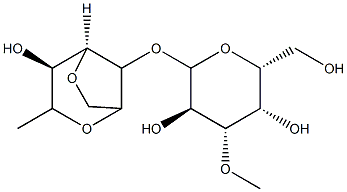
??
|
|
?? ??
- ???
- 85-95 °C
- ?? ??
- 720kg/m3
- ?? ??
- room temp
- ???
- H2O:1.5% ??
- ??? ??
- ?? ?
- ??
- ??? ? ???
- ??
- ?? ??
- pH ??
- 5 - 7
- ??????(pH)
- 6.5-6.8 (1.5% in gel, after autoclaving)
- ?? ??
- ???
- ???? ??
- synthetic
- ???
- ??? ?? ???
- ??
- Moisture Sensitive & Hygroscopic
- Merck
- 14,184
- ???
- ????. ?? ???? ???? ????.
- CAS ??????
- 9002-18-0(CAS DataBase Reference)
- EPA
- Agar (9002-18-0)
??
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ??? ?? | Xn | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ???? ?? | 22-36/37/38 | ||
| ????? | 26-36-24/25 | ||
| WGK ?? | 2 | ||
| RTECS ?? | AW7950000 | ||
| F ?????? | 3 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| HS ?? | 13023100 | ||
| ?? ?? ??? | 9002-18-0(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| ?? | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 11000 mg/kg | ||
| ???? ?? | KE-00275 |
?? C??? ??, ??, ??
??? ??
Agar occurs as transparent, odorless, tasteless strips or as a coarse or fine powder. It may be weak yellowish-orange, yellowish-gray to pale-yellow colored, or colorless. Agar is tough when damp, brittle when dry.??
Agar is found in several species of red marine algae in oceans around the world.??
Agar is a gum obtained from red seaweeds of the genera gelidium, gracilaria, and eucheuma, class rhodophyceae. it is a mixture of the polysaccharides agarose and agaropectin. it is insoluble in cold water, slowly soluble in hot water, and soluble in boiling water, forming a gel upon cooling. the gels are characterized as being tough and brittle, setting at 32–40°c, and melting at 95°c. a rigid, tough gel can be formed at 0.5%. agar mainly functions in gel for- mation because of its range between melting and setting tempera- tures, being used in piping gels, glazes, icings, dental impression material, and microbiological plating. typical use levels are 0.1–2.0%.??
agar: An extract of certain species ofred seaweeds that is used as a gellingagent in microbiological culturemedia, foodstuffs, medicines, andcosmetic creams and jellies. Nutrientagar consists of a broth made frombeef extract or blood that is gelledwith agar and used for the cultivationof bacteria, fungi, and somealgae.?? ??
Agar is obtained by freeze-drying a mucilage derived from Gelidium amansii Lamouroux, other species of the same family (Gelidiaceae), or other red algae (Rhodophyta).?? ??
Tan powder.??? ?? ??
Water insoluble.?? ???
Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination of alcohols with alkali metals, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. They react with oxoacids and carboxylic acids to form esters plus water. Oxidizing agents convert them to aldehydes or ketones. They exhibit both weak acid and weak base behavior.????
Flash point data for Agar are not available. Agar is probably combustible.Pharmaceutical Applications
Agar is widely used in food applications as a stabilizing agent. In pharmaceutical applications, agar is used in a handful of oral tablet and topical formulations. It has also been investigated in a number of experimental pharmaceutical applications including as a sustained-release agent in gels, beads, microspheres, and tablets.It has also been reported to work as a disintegrant in tablets.Agar has been used in a floating controlled-release tablet; the buoyancy in part being attributed to air entrapped in the agar gel network.It can be used as a viscosity-increasing agent in aqueous systems. Agar can also be used as a base for nonmelting, and nondisintegrating suppositories.Agar has an application as a suspending agent in pharmaceutical suspensions.
Safety Profile
Mildly toxic by ingestion. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.Safety
Agar is widely used in food applications and has been used in oral and topical pharmaceutical applications. It is generally regarded as relatively nontoxic and nonirritant when used as an excipient.LD50 (hamster, oral): 6.1 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 16.0 g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, oral): 5.8 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 11.0 g/kg
??
Agar solutions are most stable at pH 4–10.Agar should be stored in a cool, dry, place. Containers of this material may be hazardous when empty since they retain product residues (dust, solids).
? ???
Agar is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Agar is dehydrated and precipitated from solution by ethanol (95%). Tannic acid causes precipitation; electrolytes cause partial dehydration and decrease in viscosity of sols.Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral tablets). Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK.?? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??
?? ?? ??
???( 591)?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aurora Industry Co., Ltd. | +86-13591747876 +86-13591747876 |
alex1_auco@126.com | China | 299 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86-15531157085 +86-15531157085 |
abby@chuanghaibio.com | China | 8809 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-29-81148696 +86-15536356810 |
1022@dideu.com | China | 3882 | 58 |
| Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12818 | 58 |
| Hebei Yanxi Chemical Co., Ltd. | +8617531153977 |
allison@yan-xi.com | China | 5855 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 |
sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5876 | 58 |
| Hebei Jingbo New Material Technology Co., Ltd | +8619931165850 |
hbjbtech@163.com | China | 1000 | 58 |
| Hebei Saisier Technology Co., LTD | +86-18400010335 +86-18034520335 |
admin@hbsaisier.cn | China | 1015 | 58 |
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +8618092446649 |
sarah@tnjone.com | China | 1143 | 58 |
| Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd | +8613343047651 |
admin@zlchemi.com | China | 3692 | 58 |
?? ?? ??:
?? ???(II) ????????? ?????? ?? ????????? ????? ??(2,2,6,6-?????-3,5-???????) ??????? ?2? ??????? ?? ????? ???? ???? ?????? ??? ???? ?????????
MALT EXTRACT AGAR
AGAROSE
CETRIMIDE AGAR
R2A AGAR
DICHLORO(ETHYLENEDIAMINE)PLATINUM(II)
TERT-BUTYL ISOCYANIDE
TRIS(2,2,6,6-TETRAMETHYL-3,5-HEPTANEDIONATO)EUROPIUM(III)
Tris(2,4-pentanedionato)chroMiuM(III)