N-Methylmethanamin, gasf?rmig Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
FARBLOSES KOMPRIMIERTES FLüSSIGGAS MIT STECHENDEM GERUCH.
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
L?SUNG IN WASSER MIT STECHENDEM GERUCH.
PHYSIKALISCHE GEFAHREN
Das Gas ist schwerer als Luft und kann sich am Boden ausbreiten. Fernzündung m?glich.
PHYSIKALISCHE GEFAHREN
Die D?mpfe sind schwerer als Luft und k?nnen sich am Boden ausbreiten. Fernzündung m?glich.
CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Starke Base in w?ssriger L?sung. Reagiert sehr heftig mit S?uren. ?tzend. Reagiert sehr heftig mit starken Oxidationsmittelnund Quecksilber unter Feuer- und Explosionsgefahr. Greift Aluminium, Kupfer, Zinklegierungen, galvanisierte Oberfl?chen und Kunststoff an.
CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Zersetzung beim Verbrennen unter Bildung giftiger Rauche mit Stickstoffoxiden. Reagiert sehr heftig mit starken Oxidationsmittelnund Quecksilber unter Feuer- und Explosionsgefahr. Greift Kupfer, Zinklegierungen, Aluminium, galvanisierte Oberfl?chen und Kunststoff an. Starke Base in w?ssriger L?sung. Reagiert sehr heftig mit S?uren. ?tzend, s. ICSC 1485 Dimethylamin, w?ssrige L?sung.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV: 5 ppm (als TWA); 15 ppm (als STEL); Krebskategorie A4 (nicht klassifizierbar als krebserzeugend für den Menschen); (ACGIH 2005).
EG Arbeitsplatz-Richtgrenzwerte: 2 ppm, 3.8 mg/m?(als TWA); 5 ppm, 9.4 mg/m?(als STEL); (EU 2004).
MAK: 2 ppm, 3,7 mg/m? Spitzenbegrenzung: überschreitungsfaktor I(2); Schwangerschaft: Gruppe D (DFG 2006).
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV: 5 ppm (als TWA); 15 ppm (als STEL); Krebskategorie A4 (nicht klassifizierbar als krebserzeugend für den Menschen); (ACGIH 2005).
EG Arbeitsplatz-Richtgrenzwerte: 2 ppm, 3,8 mg/m? (als TWA); 5 ppm, 9.4 mg/m? (als STEL); (EU 2004).
MAK: 2 ppm 3,7 mg/m? Spitzenbegrenzung: überschreitungsfaktor I(2); Schwangerschaft: Gruppe D; (DFG 2006).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation des Aerosols und durch Verschlucken.
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation.
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Eine gesundheitssch?dliche Konzentration des Gases in der Luft wird beim Entweichen aus dem Beh?lter sehr schnell erreicht, vor allem in geschlossenen R?umen.
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Beim Verdampfen bei 20°C tritt eine gesundheitssch?dliche Kontamination der Luft ein.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Die Substanz ver?tzt die Augen und die Haut. Der Dampf reizt stark die Atemwege. ?tzend beim Verschlucken.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Die Substanz reizt stark die Augen und die Atemwege. Inhalation der Substanz in hohen Konzentrationen kann zu Lungen?dem führen (s.Anm.). Die Auswirkungen treten u.U. verz?gert ein. ?rztliche Beobachtung notwendig. Schnelle Verdampfung kann zu Erfrierungen führen.
LECKAGE
Gefahrenbereich verlassen! Fachmann zu Rate ziehen! Belüftung. Zündquellen entfernen. Wasserstrahl NIEMALS auf die Flüssigkeit richten. Gas mit feinem Wassersprühstrahl niederschlagen. NICHT in die Umwelt gelangen lassen. Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Vollschutzanzug mit umgebungsluftunabh?ngigem Atemschutzger?t.
LECKAGE
Gefahrenbereich verlassen! Zündquellen entfernen. Verschüttetes Material mit Schaum abdecken. Ausgelaufene Flüssigkeit in abgedeckten Beh?ltern sammeln. Reste mit Sand oder inertem Absorptionsmittel aufnehmen und an einen sicheren Ort bringen. NICHT in die Kanalisation spülen. NICHT in die Umwelt gelangen lassen. Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Atemschutzfilter für organische Gase und D?mpfe.
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R12:Hochentzündlich.
