194798-83-9
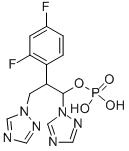 194798-83-9 結(jié)構(gòu)式
194798-83-9 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
氟氟康唑
磷氟康唑
福司氟康唑
福斯氟康唑雜質(zhì)
磷氟康唑(福司氟康唑)
2-(2,4-二氟苯基)-1,3-二(1H-1,2,4-三氮唑-1-基)丙基二氫磷酸酯
CS-969
Fosfluconazole(INN)
Fosfluconazole, >=98%
Dihydrogen phosphate ester
2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-1,3-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propyl dihydrogen phosphate
PHARMA PRODUCT FLUCONAZOLE USP 2-(2,4-DIFLUOROPHENYL)-1,3-BIS(1,2,4-TRIAZOL-1-YL) PROPAN-2-OL
1H-1,2,4-Triazole-1-ethanol, a-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-a-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-,1-(dihydrogen phosphate)
1H-1,2,4-Triazole-1-ethanol, α-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-α-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-, 1-(dihydrogen phosphate)
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
| 報(bào)價(jià)日期 | 產(chǎn)品編號(hào) | 產(chǎn)品名稱 | CAS號(hào) | 包裝 | 價(jià)格 |
| 2024/11/08 | S6467 | 磷氟康唑 Fosfluconazole | 194798-83-9 | 5mg | 794.47元 |
| 2023/03/20 | S6467 | 磷氟康唑 Fosfluconazole | 194798-83-9 | 25mg | 1392.34元 |
常見(jiàn)問(wèn)題列表
Antifungal
To investigate the polarized bioconversion and the Transwell transport of phosphate prodrugs in Caco-2 monolayer, 10 μM Fosfluconazole or Fosphenytoin is dosed either in the apical or basal compartment in Transwell plates. Both prodrugs are efficiently cleaved in the apical compartment after a 2 h incubation. To further investigate the kinetics of ALP-mediated bioconversion, the concentration-dependent ALP-mediated bioconversions are conducted to determine the Michaelis-Menten constant (K m ) of prodrug bioconversion in Caco-2 monolayers. The saturation curves of Fosphenytoin and Fosfluconazole with the concentration increase are found. The estimated K m values of Fosphenytoin and Fosfluconazole are 1160 and 357 μM, respectively.
The apparent half-life for Fosfluconazole bioconversion in intestinal mucosa scraps is 10 min. Fluconazole (FLCZ) is an antifungal agent that is efficacious in the treatment of fungal peritonitis. Fosfluconazole (F-FLCZ) is the phosphate prodrug of FLCZ, which is highly soluble compared with FLCZ. F-FLCZ is useful against fungal peritonitis in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) patients because it has a high water solubility. The aims of the present study are to characterize the peritoneal permeability of FLCZ and the pharmacokinetics of FLCZ and F-FLCZ after intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration to peritoneal dialysis rats. FLCZ or F-FLCZ is administered intravenously and intraperitoneally. After the i.p. administration of F-FLCZ, FLCZ is detected in circulating blood and the dialyzing fluid in peritoneal dialysis rats. The concentration of plasma FLCZ after the i.p. F-FLCZ administration is lower than that after the intravenous (i.v.) F-FLCZ administration. It is considered that the dose should be increased appropriately when F-FLCZ is administered intraperitoneally. The profiles of plasma FLCZ after i.v. and i.p. administrations are analyzed using a two-compartment model in which the distribution volume of the peripheral compartment is fixed at a volume of the dialyzing fluid (peritoneal dialysis PK model). The peritoneal dialysis PK model could describe the profiles of plasma and dialyzing fluid FLCZ. These results suggest that FLCZ and F-FLCZ could be administered intraperitoneally for the treatment of fungal peritonitis in CAPD patients.