| Identification | More | [Name]
Phlorizin | [CAS]
60-81-1 | [Synonyms]
1-[2-(BETA-D-GLUCOPYRANOSYLOXY)-4,6-DIHYDROXYPHENYL]-3-(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)-1-PROPANONE
2'-O-GLUCOSYL-4',6',4-TRIHYDROXYDIHYDROCHALCONE
2'-O-GLUCOSYL-4',6',4-TRIHYDROXYDIHYDROCHALCONE DIHYDRATE
4',6'-DIHYDROXY-2'-(BETA-D-GLUCOSIDO)-3-(4-HYDROXYPHENYL) PROPIOPHENONE
PHLORETIN-2'-BETA-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE DIHYDRATE
PHLORETIN-2'-BETA-D-GLUCOSIDE
PHLORETIN 2'-BETA-D-GLUCOSIDE DIHYDRATE
PHLORETIN-2'-O-GLUCOSIDE DIHYDRATE
PHLORIDZIN
PHLORIDZIN DIHYDRATE
PHLORIZIN
PHLORIZIN DIHYDRATE
PHLORIZIN HYDRATE
TIMTEC-BB SBB005924
1-propanone,1-(2-(beta-d-glucopyranosyloxy)-4,6-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyp
phlorhizin
phloridzine
phlorizine
phlorizoside
phlorrhizin | [EINECS(EC#)]
200-487-1 | [Molecular Formula]
C21H24O10 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00006591 | [Molecular Weight]
436.41 | [MOL File]
60-81-1.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
Light Yellow Powder | [Melting point ]
113-114 °C(lit.)
| [Boiling point ]
468.89°C (rough estimate) | [density ]
1.3178 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
-54 ° (C=3.2, 95% EtOH) | [storage temp. ]
2-8°C
| [solubility ]
DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) | [form ]
Solid | [pka]
7.15±0.40(Predicted) | [color ]
Light Yellow to Tan | [Usage]
It is a dihydrochalcone occurring in all parts of the apple tree except the mature fruit. Once thought to occur in pear, plum, cherry trees and other Rosaceae | [Merck ]
7327 | [InChIKey]
IOUVKUPGCMBWBT-LKLLPNDVNA-N | [SMILES]
C(C1C(=CC(O)=CC=1O[C@H]1[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1)O)O)(=O)CCC1C=CC(O)=CC=1 |&1:9,10,11,13,15,r| | [LogP]
0.452 (est) | [CAS DataBase Reference]
60-81-1(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
60-81-1(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing . | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
UC2080000
| [F ]
3-10-23 | [HS Code ]
29389090 |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Summary]
Phlorizin is the glucoside of phloretin. Its chemical name is 1- (2- (beta-D- glucopyranose oxygroup) -46- dihydroxy phenyl) -3- (4- hydroxycyclohexyl phenyl ketone) acetone, which belongs to dihydrochlcone of flavonoid. Phloridzin mainly exists in root barks, stems, leaflets and fruit of the apple tree, it can also be found in small amounts in the plants such as compositae, leguminosae, fagaceae, ericaceae, liliaceae and so on. It has many important biological activities, such as reducing blood sugar, improving memory, anti-allergy, anticancer, etc., as well as potential use values in food, beauty and health care products and other industry.
| [Distribution]
Phloridzin exists mainly in Malus of Rosace, it has been reported in plants such as compositae, leguminosae, fagaceae, ericaceae, liliaceae and so on, but their amount is very low. In recent years, phlorizin is also found in litchi peel, leaves of pyrus betulaefolia, cynomorium songaricum, etc. though with a small amount. However, there are plenty of phloridzin in Lilhocarpus Polystachys Rehd. In general, the Malus plants are the main source of glucoside and can be used as the raw material to extract glucoside. Phloridzin is rich in branches, leaflets and barks of the apple tree. It can The distribution of phloridzin in apple fruits concentrate in seeds and rinds. The apple branches, leaves, bark and so on contain a large number of glucoside. The distribution of glucoside in apple fruit is concentrated on seeds and pericarp.
| [Extraction method]
- Material crushing: The dried branches or leaves of apple trees are crushed into coarse powders (10~20 mesh or 20~30 mesh).