R20:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Einatmen.
R37/38:Reizt die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
R41:Gefahr ernster Augensch?den.
R34:Verursacht Ver?tzungen.
R20/22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Einatmen und Verschlucken.
R11:Leichtentzündlich.
R39/23/24/25:Giftig: ernste Gefahr irreversiblen Schadens durch Einatmen, Berührung mit der Haut und durch Verschlucken.
R23/24/25:Giftig beim Einatmen, Verschlucken und Berührung mit der Haut.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S3:Kühl aufbewahren.
S16:Von Zündquellen fernhalten - Nicht rauchen.
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S29:Nicht in die Kanalisation gelangen lassen.
S36/37/39:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung,Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
S45:Bei Unfall oder Unwohlsein sofort Arzt zuziehen (wenn m?glich, dieses Etikett vorzeigen).
S39:Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
Aussehen Eigenschaften
C2H7N; Farbloses, in Wasser leicht lösliches Flüssiggas mit fisch- oder ammoniakartigem Geruch und niedriger Geruchsschwelle. Verdichtet oder verflüssigt in Gasflaschen im Handel.
Gefahren für Mensch und Umwelt
Reizt die Augen und die Atmungsorgane. Allergische Reaktion und Lungenödem möglich. Stark ätzend, auch in wässriger Lösung.
Nicht mit Oxidationsmitteln, Quecksilberverbindungen (Explosionsgefahr), Nitriten und salpetriger Säure in Berührung bringen.
Hochentzündlich. Bildet mit Luft explosionsfähigeGemische.
LD
50 (oral, Ratte): 698 mg/kg.
Nicht in die Kanalisation gelangen lassen.
Schutzma?nahmen und Verhaltensregeln
Schutzhandschuhe als kurzzeitiger Schutz.
Verhalten im Gefahrfall
Dämpfe nicht einatmen.
Leck schließen, Zylinder ins Freie bringen, wenn ohne Risiko möglich. Gut Lüften oder Dämpfe mit Wasser niederschlagen.
Kohlendioxid, Wasser, Pulver.
Brennbar. Dämpfe schwere als Luft. Mit Luft Bildung explosionsfähiger Gemische möglich.
Erste Hilfe
Nach Hautkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser abwaschen. Abtupfen mit Polyethylenglycol 400.
Nach Augenkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser bei geöffnetem Lidspalt mindestens 10 Minuten ausspülen. Augenarzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Einatmen: Frischluft, ggf. Atemspende. Atemwege freihalten. Bei Bewußtlosigkeit : stabile Seitenlage.
Nach Verschlucken: Viel Wasser trinken lassen. Erbrechen vermeiden (Perforationsgefahr). Sofort Arzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Kleidungskontakt: Kontaminierte Kleidung sofort entfernen.
Ersthelfer: siehe gesonderten Anschlag
Sachgerechte Entsorgung
Mit verdünnter Salzsäure vorsichtig neutralisieren. Dann in wässrige, neutrale Lösemittelabfälle.
Beschreibung
Dimethylamine is a colourless flammable gas at room temperature. It has a pungent, fishy, or ammonia-like odour at room temperature and is shipped and marketed in compressed liquid form. It is very soluble in water and soluble in alcohol and ether. It is incompatible with oxidising materials, acrylaldehyde, fluorine, maleic anhydride, chlorine, or mercury. Dimethylamine is a precursor to several industrially important compounds. For instance, it used in the manufacture of several products, for example, for the vulcanisation process of rubber, as detergent soaps, in leather tanning, in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, and also for cellulose acetate rayon treatment.
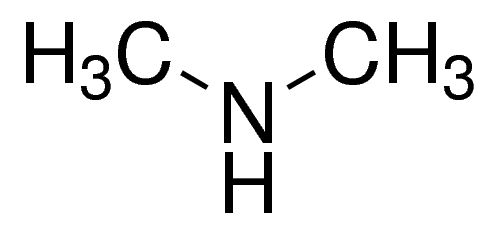
dimethylamine structure
Chemische Eigenschaften
Dimethylamine reacts readily with acids to produce salts due to the presence of the unshared electron pair on the nitrogen atom. Similarly, dimethylamine reacts with acid anhydrides, halides, and esters, with CO
2 or CS
2, or with isocyanic or isothiocyanic acid derivatives. It can also react with nitrite, especially under acidic conditions, and possibly nitrogen oxides (Iqbel 1986) to form N-nitrosodimethylamine, a potent carcinogen in various animal species and a suspect human carcinogen (ATSDR 1989; Scanlan 1983; Zeisel et al 1988). N-Nitrosodimethylamine also can be formed upon storage of aqueous dimethylamine solutions or formulations of the dimethylamine salts of the herbicides 2,4D and MCPA (Wigfield and McLenaghan 1987a,b). Dimethylamine also can be nitrosated photochemically in aqueous solutions containing nitrite with the reaction occurring most readily at alkaline pH (Ohta et al 1982).
