物物理化學性質
外觀性狀淡黃色粉末,可溶于甲醇、乙醇、DMSO等有機溶劑,來源于虎耳草,蛇床子。
熔點150-151°C
沸點448.7±45.0 °C(Predicted)
密度1.352±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
儲存條件2-8°C
溶解度Soluble in acetone and chloroform;
形態(tài)粉末晶體
顏色淡黃色到黃色到綠色
水溶解性幾乎不溶于水
最大波長(λmax)268nm(MeOH)(lit.)
BRN262337
LogP1.407 (est)
CAS 數(shù)據庫482-27-9(CAS DataBase Reference)
安全數(shù)據
警示詞危險
危險性描述H300+H310+H330
危險品標志T+
危險類別碼R20/21/22
安全說明S22-S36/37/39
危險品運輸編號UN 2811 6.1 / PGII
WGK Germany3
RTECS號LV1049200
海關編碼2932202000
毒害物質數(shù)據482-27-9(Hazardous Substances Data)
常見問題列表
生物活性
Isopimpinellin 是從Pimpinella saxifrage 根部分離得到的一種具有口服活性的化合物。Isopimpinellin 通過7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene.阻斷 DNA加合物的形成和皮膚腫瘤的發(fā)生。Isopimpinellin 具有抗利什曼病的活性。體內研究
Isopimpinellin (oral gavage, 35-150 mg/kg) inhibits B[a]P-DNA adduct formation and DMBA–DNA adduct formation in SENCAR mice with skin tumor.
| Animal Model: | Female SENCAR mice (7-9 weeks of age) were fed AIN-76A semi-purified diet (Dyets, Bethlehem, PA) for 2 weeks prior to and during the study. |
| Dosage: | 35–150 mg/kg. |
| Administration: | Oral gavage, suspended in 0.1 mL corn oil at 24 h and 2 h prior to topical treatment with [3H]B[a]P (200 nmol, 1 Ci/mmol) or [3H]DMBA (10 nmol, 10 Ci/mmol) (each in 0.2 mL acetone). |
| Result: |
Significantly inhibited B[a]P-DNA adduct formation by 37 and 26%, respectively.
Isopimpinellin (35, 70 and 150 mg/kg) blocked DMBA–DNA adduct formation by 23, 56 and 69%, respectively |
