| Identification | More | [Name]
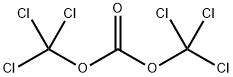
Triphosgene | [CAS]
32315-10-9 | [Synonyms]
BIS(TRICHLOROMETHYL) CARBONATE
CARBONIC ACID BISTRICHLOR METHYL ESTER
TRIPHOSGEN
TRIPHOSGENE
TriphosgeneForSynthesis
Triphosgene98+%
Triphosgene, 98% [Bis-(trichloromethyl)-carbonat]
Methanol, trichloro-, carbonate (2:1)
TRICHLOROMETHANOLCARBONATE
TRIPHOSGENE (BIS-(TRICHLOROMETHYL)CARBONATE)
tri-Phosgene, Triphosgene
Carbonic acid bis(trichloromethyl)
Carbonic acid bis(trichloromethyl) ester
Trichloromethoxyformic acid trichloromethyl ester | [EINECS(EC#)]
250-986-3 | [Molecular Formula]
C3Cl6O3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00062848 | [Molecular Weight]
296.75 | [MOL File]
32315-10-9.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
White solid | [Melting point ]
79-83 °C (lit.) | [Boiling point ]
203-206 °C (lit.) | [density ]
1.78
| [vapor pressure ]
16 hPa (90 °C) | [Fp ]
203-206°C | [storage temp. ]
2-8°C
| [solubility ]
Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | [form ]
Crystalline Powder, Crystals and/or Chunks | [color ]
White to off-white | [Water Solubility ]
practically insoluble | [Sensitive ]
Moisture Sensitive | [BRN ]
1787583 | [InChIKey]
UCPYLLCMEDAXFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [CAS DataBase Reference]
32315-10-9(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
32315-10-9(EPA Substance) |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Toxicity]
As a common production raw material for chemical enterprises, Sanguang gas is not listed in the list of hazardous chemicals, and its risk is not familiar and understood by many users, which often leads to decomposition and poisoning accidents. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to study the hazards and safety measures in the use of Triphosgene. Based on the characteristic identification of triphosgene, the hazards in the process of dissolution and reaction are identified and analyzed, and the corresponding safety measures in the use of Triphosgene are put forward according to the results of hazard identification and analysis. Triphosgene has gradually become the raw material for acyl chlorination in many enterprises because it is a non hazardous chemical, relatively stable material properties, easy transportation and easy treatment of tail gas. However, if the safety measures are not appropriate during the transportation, storage and use of triphosgene, it is very easy to cause poisoning accidents. |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
T+,Xn | [Risk Statements ]
R26:Very Toxic by inhalation.
R34:Causes burns.
R29:Contact with water liberates toxic gas.
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin .
R20/21/22:Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed . | [Safety Statements ]
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection .
S45:In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show label where possible) .
S9:Keep container in a well-ventilated place .
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing .
S7/9:Keep container tightly closed and in a well-ventilated place . | [RIDADR ]
UN 2928 6.1/PG 2
| [WGK Germany ]
2
| [F ]
10-19-21 | [TSCA ]
Yes | [HazardClass ]
6.1 | [PackingGroup ]
II | [HS Code ]
29209010 |
| Raw materials And Preparation Products | Back Directory | [Raw materials]
Chlorine-->Formaldehyde-->2,2'-Azobis-(2,4-dimethylvaleronitrile) (V-65) | [Preparation Products]
