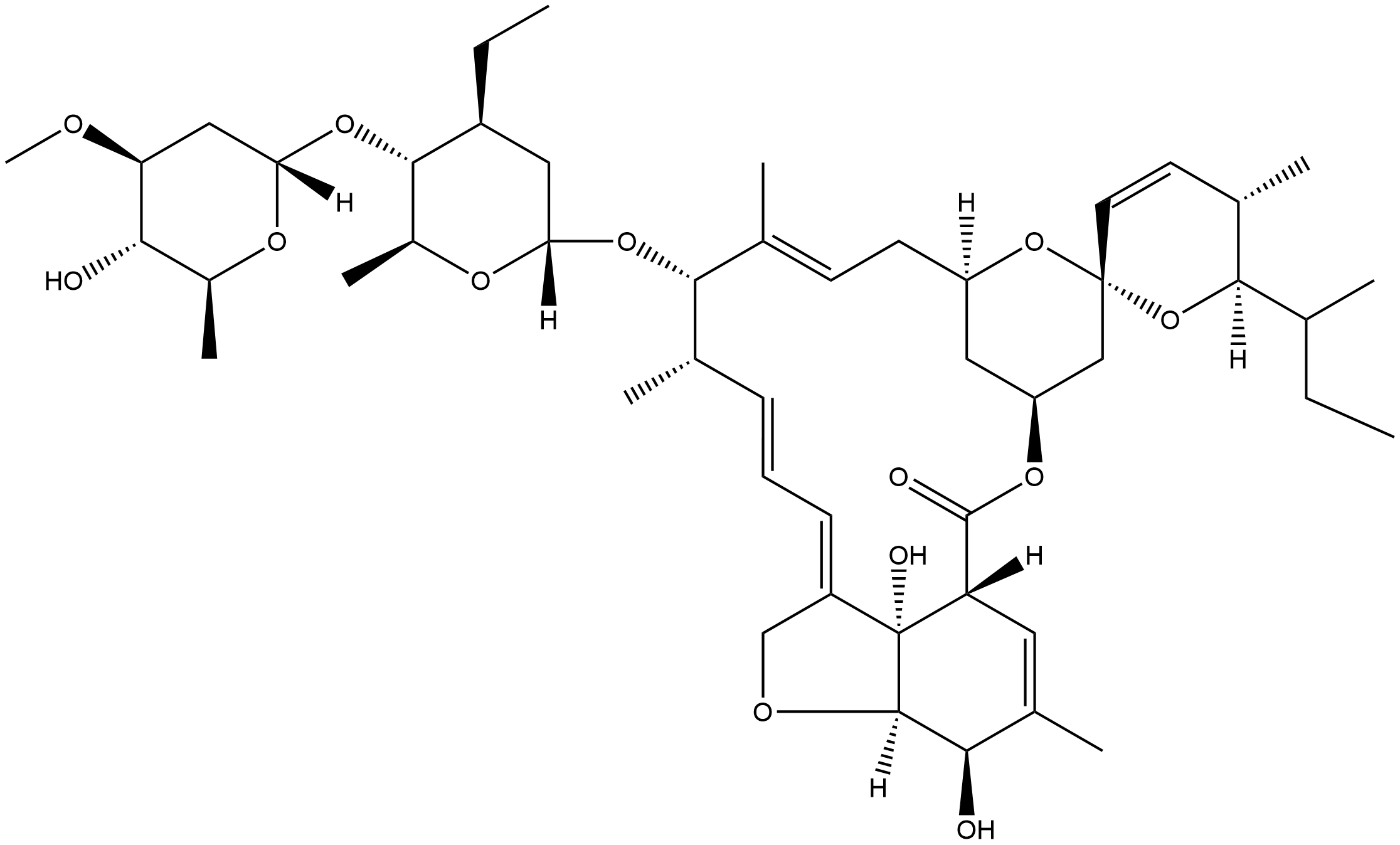
???? B1
|
|
???? B1 ??