Physikalische Eigenschaften
Clear, colorless liquid or gas with a strong, ammonia-like odor. Odor threshold concentrations of
33 ppb
v and 47 ppb
v were experimentally determined by (Leonardos et al., 1969) and Nagata and
Takeuchi (1990), respectively.
Verwenden
Dimethylamine is used in the manufactureof N-methylformamide, N-methylacetamide,and detergent soaps; in tanning; and as anaccelerator in vulcanizing rubber. It is commercially sold as a compressed liquid intubes or as a 33% aqueous solution..
Definition
ChEBI: A secondary aliphatic amine where both N-substituents are methyl.
Air & Water Reaktionen
Highly flammable. Water soluble.
Reaktivit?t anzeigen
DIMETHYLAMINE is a base, neutralizing acids in exothermic reactions, and a reducing agent. Dimethylamine is temperature sensitive. Reacts vigorously with mercury and chlorine . Reacts violently with strong oxidizing agents and attacks copper and copper compounds [Handling Chemicals Safely, 1980 p. 123]. Reacts with hypochlorites to give N-chloroamines, some of which are explosives when isolated [Bretherick, 1979 p. 108].
Hazard
Dimethylamine is an irritant, with a TLV of 10 ppm in air. The four-digit UN identification number is 1032. The NFPA 704 designation is health 3, flammability 4, and reactivity 0. The primary uses are in electroplating and as gasoline stabilizers, pharmaceuticals, missile fuels, pesticides, and rocket propellants.
Health Hazard
Dimethylamine is a strong irritant to the eyes,skin, and mucous membranes. Spill of liquidinto the eyes can cause corneal damage andloss of vision. Skin contact with the liquidcan produce necrosis. At sublethal concentra tions, inhalation of dimethylamine producedrespiratory distress, bronchitis, pneumonitis,and pulmonary edema in test animals. Theacute oral toxicity was moderate, greater thanfor monomethylamine.
LC50 value, inhalation (rats): 4540 ppm/6 hLD50 value, oral (mice): 316 mg/kg
Buckley and coworkers (1985) have investigated the inhalation toxicity of dimethylamine in F-344 rats and B6C3F1 mice.Animals exposed to 175 ppm for 6 h/day,5 days/week for 12 months showed significant lesions in the nasal passages. Rats developed more extensive olfactory lesions thandid mice. The study indicated that olfactory sensory cells were highly sensitive todimethylamine. Even at a concentration of10 ppm, the current threshold limit value,the rodents developed minor lesions fromexposure.
Brandgefahr
FLAMMABLE. Flashback along vapor trail may occur. May explode if ignited in an enclosed area. Vapors are eye, skin and respiratory irritants.
Industrielle Verwendung
Dimethylamine is used as an accelerator in vulcanizing rubber, as an antiknock
agent for fuels, in photography, as a plasticizer, ion exchange agent, as an acid gas
absorbent, a flotation agent, a dehairing agent in the tanning of leather and in
electroplating (HSDB 1989; Sax and Lewis 1987; Windholz et al 1983). Dimethylamine
also serves as the base for a large number of commercial products
including detergent soaps, dyes, pharmaceuticals, textile chemicals, surfactants
and in the manufacture of unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (used in missile
fuels), the solvent dimethylacetanilide and in the synthesis of dimethylformamide,
one of the most commonly used organic solvents. Usage of dimethylamine in 1972
was estimated at 50% for production of dimethylformamide and dimethylacetamide
(used as spinning solvents for acrylic fibers), 15% as an intermediate in the
preparation of the surfactant laurel dimethylamine oxide, 15% as an intermediate
for rubber chemicals (including thorium accelerators), and 20% for other applications
including the production of unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine in rocket fuels
and the dimethylamine salt of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (HSDB 1989). U.S.
production and sales of dimethylamine in 1985 was 65.9 million pounds.