4-(2-KETO-1-BENZIMIDAZOLINYL)PIPERIDINE-->N-Boc-N'-(2-chlorobenzyloxycarbonyl)-L-lysine-->H-LYS(2-CL-Z)-OH-->3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl isocyanate-->Phenyl chloroformate-->3,4-(METHYLENEDIOXY)PHENYL ISOCYANATE-->5-FLUORO-2H-3,1-BENZOXAZINE-2,4(1H)-DIONE-->3,5-DIMETHYLISOXAZOL-4-YL ISOCYANATE-->1,5-Diphenylcarbazide-->2,2,2-Trichloroethyl chloroformate-->(S)-3-TERT-BUTYL-2,5-PIPERAZINEDIONE-->Ritonavir-->DIRECT YELLOW 50-->5-Bromothiophene-2-carbaldehyde-->4-DIMETHYLAMINOPHENYL ISOCYANATE-->1-Naphthyl isocyanate-->(1-METHYL-1H-PYRROL-2-YL)METHYLAMINE-->3-METHOXYPHENYL ISOCYANATE-->2-CHLOROBENZYL CHLOROFORMATE-->2-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PHENYL ISOCYANATE-->Pentyl isocyanate-->2-NAPHTHYL ISOCYANATE-->4-Cyanophenyl isocyanate-->3-Bromophenyl isocyanate-->Fluoro-N,N,N',N'-tetramethylformamidinium hexafluorophosphate-->2-Chlorophenyl isocyanate-->2-CHLORO-5-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PHENYL ISOCYANATE-->2-Methoxyphenyl isocyanate-->4-Methylbenzyl isocyanate-->4-Methoxybenzyl isocyanate-->3,4-(METHYLENEDIOXY)PHENYL ISOCYANATE-->3-FLUOROPHENYL ISOCYANATE-->4-Fluorophenyl isocyanate-->4-Methoxyphenyl isocyanate-->2-FLUOROPHENYL ISOCYANATE-->1-CHLORO-2-METHYLPROPYL CHLOROFORMATE-->(S)-(-)-4-tert-Butyloxazolidine-2,5-dione-->Direct Red 75 tetrasodium salt-->BIS(4-NITROPHENYL) CARBONATE |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Triphosgene is also known as solid phosgene. Its chemical name is bis (Trichloromethyl) carbonate, and its English name is bisgriehloromethyl) carbonate or triphosgene, abbreviated as BTC. Triphosgene is a white crystal, similar to the smell of phosgene. It is mainly used to synthesize chloroformate, isocyanate, polycarbonate and acyl chloride. It is widely used as an intermediate in plastics, medicine, herbicides and pesticides. | [Chemical Properties]
White solid | [Uses]
An efficient carbonylating agent for liquid and solid-phase aza-peptide synthesis. | [Reactions]
The Triphosgene reaction is quenched very carefully by dropwise addition of 75 mL of saturated aqueous sodium sulfate solution (Notes 5 and 6). The resulting white granular precipitate or slurry is removed by vacuum filtration through Celite, and the filter cake is washed with three portions of 75 mL of chloroform . | [General Description]
Triphosgene [Bis(trichloromethyl)carbonate] is a versatile organic reagent used in organic synthesis alternative to phosgene. A catalytic amount of triphosgene is particularly used in chloroformylations, carbonylations, chlorinations, and dehydration reactions. | [reaction suitability]
reaction type: Coupling Reactions | [Safety]
Triphosgene's low vapor pressure makes it possible for it to reach concentrations that are considered toxicologically unsafe. While several properties of triphosgene are not yet readily available, it is known that it is extremely toxic if inhaled. A toxic gas is emitted if it comes in contact with water. There is a lack of information and variability regarding the proper handling of triphosgene. It is assumed to have the same risks as phosgene. | [Synthesis]
Triphosgene is synthesized by exhaustive free radical chlorination of dimethyl carbonate:
CH3OCO2CH3 + 6 Cl2 → CCl3OCO2CCl3 + 6 HCl
Triphosgene can be easily recrystallized from hot hexanes. | [Purification Methods]
It is a good solid substitute for phosgene (using a third mol per mol). Crystallise it from pet ether (b 60-80o), wash it with anhydrous cold Et2O, de-gas it at 200mm then dry at 0.1mm (over H2SO4). It has IR: max 900 and 1900 cm-1 . It is a lachrymator, is TOXIC and should be handled with gloves and in an efficient fume hood. [Hales et al. J Chem Soc 620 1957, Eckert & Forster Angew Chem, Int Ed Engl 26 894 1987, Aldrichimica Acta 21 47 1988, Beilstein 3 H 17, 3 I 8, 3 II 16, 3 III 36, 3 IV 33.] |
|
|