- ???
- 150-155°C
- ??
- D +55.7 ±2° (c = 0.87 in CHCl3)
- ?? ?
- 717.52°C (rough estimate)
- ??
- 1.16
- ???
- <2 x 10-7 Pa
- ???
- 1.6130 (estimate)
- ???
- 150 °C
- ?? ??
- Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C
- ???
- DMSO? ???
- ??? ??
- Solid
- ???
- 0.007-0.01mg l-1(20°C)
- ??
- White to off-white
- Merck
- 13,2
- InChIKey
- GVWIWZFXCGTSLL-MSTMYQEVSA-N
- CAS ??????
- 71751-41-2(CAS DataBase Reference)
??
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ??? ?? | T+,N | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ???? ?? | 20-28-50 | ||
| ????? | 36/37/39-45-60-61 | ||
| ????(UN No.) | 2588 | ||
| WGK ?? | 3 | ||
| RTECS ?? | CL1203000 | ||
| ?? ?? | 6.1(a) | ||
| ???? | II | ||
| ?? ?? ??? | 71751-41-2(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| ?? | LD50 (technical grade) orally in sesame oil in mouse, rat: 13.5, 10.0 mg/kg; dermally in rabbit: >2000 mg/kg; LD50 in mallard duck, bobwhite quail: 84.6, >2000 mg/kg; LC50 (96 hr) in rainbow trout, bluegill: 3.6, 9.6 mg/l; LC50 (48 hr) in Daphnia magna: 0.34 mg/l (Merck Technical Data Sheet) | ||
| ???? ?? | KE-04279 |
???? B1 C??? ??, ??, ??
??? ??
Abamectin is a colorless to yellowish crystalline powder. It is soluble in acetone, methanol, toluene, chloroform, and ethanol, but insoluble in water. It is stable, and incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Abamectin is a mixture of Abamectins containing about 80% Abamectin B1a and 20% Abamectin B1b. These two components, B1a and B1b, have very similar biological and toxicological properties. The Abamectins are insecticidal/miticidal compounds derived from the soil bacterium Streptomyces avermitilis. Abamectin is used to control insect and mite pests of citrus, pear, and nut tree crops, and is used by homeown- ers to control fi re ants. It acts on the nervous system of insects, causing paralyzing effects. Abamectin is a general use pesticide (GUP). It is grouped as toxicity class IV, meaning practically non-toxic, requiring no precautionary statement on its label??
Mixture of Abamectins, containing at least 80% of Abamectin B1a (C48H72O14) and not more than 20% of Abamectin B1b (C47H70O14). Used as acaricide, insecticide??
Any of a group of broad spectrum antiparasitic antibiotics produced by the actinomycete, Streptomyces avermitilis.?? ??
Odorless off-white to yellow crystals from methanol. Does not hydrolyze in water at pH 3, 5, 7. Used as an acaricide and insecticide.?? ???
A lactone.???
A poison by ingestion. Moderately toxic by inhalation and skin contact.????
Abamectin is an insecticide and miticide. It is very toxic and causes adverse health effects if swallowed and/or inhaled. Emulsifi able concentrate formulations of Abamectin cause slight to moderate eye irritation and mild skin irritation. The symptoms of poisoning observed in laboratory animals include pupil dilation, vomiting, convulsions and/or trem- ors, and coma. Abamectin acts on insects by interfering with the nervous system. At very high doses, laboratory mammals develop symptoms of nervous system depression, inco- ordination, tremors, lethargy, excitation, and pupil dilation. Very high doses have caused death from respiratory failure in animals. Additionally, Abamectin has been reported to cause reproductive effects. Abamectin blocks the nerval conduct system in insects, caus- ing paralysis and death. Laboratory studies have indicated that abamectin may affect the nervous system in experimental animals. A 1-year study with dogs given oral doses of abamectin (0.5 and 1 mg/kg/day) caused adverse health effects, such as pupil dilation, weight loss, lethargy, tremors, and recumbency.???
