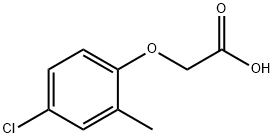
MCPA (ISO)
|
|
MCPA (ISO) Eigenschaften
- Schmelzpunkt:
- 114-118 °C (lit.)
- Siedepunkt:
- 288.02°C (rough estimate)
- Dichte
- 1.2799 (rough estimate)
- Brechungsindex
- 1.5230 (estimate)
- Flammpunkt:
- 2 °C
- storage temp.
- Sealed in dry,Room Temperature
- L?slichkeit
- water: insoluble(lit.)
- Aggregatzustand
- Solid
- pka
- 3.14±0.10(Predicted)
- Farbe
- White to Light yellow to Light orange
- Wasserl?slichkeit
- 1.174g/L(25 ºC)
- Merck
- 14,5764
- BRN
- 2051752
- CAS Datenbank
- 94-74-6(CAS DataBase Reference)
- NIST chemische Informationen
- [(4-Chloro-o-tolyl)oxy]acetic acid(94-74-6)
- EPA chemische Informationen
- MCPA (94-74-6)
Sicherheit
- Risiko- und Sicherheitserkl?rung
- Gefahreninformationscode (GHS)
| Kennzeichnung gef?hrlicher | Xn,F,N | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| R-S?tze: | 22-38-41-36-20/21/22-11-50/53 | ||
| S-S?tze: | 26-37-39-36-16-61-60-36/37 | ||
| RIDADR | UN 2765 | ||
| WGK Germany | 2 | ||
| RTECS-Nr. | AG1575000 | ||
| HazardClass | 9 | ||
| PackingGroup | III | ||
| HS Code | 29189900 | ||
| Giftige Stoffe Daten | 94-74-6(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| Toxizit?t | LD50 orally in rats: 700 mg/kg (Rowe, Hymas) |
| Bildanzeige (GHS) |
  
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alarmwort | Achtung | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gefahrenhinweise |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheit |
|
MCPA (ISO) Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
WEISSES KRISTALLINES PULVER.CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Zersetzung beim Erhitzen unter Bildung giftiger und ?tzender Rauche mit Chlorwasserstoff. Schwache S?ure.ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV nicht festgelegt (ACGIH 2005).MAK nicht festgelegt (DFG 2005).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation des Aerosols, über die Haut und durch Verschlucken.INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Verdampfung bei 20 °C vernachl?ssigbar; eine gesundheitssch?dliche Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann jedoch beim Versprühen oder Dispergieren schnell erreicht werden, vor allem als Pulver.WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION:Die Substanz reizt die Augen, die Haut und die Atmungsorgane.
WIRKUNGEN NACH WIEDERHOLTER ODER LANGZEITEXPOSITION
Tierversuche zeigen, dass die Substanz m?glicherweise fruchtbarkeitssch?digend oder entwicklungssch?digend wirken kann. (S. Anm.).LECKAGE
Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Atemschutzger?t, P2-Filter für sch?dliche Partikel. NICHT in die Umwelt gelangen lassen. Verschüttetes Material in abdichtbaren Beh?ltern sammeln; falls erforderlich durch Anfeuchten Staubentwicklung verhindern. Reste sorgf?ltig sammeln. An sicheren Ort bringen.R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Verschlucken.R38:Reizt die Haut.
R41:Gefahr ernster Augensch?den.
R36:Reizt die Augen.
R20/21/22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Einatmen,Verschlucken und Berührung mit der Haut.
R11:Leichtentzündlich.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.S37:Geeignete Schutzhandschuhe tragen.
S39:Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
S36:DE: Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung tragen.
S16:Von Zündquellen fernhalten - Nicht rauchen.