- Extraction: Put pulverized crude powders into round flask, add 70% methanol for reflux extraction for 3 times, add 6, 4 and 4BV liquid independently, keep for 1h each time and combine the extracted solutions; (three extracts are brown to tan respectively).
- Inspissation: The antioxidant (VC) is added into the combined extract according to 0.2% of the total weight. Methanol can be recovered by reduced pressure distillation at 60℃.( The outcome solution is brownish turbid liquid)
- Removing impurities: Add polymerization alumina according to 0.5% of weight into the recovered concentrated solution without alcohol, adjust pH value to 7.5 with calcium hydroxide, put in the conical flask, hold 30min at 60℃, obtain the liquor after filtration; (flocculent is generated at the bottom after adding polymerization alumina)
- Extraction: the extraction condensate is cooled, the ethyl acetate is extracted with 1 times the ethyl acetate 3 times and the ethyl acetate solution is obtained; (the solution is stratified rapidly).
- Concentration: the ethyl acetate extract is decompressed and refluxed, concentrated to 10: 1, and the concentrated solution is obtained.
- Purification: Dissolve the concentrated liquid with 40% methanol, filter, place the filtrate for 24h, get the crystallization after extraction filtration, obtain the phlorizin by prevailing pressure drying or reducing pressure drying. (yellow powder) The activated carbon is used to decolorize the crude products because its decolorization principle is physical adsorption without damage to the biological activity of the root bark. The activated carbon is dried in a vacuum drying box to be activated. Then the activated carbon is added into aqueous solutions of crude products. The supernatant liquid can be obtained after stir and filtration. The liquid is placed to crystalize under natural conditions and the white needle crystal occurs eventually.
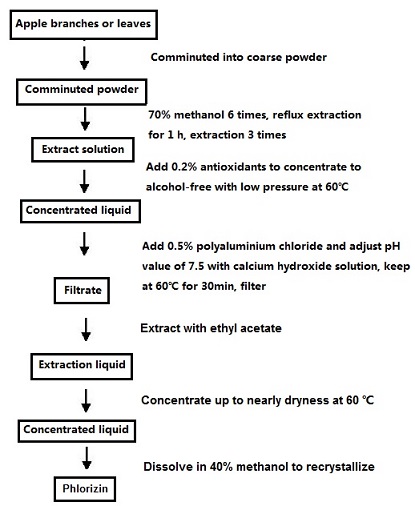 Figure 1. the p technological process of the phlorizin extraction Figure 1. the p technological process of the phlorizin extraction | [Synthetic method]
The precusor substance used to synthetize phlorizin is Malonyl-CoA and p-coumaroyl-CoA.
Firstly, we use p-coumaroyl-CoA to generate 4-hydroxydihydrocinnamoyl-CoA by NADPH; then, phloretin is synthesized by Malonyl-CoA and 4-hydroxydihydrocinnamoyl-CoA under the action of tecatone synthetase; finally, phloridzin is generated by phloretin glucosylation. The overviews, extraction methods and synthesis methods of the phlorizin are compiled by Shi yan of Chemicalbook. (2015-12-02)
| [Biological activity]
Diabetes is a major disease that threatens human health and its typical symptom is hyperglycemia. Now the main drugs for the treatment of diabetes include traditional sulfonylurea, metformin and some new hypoglycemic agents such as rosiglitazone, pioglitazone, etc. The mechanisms of action are mostly used to promote insulin secretion or increase insulin sensitivity. A large number of studies have shown that phlorizin has the effect of reducing fasting blood glucose. The mechanism of decreasing glucose is competitively inhibiting the transport of glucose molecules on glucose transporters (SGLTs and GLUTs).
Phlorizin has obvious protective effects on oxidative damage induced by high-fat diet in drosophila, as well as strong antioxidant effect, and enhance the activity of SOD and CAT to prolong life spans of drosophila significantly.
- The physiological relationship with plants.
Phlorizin is closely related to the growth and stress resistance and other physiological phenomena of plants. It can resist various pathogenic bacterias, such as apple scab, fire blight, etc. However, it may inhibit the growth of some plants. Low concentration of phlorizin can promote the growth of Pingyi sweet tea seedlings, but high concentration will cause plant replant disorders. Phlorizin can promote the regeneration of papaya embryos and stimulate the root growth particularly. Therefore, as a plant growth regulator, its dosage is the key factor.
