111-58-0
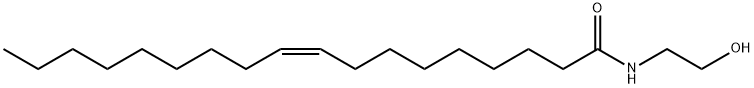 111-58-0 結(jié)構(gòu)式
111-58-0 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
油酰乙醇胺
油酰胺 MEA
油酰單乙醇胺
ODA
OLEIC ACID-2,6-DIISOPROPYL ANILIDE
N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-,(Z)-9-Octadecenamide
Oleoylmonoethanolamide
OLEAMIDE MEA
9-Octadecenamide, N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-, (9Z)-
(Z)-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)octadec-9-enamide
LSUREMONOETHANOLAMID
Oleyl monoethanolamide
N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)oleamide
N-(cis-9-Octadecenoyl)ethanolamine
N-Oleoylethanolamine
OEA
N-(cis-9-Octadecenoyl)ethanolamine, N-(Hydroxyethyl)oleamide, OEA, oleoylethanolamide
(Z)-N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-9-octadecenamide
AM-3101
N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)oleic amide
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
安全數(shù)據(jù)
常見問題列表
|
Human Endogenous Metabolite
|
PPAR-α
|
Oleoylethanolamide (OEA), an endogenous PPAR-α ligand, attenuates liver fibrosis targeting hepatic stellate cells. Oleoylethanolamide suppresses TGF-β1 induced hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) activation in vitro via PPAR-α. To assess the impact of Oleoylethanolamide on HSCs activation, the expression levels of α-SMA and Col1a in TGF-β1-stimulated HSCs are examined by qPCR. The mRNA levels of α-SMA and Col1a are markedly induced in the group of CFSC cells with TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) stimulation for 48h, while the mRNA levels are suppressed when treated with Oleoylethanolamide in a dose-dependent manner. Immunofluorescence and western blot results show that Oleoylethanolamide treatment dose-dependently inhibits the protein expression of α-SMA, the marker of HSC activation. The inhibitory effects of Oleoylethanolamide on HSCs activation are completely blocked by PPAR-α antagonist MK886 (10 μM). Moreover, the mRNA and protein expression levels of PPAR-α are down-regulated with TGF-β1 stimulation, while Oleoylethanolamide treatment restores these changes in dose-dependent manner. In addition, the phosphorylation of Smad 2/3 is upregulated in the presence of TGF-β1 stimulation, consistent with the observed effects on HSC activation, while Oleoylethanolamide (10 μM) reduces the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 in CFSC simulated with TGF-β1.
Oleoylethanolamide (OEA) can significantly suppress the pro-fibrotic cytokine TGF-β1 negatively regulate genes in the TGF-β1 signaling pathway (α-SMA, collagen 1a, and collagen 3a) in mice models of hepatic fibrosis. Treatment with Oleoylethanolamide (5 mg/kg/day, intraperitoneal injection, i.p.) significantly attenuates the progress of liver fibrosis in both two experimental animal models by blocking the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs).