Chemische Eigenschaften
White, crystalline solid. Free acid insoluble in water but sodium and amine salts are soluble.Verwenden
Labelled MCPA (C369470). Herbicide.Definition
ChEBI: A chlorophenoxyacetic acid that is (4-chlorophenoxy)acetic acid substituted by a methyl group at position 2.Allgemeine Beschreibung
Colorless plates. Corrosive. Practically insoluble in water. Used as an herbicide.Air & Water Reaktionen
Insoluble in water.Landwirtschaftliche Anwendung
Herbicide: A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP) as MCPA, sodium salt. MCPA is a systemic post-emergence phenoxy herbicide used to control broadleaf annual and perennial weeds (including thistle and dock) in cereals, flax, rice, vines, peas, potatoes, grasslands, forestry applications, and on rights-of-way. It is very compatible with many other compounds and may be used in formulation with many other products, including bentazone, bromoxynil, 2,4-D, dicamba, fenoxaprop, MCPB, mecoprop, thifensulfuron, and tribenuron.Handelsname
ACME MCPA AMINE 4®; AGRITOX®; AGROXONE®; AGROZONE®; AGSCO®; ANICON KOMBI®; ANICON M®; BANLENE®; BLESEL MC®; BORDERMASTER®; BROMINAL M & PLUS®; CAMBILENE®; CHEYENNE®; CHIMAC OXY®; CHIPTOX®; CHWASTOX®; CORNOX M®; DAKOTA®; DED WEED®; DICOPUR-M®; DICOTEX®; DOW MCP AMINE WEED KILLER®; DYVEL®; EH1356 HERBICIDE®; EMCEPAN®; EMPAL®; ENVOY®; HEDAPUR M 52®; HEDAREX M®; HEDONAL M®; HERBICIDE M®; HORMOTUHO®; HORNOTUHO®; KILSEM®; 4 K-2 M®; KVK®; LEGUMEX DB®; LEUNA M®; LEYSPRAY®; LINORMONE®; M 40®; 2 M-4C®; 2 M-4KH®; MALERBANE®; MAYCLENE®; MEPHANAC®; MIDOX®; MXL®; OKULTIN®; PHENOXYLENE 50®; PHENOXYLENE PLUS®; PHENOXYLENE SUPER®; RAZOL DOCK KILLER®; RHOMENE®; RHONOX®; SHAMOX®; B-SELEKTONON M®; SEPPIC MMD®; TILLER®; TRIMEC®; U 46®; VACATE®; VESAKONTUHO®; WEEDAR®; WEEDAR MCPA CONCENTRATE®; WEEDONE MCPA ESTER®; WEED RHAP®; ZELAN®Sicherheitsprofil
Suspected carcinogen. Poison by subcutaneous and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Human systemic effects by ingestion: blood pressure decrease and coma. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. An herbicide. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-.m?gliche Exposition
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this postemergence herbicide, used for control of broadleaf weeds in agricultural applications.Environmental Fate
Biological. Cell-free extracts isolated from Pseudomonas sp. in a basal salt medium degraded MCPA to 4-chloro-o-cresol and glyoxylic acid (Gamar and Gaunt, 1971).Soil. Residual activity in soil is limited to approximately 3–4 months (Hartley and Kidd, 1987).
Plant. The penetration, translocation and metabolism of radiolabeled MCPA in a cornland weed (Galium aparine) was studied by Leafe (1962). Carbon dioxide was identified as a metabolite but this could only account 7% of the applied MCPA. Though no
Photolytic. When MCPA in dilute aqueous solution was exposed to summer sunlight or an indoor photoreactor (l >290 nm), 2-methyl-4-chlorophenol formed as the major product as well as o-cresol and 4-chloro-2-formylphenol (Soderquist and Crosby, 1975). Clapés et al. (1986) studied the photodecomposition of aqueous solution of MCPA (120 ppm, pH 5.4, 25°C) in a photoreactor equipped with a high pressure mercury lamp. After three minutes of irradiation, 4-chloro-2-methylphenol formed as an intermediate which degraded to 2-methylphenol. Both compounds were not detected after 6 minutes of irradiation; however, 1,4-dihydroxy-2-methylbenzene and 2-methyl-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4- dione formed as major and minor photodecomposition products, respectively. The same experiment was conducted using simulated sunlight (l <300 nm) in the presence of riboflavin, a known photosensitizer. 4-Chloro-2-methylphenol and 4-chloro-2-methylbenzyl formate formed as major and minor photoproducts, respectively (Clapés et al., 1986). Ozone degraded MCPA in dilute aqueous solution with and without UV light (l >300 nm) (Benoit-Guyod et al., 1986).