In addition to antidiabetics, antioxidant and other biological activities, phlorizin has effects of anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and so on.
| [Application]
It has many important biological activities, such as reducing blood sugar, improving memory, anti allergy, anticancer, etc., as well as potential use values in food, beauty and health care products and other industry.
Phlorizin has been approved as a kind of food additive. It is a characteristic phenolic substance in apple. Due to species, producers and other issues, the contents of phlorizin in different apples are quite different. Therefore, its content can be used as an index to distinguish the producers and qualities of apple juice. Phlorizin can promote the absorption and utilization of genistein (inhibit the growth and metastasis of tumor cells). It has a broad market in prevention and treatment of cancer to develop functional foods which rich in phlorizin and genistein. It is a high sweet natural sweetener, which can be used as an alternative food for diabetic patients. After phlorizin is oxidized by polyphenol oxidase, the products can be converted into bright yellow dyes. The dye has strong water solubility and can be used in food processing industry instead of artificial dyes to avoid the toxic effects caused by synthetic pigments. It has potential application values in the development and utilization either as a kind of food additive or as a functional food.
As phlorizin is easily hydrolyzed in human body to yield the phloretin and has lower intestinal absorption rate, it is often designed to be high molecular polymer for the development of drugs with other compounds.
The antioxidant activity and antiaging function of phlorizin have been confirmed by modern scientific researches. The hydrolysate of phlorizin, which is called phloretin, can inhibit the tyrosinase activity competitively and interfere the synthesis of melanin. Its whitening effect is better than many whitening products on the market. However, it is important to note that phlorizin increases the expression of tyrosinase genes by activating the cAMP signaling pathway, which leads to the formation of melanin.
|
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
Light Yellow Powder | [Uses]
induces experimental glucosuria, antifeedant | [Uses]
It is a dihydrochalcone occurring in all parts of the apple tree except the mature fruit. Once thought to occur in pear, plum, cherry trees and other Rosaceae | [Uses]
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) is a high affinity, low capacity transporter abundant in the small intestine, with some expression in the kidney as well. SGLT2 is a low affinity, high capacity transporter in the kidney that accounts for approximately 90% of glucose reabsorption into the blood stream. Selective inhibition of SGLT2 is a potential strategy for reducing plasma glucose levels as a treatment for diabetes. Phlorizin is a natural product, first isolated from the bark of apple trees, that reduces plasma glucose levels by blocking renal and intestinal glucose absorption through inhibition of SGLT1 and SGLT2. It competitively inhibits the initial rate of a-methyl-D-glucopyranoside (a-MDG) uptake in human COS-1 cells expressing hSGLT1 and hSGLT2 with IC50 values of 400 and 65 nM, respectively. In HEK293T cells expressing human SGLT1 and SGLT2, phlorizin exhibits Ki values of 140 and 11 nM, respectively, at 37°C. | [Definition]
ChEBI: An aryl beta-D-glucoside that is phloretin attached to a beta-D-glucopyranosyl residue at position 2' via a glycosidic linkage. | [in vivo]
Prior to Phlorizin treatment, the blood glucose level in SDT fatty rats is 370±49 mg/dL. Six hours after dosing, the blood glucose level in the Phlorizin treated group decreases to an almost normal level (139±32 mg/dL). Phlorizin-treated SDT fatty rats are heavier than vehicle-treated SDT fatty rats after 12 weeks. Phlorizin treatment significantly decreases glucose excretion and delays insulin decreases. Creatinine clearance decreases significantly with Phlorizin treatment. 23 weeks of Phlorizin treatment prevents the decrease of nerve fibers (23.6±3.2 fibers/mm). Retinal abnormalities are completely prevented with Phlorizin[4]. | [IC 50]
SGLT1; SGLT2 | [storage]
Store at -20°C | [Purification Methods]
-D-glucoside] [60-81-1] M 472.5, m 110o, [�] 20 -62o (c 3.2, EtOH). Phlorizin crystallises as the dihydrate from water and causes glycosuria. [Brazy & Dennis Am J Physiol 234 1279 1978, Zemplen & Bognár Chem Ber 17B 1040 1943, Beilstein 17/7 V 177.] |
|
|