?????
|
|
????? ??
- ???
- 138-140°C
- ?? ?
- 579.8±60.0 °C(Predicted)
- ??
- 1.05
- ???
- 9℃
- ?? ??
- 2-8°C
- ???
- DMSO: 5mg/mL ? ???
- ??? ??
- ??
- ??? ??
- ??? ??
- ?? ?? (pKa)
- pKa 1.76±0.1(H2O t=24 I=0.1(NaCl)) (Uncertain)
- ??
- ???? ?????
- ???
- 1g/L(?? ???)
- Merck
- 14,4122
- BCS Class
- 1,3
- InChI
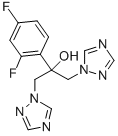
- InChI=1S/C13H12F2N6O/c14-10-1-2-11(12(15)3-10)13(22,4-20-8-16-6-18-20)5-21-9-17-7-19-21/h1-3,6-9,22H,4-5H2
- InChIKey
- RFHAOTPXVQNOHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- SMILES
- C1(C=CC(F)=CC=1F)C(O)(CN1N=CN=C1)CN1N=CN=C1
- CAS ??????
- 86386-73-4(CAS DataBase Reference)
??
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ??? ?? | Xn,Xi,T,F | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ???? ?? | 22-36/37/38-20/21/22-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11 | ||
| ????? | 26-36-36/37/39-24/25-45-36/37-16-7 | ||
| ????(UN No.) | UN1230 - class 3 - PG 2 - Methanol, solution | ||
| WGK ?? | 3 | ||
| RTECS ?? | XZ4810000 | ||
| HS ?? | 29336990 | ||
| ?? ?? ??? | 86386-73-4(Hazardous Substances Data) |
????? C??? ??, ??, ??
??
Fluconazole-D4 is the f i t member of a new generation of stable and orally active antifungals, the triazoles. It is highly effective in the treatment of dermal and vaginal fungal infections; new indications currently under investigation include severe systemic mycoses such as disseminated candidiasis and cryptococcal meningitis in immunocompromised patients.??? ??
Fluconazole-D4 is White to Off-White Solid??
Labelled Fluconazole (F421000). Used as an antifungal.Indications
Fluconazole (Diflucan) may be better absorbed and is possibly less hepatotoxic than ketoconazole, but it is considerably more expensive, an important consideration given the required length of therapy for most cutaneous fungal diseases.Antimicrobial activity
The spectrum is limited, but includes most Candida spp., Cryptococcus spp., dermatophytes and dimorphic fungi (Blast. dermatitidis, Coccidioides spp., Hist. capsulatum and Paracoccidioides brasiliensis). Strains of C. krusei appear to be insensitive.??
Resistant strains of C. albicans have been isolated from AIDS patients given long-term treatment for oral or esophageal candidosis. Strains of C. glabrata frequently become resistant during short courses of treatment. There are a few reports of fluconazole-resistant strains of Cryp. neoformans recovered from AIDS patients with relapsed meningitis. Most, but not all, C. albicans and C. glabrata strains resistant to fluconazole are cross-resistant to other azoles.?? ??
Fluconazole is used to treat adult neutropenic patients with invasive candidiasis (IC).Pharmaceutical Applications
A synthetic bis(triazole) available for oral or parenteral administration. A prodrug formulation, fosfluconazole, is available for intravenous use in Japan.???? ??
Triazole antifungal agent. Effective against Candida strains in vitro and in vivo .Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: >93%Cmax 50 mg oral: c. 1 mg/L after 2 h
Plasma half-life: 25–30 h
Volume of distribution: 0.6–0.8 L/kg
Plasma protein binding; <10%
Absorption
Oral absorption is rapid (1–3 h) and is not affected by food or intragastric pH. Blood concentrations increase in proportion to dosage. Maximum serum concentrations increase to about 2–3 mg/L after repeated dosing with 50 mg.
Distribution
It is widely distributed, achieving therapeutic concentrations in most tissues and body fluids. Concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are 50–60% of the simultaneous serum concentration in normal individuals and even higher in patients with meningitis.