Chemical/Physical. Reacts with alkalies forming water soluble salts (Hartley and Kidd, 1987). Ozonolysis of MCPA in the dark yielded the following benzenoid intermediates: 4-chloro-2-methylphenol, its formate ester, 5-chlorosalicyaldehyde, 5-chlo
Versand/Shipping
UN3345 Phenoxyacetic acid derivative pesticide, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Requiredl?uterung methode
It is insoluble in H2O (solubility is 0.55g/L at 20o) and recrystallises from *C6H6 or chlorobenzene as plates [J.nsson et al. Acta Chem Scand 6 993 1952]. The S-benzylisothiouronium salt has m 164-165o, and the Cu2+ salt has m 247-249o(dec) [Armarego et al. Nature 183 1176 1959, UV: Duvaux & Grabe Acta Chem Scand 4 806 1950, IR: J.berg Acta Chem Scand 4 798 1950]. [Beilstein 6 IV 1991.] It is a plant growth substance and a herbicide.Inkompatibilit?ten
A weak acid. Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides (releasing heat, toxic, and possibly flammable gases), thiosulfates and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur). Incompatible with alkalis.Waste disposal
Incineration with added flammable solvent; incinerator equipped with fume scrubber. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA officeMCPA (ISO) Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
MCPA (ISO) Anbieter Lieferant Produzent Hersteller Vertrieb H?ndler.
Global( 265)Lieferanten
| Firmenname | Telefon | Land | Produktkatalog | Edge Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86-15531157085; +8615531157085 |
abby@chuanghaibio.com | China | 8807 | 58 |
| Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12790 | 58 |
| Qingdao Trust Agri Chemical Co.,Ltd | +8613573296305 |
aroma@qdtrustagri.com | China | 301 | 58 |
| Wuhan Quanjinci New Material Co.,Ltd. | +86-15271838296; +8615271838296 |
kyra@quanjinci.com | China | 1512 | 58 |
| Shanghai Daken Advanced Materials Co.,Ltd | +86-2158073036 |
info@dakenam.com | China | 19921 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21628 | 55 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 |
sales@coreychem.com | China | 29856 | 58 |
| Klong Industrial Co., Ltd | 0086-519-68231162 |
info@klongchem.com | CHINA | 131 | 58 |
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28172 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22963 | 58 |
94-74-6(MCPA (ISO))Verwandte Suche:
Methanol
Kresoxim-methyl
1-Chlor-2,3-epoxypropan
Basic Violet 1
α,α-Dimethylphenethylacetat
Paraquat-dichlorid
Methylacrylat
Methylacetat
p-Chlorphenylessigsure
Methyl-4-hydroxybenzoat
Acetonitril
Methyl 2,2-dimethylphenylacetate
ACETIC ACID
Ethylacetat
4-CPA
Pivalins?ure
o-Chlorphenylessigsure
o-Tolylessigsure
- (4-CHLORO-O-TOLYOXY)ACETICACID
- 4-CHLORO-2-METHYLCHLOROPHENOXYACETICACID
- 2-Methyl-4-chlorphenoxyessigsure
- Atlas MCPA
- banleneplus
- banvelm
- basagran-m
- BH MCPA
- BH MCPA 75
- bhmcpa
- Bordermaster
- Brominal M & plus
- brominalm&plus
- B-Selektonon M
- b-selektononm
- Campbell's MCPA 25, 50
- Cekherbex
- Chafer MCPA 675
- Chiptox
- Chloro-(O-cresoxy)acetic acid
- Chloro-(O-tolyloxy)acetic acid
- Chwastox
- Chwastox 30
- Chwastox F
- chwastox30
- chwastoxextra
- CMP acetate
- cornox
- Cornox-M
- Dicotex
- Dikotes
- Dikotex
- Dow MCP amine weed killer
- Emcepan
- ethanoicacid,(4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy)-
- Farmon MCPA 50
- FBC MCPA
- FLUID 4
- Hedapur M 52
- hedapurm52
- Hedarex M
- hedarexm
- Hedonal M
- hedonalm
- Herbicide M
- herbicidem
- Hormotuho
- Hornotuho
- Kilsem
- Kilsem4k-2m
- Krezone
- Kwas 4-chloro-2-metylofenoksyoctowy
- kwas4-chloro-2-metylofenoksyoctowy
- Kyselina 4-chlor-2-methylfenoxyoctova
- kyselina4-chlor-2-methylfenoxyoctova
- Legumex db
- legumexdb
- Leuna M