Acaricide, Miticide, Insecticide, Anthelmentic: Used on fruit, vegetable and ornamental crops; pears, citrus fruits, and nut crops; to control mite and insect pests, and also to control household and lawn insects, including fire ants. Approved by the EPA for use in ash trees for control of emerald ash borer. A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP).???
ABACIDE®; AFFIRM®; AVID®, AVID-EC®; AVOMEC®; DYNAMEC®; INJECT-A- CIDE AV®; MK 936®(B 1A ); BOVITIN®; DORATECT®; DUOMECTIN®; DUOTIN®; ENDECTO®; ENZEC®; L 676,863® (B 1A ); MK 0936®; MK 936®; PARAFOIL®; VERTIMEC®, VERTIMIL®; VIVID®; ZECTIN®; ZEPHEYR®; ZEPHYR®?? ?? ??
Abamectin contains the closely related avermectin B1a and B1b as the active ingredients. Avermectin B1a contains a sec-butyl moiety whereas avermectin B1b contains an isopropyl moiety. Chemical degradation and metabolism studies were conducted with avermectin B1a radiolabelled with 3H or 14C at various positions of this large molecule. The overall fates of avermectin B1a and B1b are similar since transformations at the butyl or propyl moiety were not observed.Avermectin B1a is stable to hydrolytic degradation, but it is readily degraded to numerous products in aqueous solutions, soil, glass and plant foliage/fruit surfaces after light irradiation. Isomerisation and O-demethylation appear to the primary degradation reactions. In addition, hydroxylation is a major metabolic reaction in animals. Significant amounts of the residues in plants and animals were characterised as unidentified polar components.
?? ??
During use of Abamectin, occupational workers should use safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing to prevent prolonged skin contact, and work in good ventilation.???? B1 ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??
???? B1 ?? ??
???( 688)?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Jingbo New Material Technology Co., Ltd | +8619931165850 |
hbjbtech@163.com | China | 1000 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12829 | 58 |
| Henan Suikang Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd. | +86-18239973690 +86-18239973690 |
sales@suikangpharm.com | China | 311 | 58 |
| Shanghai Likang New Materials Co., Limited | +86-16631818819 +86-17736933208 |
3684455296@qq.com | China | 9300 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615350571055 |
Sibel@weibangbio.com | China | 6087 | 58 |
| Shandong Deshang Chemical Co., Ltd. | +86-0531-8875-2665 +8613153039501 |
info@deshangchem.com | China | 660 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 |
sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5893 | 58 |
| Henan Bao Enluo International TradeCo.,LTD | +86-17331933971 +86-17331933971 |
deasea125996@gmail.com | China | 2472 | 58 |
| Xiamen Wonderful Bio Technology Co., Ltd. | +8613043004613 |
Sara@xmwonderfulbio.com | China | 283 | 58 |
| Anhui Ruihan Technology Co., Ltd | +8617756083858 |
daisy@anhuiruihan.com | China | 973 | 58 |
???? B1 ?? ??:
????? ?? ????? ????? D-??? ?????(????) ???? B1
Avermectin B1a
(4''r)-4''-(acetylamino)-4''-deoxy-avermectin b1solution,Avermectin B1, 4-(acetylamino)-4-deoxy-, (4R)-,(4''R)-4''-(ACETYLAMINO)-4''-DEOXY-AVERMECTIN B1
Methylamino abamectin
Catonic Black O
Tetrahydropyranyl-4-acetic acid
ETHYL 2-METHYL-3-PENTENOATE
ETHYL TETRAHYDROPYRAN-4-YL-ACETATE
CARVEOL
Doramectin
avermectin b1b,Avermectin A1a, 5-O-demethyl-25-de(1-methylpropyl)-25-(1-methylethyl)-
Emamectin benzoate
Avermectin (type unspecified)