Metabolism and excretion
More than 90% of an oral dose is eliminated in the urine: about 80% as unchanged drug and 10% as inactive metabolites. The drug is cleared by glomerular filtration, but there is significant tubular reabsorption. The plasma half-life is prolonged in renal failure, necessitating adjustment of the dosage.Fluconazole-D4 is removed during hemodialysis and, to a lesser extent, during peritoneal dialysis. In children the volume of distribution and plasma clearance are increased, and the half-life is considerably shorter (15–25 h).
Pharmacology
It has good oral absorption, is well tolerated, and is preferentially taken up in keratinized tissues, reaching concentrations up to 50 times that in plasma. This allows for once-weekly dosing in most cases.Clinical Use
Fluconazole is very effective in the treatment of infections with most Candida spp. Thrush in the end-stage AIDS patient, often refractory to nystatin, clotrimazole, and ketoconazole, can usually be suppressed with oral fluconazole.AIDS patients with esophageal candidiasis also usually respond to fluconazole.Fluconazole may be an acceptable alternative to amphotericin B in the initial treatment of mild cryptococcal meningitis, and it has been shown to be superior to amphotericin B in the long-term prevention of relapsing meningitis (such patients require lifelong treatment.). Coccidioidal meningitis, previously treated with both intravenous and intrathecal amphotericin B, appears to respond at least as well to prolonged oral fluconazole therapy. Aspergillosis, mucormycosis, and pseudallescheriasis do not respond to fluconazole treatment. Sporotrichosis, histoplasmosis, and blastomycosis appear to be better treated with itraconazole, although fluconazole does appear to have significant activity against these dimorphic fungi.
???
Fluconazole is well tolerated. Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and skin rash have been reported in fewer than 3% of patients. Asymptomatic liver enzyme elevation has been described, and several cases of drugassociated hepatic necrosis have been reported. Alopecia has been reported as a common adverse event in patients receiving prolonged high-dose therapy. Coadministration of fluconazole with phenytoin results in increased serum phenytoin levels.????? ?? ?? ? ???
???
METHYL 2,4-DIFLUOROBENZOATE
Grignard reagent
1,2,4-????
?????
1-???-2,4-??????
?????
?? (?????) ??
???????
???
?? ??
tert-?????
??????
M-???????
????????
2,4 DIFLUOROBENZENE
???????(1,3-)
??????
?????? ?????
???????? ??????
?????
?? ??
????? ?? ??
???( 1124)?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531157085 |
abby@chuanghaibio.com | China | 8808 | 58 |
| Hebei Yanxi Chemical Co., Ltd. | +8617531153977 |
allison@yan-xi.com | China | 5854 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 |
sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5868 | 58 |
| Hebei Dangtong Import and export Co LTD | +86-86-4001020630 +8619831957301 |
admin@hbdangtong.com | China | 998 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531151365 |
mina@chuanghaibio.com | China | 18137 | 58 |
| Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-371-86557731 +86-13613820652 |
info@fdachem.com | China | 20235 | 58 |
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +86-17396673057 |
linda@tnjone.com | China | 1143 | 58 |
| BEIJING SJAR TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT CO., LTD. | +86-18600796368 +86-18600796368 |
sales@sjar-tech.com | China | 485 | 58 |
| HEBEI SHENGSUAN CHEMICAL INDUSTRY CO.,LTD | +8615350851019 |
admin@86-ss.com | China | 1001 | 58 |
| Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co Ltd | +86-16264648883 +86-16264648883 |
niki@zlchemi.com | China | 7245 | 58 |
????? ?? ??:
1-((??(4-??????)????)??)-1H-1,2,4-???? ?? ??? ??? ??? ???? ?? ?? 1,1,1,3,3,3-??????-2-???? ?????? ??????? ?? ??? ????(??) ?????
1-PHENYL-2-PROPANOL
1-[[(2S,3S)-3-(2-Chlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)oxiran-2-yl]methyl]-1,2,4-triazole
beta-Methylphenethyl alcohol
1-METHYL-1,2,4-TRIAZOLE
Trimethylsulfoxonium iodide
2-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol
Faropenem sodium