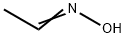?????? C??? ??, ??, ??
??? ??
WHITE LOW MELTING SOLID OR CLEAR LIQUID
??
Acetaldoxime is used as an oxygen scavenger in boiler water. It is also used as an intermediate in chemical synthesis and pharmaceuticals. It is involved in the rearrangement reaction to prepare acetamide by using nickel(II) acetate as a catalyst. It acts as a precursor to prepare heterocyclic compound such as spiroisoxazoline. Further, it is used to prepare alkylated(Z)-oximes by deprotonation followed by reaction with benzyl bromide.
??
The –CH:NOH radical resulting from reactions between aldehydes and hydroxylamine or by the oxidation of primary amines by persulfuric acid.
?? ??
A colorless liquid with a pungent odor. Density 0.966 g / cm3. Flash point 75°F. Boiling point 235°F. Has two crystalline modifications, one melting at 12°C and the other at 46.5°C.
??? ?? ??
Highly flammable. Easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Very soluble in water.
?? ???
Acetaldoxime may explode or decompose violently during distillation if samples have been previously been exposed to the air, which causes formation of peroxides of various types. Reacts as both a weak acid and as a weak base. Gives acetaldehyde and a hydroxylammonium salt if heated with aqueous acid. A nickel-catalyzed aldoxime rearrangement to an amide went out of control when a different solvent was employed [J. Loss Prev., 1993, 6(2), 69].
????
May cause toxic effects if inhaled or absorbed through skin. Inhalation or contact with material may irritate or burn skin and eyes. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
????
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Safety Profile
Poison via intraperitoneal route. Mutation data reported. A dangerous fire hazard with a flash point at room temperature. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also ALDEHYDES.
??? ??
Used as a chemical intermediate and as an antioxidant and radical scavenger with applications in many industries, including detergents, pharmaceuticals, plastics, paints and lacquers, rubber, and textiles
?? ??
UN2332 Acetaldehyde oxime, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
? ???
Vapor may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong acids (such as hydrochloric, sulfuric, and nitric), strong bases. The beta-form is able to form unstable peroxides
??? ??
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed
?????? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??