Benzamid Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Verschlucken.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S22:Staub nicht einatmen.
S24/25:Berührung mit den Augen und der Haut vermeiden.
Aussehen Eigenschaften
C7H7NO; Benzolcarboxamid, Benzoesäureamid. Farbloser, feinkristalliner Feststoff.
Gefahren für Mensch und Umwelt
Gesundheitsschädlich beim Verschlucken.
Brennbar.
LD
50 (oral, Maus): 1160 mg/kg
Schutzma?nahmen und Verhaltensregeln
Geeignete Schutzhandschuhe als kurzzeitiger Staubschutz.
Verhalten im Gefahrfall
Staubentwicklung vermeiden.
Trocken aufnehmen. Der Entsorgung zuführen. Nachreinigen.
Kohlendioxid, Wasser, Pulver.
Brennbar. Im Brandfall können nitrose Gase entstehen.
Erste Hilfe
Nach Hautkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser abwaschen.
Nach Augenkontakt: Mit reichlich Wasser bei geöffnetem Lidspalt mindestens 10 Minuten ausspülen. Sofort Augenarzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Einatmen: Frischluft.
Nach Verschlucken: Reichlich Wasser trinken lassen. Erbrechen auslösen. Sofort Arzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Kleidungskontakt: Kontaminierte Kleidung entfernen.
Ersthelfer: siehe gesonderten Anschlag
Sachgerechte Entsorgung
Gelöst in z.B. Aceton als halogenfreie, organische Lösemittelabfälle.
Beschreibung
Benzamide appears as off-white crystals or powder. It is combustible and incompatible with strong oxidising agents and strong bases. On combustion and thermal decomposition, it emits nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide.
Benzamide is a carbonic acid amide of benzoic acid. Benzamide exhibits an angle of about 15º with the plane of the amide group; this shows that benzamide molecule is not flat. The rotation of the amide group relative to the aromatic ring may result from the repulsion interaction between the hydrogen atoms of the amide group and those of the aromatic ring.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Benzamide is a combustible, colorless to beige, off-white, crystalline solid; freezing/melting point=132-133° C. It is slightly soluble in water, and soluble in many organic solvents.

Benzamide was used to study the mechanism of photocatalytic decomposition of aqueous solution of acetic acid, acetamide and acetonitrile in the presence of semiconductors. It was used to develop a robust screening method to study biotransformations using (+)-γ-lactamase enzyme.
Verwenden
Organic synthesis.
Benzamide on radioiodination by different labeling procedures results in large-scale production of radioiodinated benzamides having potential therapeutic application for patients with metastatic malignant melanoma.
Definition
ChEBI: An aromatic amide that consists of benzene bearing a single carboxamido substituent. The parent of the class of benzamides.
synthetische
Take a mixture of 5 ml concentrated ammonia and 5 ml water in a conical flask with a well-fitting cork. Add 2 ml (2.4 g.) benzoyl chloride, cork the flask and shake vigorously. Heat generates due to the reaction, hence hold the cork securely during shaking. After 15 min not even a trace of oily benzoyl chloride remains. Filter the fine flakes, wash with cold water and recrystallise from hot water: yield, 1-5 g. Colourless crystals of benzamide.
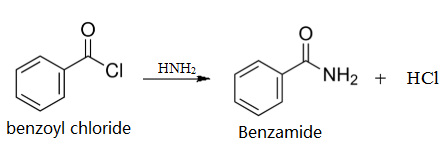
Preparation of benzamide from benzoyl chloride
Allgemeine Beschreibung
White powder.
Air & Water Reaktionen
Insoluble in water.
Reaktivit?t anzeigen
Benzamide reacts with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Forms flammable gases with strong reducing agents. Mixing with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. Combustion generates toxic mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Hazard
Depresses the central nervous system;
toxic.
Brandgefahr
Flash point data for Benzamide are not available, however Benzamide is probably combustible.
Clinical Use
Benzamide on radioiodination by different labeling procedures results in large-scale production of radioiodinated benzamides having potential therapeutic application for patients with metastatic malignant melanoma.
m?gliche Exposition
Benzamide is used in organic
synthesis.
l?uterung methode
Crystallise it from hot water (about 5mL/g), EtOH or 1,2-dichloroethane, and dry it in air. It has also been crystallised from dilute aqueous NH3, H2O, Me2CO, then *C6H6 using a Soxhlet extractor. Dry it in an oven at 110o for 8hours and store in a desiccator over 99% H2SO4. [Bates & Hobbs J Am Chem Soc 73 2151 1951, Beilstein 9 IV 725.]
Benzamid Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