Sicherheitsprofil
Poison by ingestion.
Moderately toxic by inhalation and
intravenous routes. Mutation data reported.
An eye irritant. Corrosive to the eyes, skin,
and mucous membranes. A flammable gas.
When heated to decomposition it emits
toxic fumes of Nx,. Incompatible with
acrylddehyde, fluorine, and maleic
anhydride
Carcinogenicity
In a 2 year inhalation study in male F344 rats exposed to
175 ppm, no evidence of carcinogenicity was observed, and
in addition, despite severe tissue destruction in the anterior
nose following a single 6 h exposure, the nasal lesions
exhibited very little evidence of progression, even at
2 years of exposure. The authors concluded that this
indicated possible regional susceptibility to DMA toxicity or
a degree of adaptation by the rat to continued DMA exposure.
A detailed evaluation of mucociliary apparatus function
and response to alterations of nasal structure was presented
by the authors.
Lager
Dimethylamine should be stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area in tightly sealed containers
that are labeled in accordance with OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard [29
CFR 1910.1200]. Containers of dimethylamine should be protected from physical damage
and ignition sources, and should be stored separately from oxidizing materials, acrylaldehyde,
fl uorine, maleic anhydride, chlorine, and mercury. Outside or detached storage is
preferred. If stored inside, a standard flammable liquids cabinet or room should be used.
Ground and bond metal containers and equipment when transferring liquids. Empty
containers of dimethylamine should be handled appropriately.
l?uterung methode
Dry dimethylamine by passage through a KOH-filled tower, or by standing with sodium pellets at 0o during 18hours. [Beilstein 4 IV 128.]
Vorsichtsma?nahmen
During handling of dimethylamine, workers should use proper fume hoods, personal
protective clothing and equipment, avoid skin contact, and use gloves, sleeves, and encapsulating suits. Dimethylamine is extremely flammable and may be ignited by heat,
sparks, or open flames. Liquid dimethylamine will attack some forms of plastic, rubber,
and coatings and is flammable. The vapors of dimethylamine are an explosion and poison
hazard. Containers of dimethylamine may explode in the heat of a fi re and require proper
disposal. Workers should use dimethylamine with adequate ventilation and containers
must be kept properly closed.
N-Methylmethanamin, gasf?rmig Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
Dimethylammonium-2,4-dichlorphenoxyacetat
6-Dimethylaminopurin
2-Hydroxy-3-methylcyclopent-2-enon
Difenoxuron
Topotecan
3-Dimethylaminopropan-1-ol
Kaliumoleat
Ethyl 3-(N,N-dimethylamino)acrylate
Chlorpromazin-hydrochlorid
N,N-Dimethylcyclohexanamin
Camazepam
Hexadecyltrimethylammoniumchlorid
AsoMate
Insecticide double agent
3-Chlorpropyl(dimethyl)amin
3-DIMETHYLAMINOPROPIONIC ACID
2-Brom-N,N-dimethylbenzylamin
Diallyldimethylammoniumchlorid
Dye-fixing agent,no formaldehyde
Diethyl-[[3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl]methyl]phosphonat
Polyquaternium-7
3-Dimethylaminopropiononitril
(E)-N,N,N',N'-Tetramethylbut-2-en-1,4-diamin
2-Hydrazinyl-N,N-dimethylacetamide
3-(CHLOROMETHYL)-N,N-DIMETHYLBENZENESULFONAMIDE
DOXEPIN
N,N-DIMETHYLDITHIOCARBAMIC ACID
Dimethyl(2-phenoxyethyl)amin
2-(Diphenylmethoxy)-N,N-dimethyl-ethanamin
Metforminhydrochlorid
Light stabilizer 2002
Indol-3-ylmethyldimethylamin
5-Chlor-1-methyl-1H-imidazol
N,N-Dimethyl-2-propens?ureamid
4-Amino-N,N-dimethylbenzylamin
2,4,6-Tri-(dimethylamino-methyl)phenol
Dimethyldioctadecylammoniumbromid
3-Chlorpropyldimethylammoniumchlorid
Altretamin
2,2'-Thiobis(ethylamin)

