99247-33-3
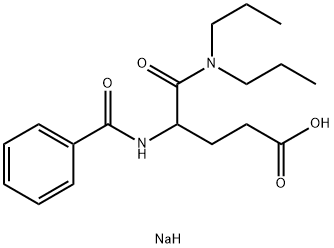 99247-33-3 結(jié)構(gòu)式
99247-33-3 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
4-苯酰胺-5-二丙氨基-5-氧戊酸鈉鹽
PROGLUMIDE, SODIUM SALT
Proglumide sodium salt solid
4-benzamido-5-(dipropylamino)-5-oxopentanoate
PROGLUMIDE SODIUM SALT SELECTIVE CHOLECY STOK
dl-4-benzamido-n,n-dipropylglutaramicacidsodiumsalt
SODIUM
4-BENZAMIDO-5-(DIPROPYLAMINO)-5-OXOPENTANOATE
4-benzamido-n,n-dipropyl-,sodiumsalt,dl-glutaramicaci
4-BENZOYLAMINO-5-DIPROPYLAMINO-5-OXOPENTANOIC ACID SODIUM
Glutaramic acid, 4-benzamido-N,N-dipropyl-, sodium salt, DL-
| 報價日期 | 產(chǎn)品編號 | 產(chǎn)品名稱 | CAS號 | 包裝 | 價格 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-103354 | 4-苯酰胺-5-二丙氨基-5-氧戊酸鈉鹽 Proglumide sodium | 99247-33-3 | 50mg | 600元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-103354 | 4-苯酰胺-5-二丙氨基-5-氧戊酸鈉鹽 Proglumide sodium | 99247-33-3 | 10mM * 1mLin Water | 660元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-103354 | 4-苯酰胺-5-二丙氨基-5-氧戊酸鈉鹽 Proglumide sodium | 99247-33-3 | 100mg | 1100元 |
常見問題列表
Cholecystokinin (CCK)-A/B receptors
In an in vitro study, Proglumide at concentrations between 0.3-10 mM inhibits CCK-stimulated amylase release dose-dependently, while Proglumide does not influence the basal amylase release at concentrations between 0-3 mM. Dose-response curves to CCK for amylase release shifted to the right with increase in Proglumide concentration. This inhibition by Proglumide is reversible. In addition, the effect of Proglumide is selective for CCK and its related peptide.
The incubation of HT29 cells with Proglumide significantly reduces the [
3
H]-thymidine incorporation to HT29 cells in a dose-dependent manner, with an IC
50
of 6.5 mM. Proglumide reduces in a dose-dependent manner the percentage of necrosis with a parallel increase of apoptosis up to 70%.
Proglumide (250-750?mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; adult male Sprague Dawley rats) treatment is significantly effective in ameliorating the seizure activities, cognitive dysfunctions, and cerebral oxidative stress.
| Animal Model: | Adult male Sprague Dawley rats (200-250?g; 2 months old) are induced status epilepticus (SE) |
| Dosage: | 250 mg/kg, 500 mg/kg, and 750?mg/kg |
| Administration: | Intraperitoneal injection |
| Result: | Dose-dependently and significantly increased the latencies to seizure and SE. Significantly and dose-dependently attenuated Li-PC (SE) induced increase in thiobarbituric acid (TBARS) and catalase (CAT), attenuated Li-Pc induced decrease in SOD, and attenuated depletion of GSH and glutathione-S transferase (GST) in the hippocampus and striatum. |