| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
TAK-788 | [CAS]
1847461-43-1 | [Synonyms]
TAK-788
AP 32788
Mobocertinib
Mobocertinib (TAK788)
AP32788, MOBOCERTINIB
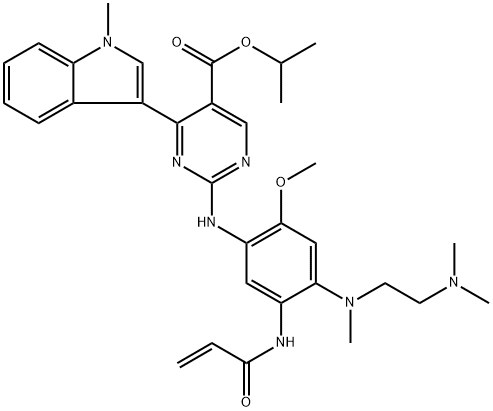
Isopropyl 2-((5-acrylamido-4-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)(methyl)amino)-2-methoxyphenyl)amino)-4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)pyrimidine-5-carboxylate
5-Pyrimidinecarboxylic acid, 2-[[4-[[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]methylamino]-2-methoxy-5-[(1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)amino]phenyl]amino]-4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-, 1-methylethyl ester | [Molecular Formula]
C32H39N7O4 | [MDL Number]
MFCD32669806 | [MOL File]
1847461-43-1.mol | [Molecular Weight]
585.71 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [storage temp. ]
Store at -20°C | [solubility ]
DMF: 10 mg/ml,DMF:PBS (pH 7.2) (1:8): 0.11 mg/ml | [form ]
A crystalline solid | [color ]
Off-white to light yellow |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Mobocertinib is derived from osimertinib, a
second-generation TKI which exhibits only limited
activity against several resistant EGFRex20ins
mutants. Both inhibitors are structurally identical
except that the pyrimidine ring of moboceritinib
incorporates a snugly fitting isopropyl ester group that targets a previously unoccupied pocket,
resulting in expanded coverage of EGFRex20ins
mutations as well as improved selectivity over wildtype EGFR vs. osimertinib. | [Uses]
Mobocertinib (TAK-788,1847461-43-1) is an orally active and irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor. Mobocertinib effectively inhibits oncogenic variants containing mutations that activate the EGFRex20ins, with selectivity superior to that of wild-type EGFR. Mobocertinib is FDA-approved for the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have a HER2 mutation or an EGFR mutation, including an exon 20 insertion mutation. Mobocertinib is approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have HER2 mutations or EGFR mutations, including exon 20 insertion mutations.
| [Brand name]
ExkivityTM | [General Description]
Class: receptor tyrosine kinase
Treatment: NSCLC with EGFR alterations
Oral bioavailability = 37%
Elimination half-life = 18 h
| [Biological Activity]
In NSCLC cell lines, mobocertinib was highly active against common EGFR-activating mutations (exon 19 deletions and L858R) (IC50 = 1.3–4.0 nM) or with a gatekeeper T790M mutant (IC50 = 9.8 nM), as well as selective for wt EGFR (IC50 = 35 nM). In Ba/F3 cells, mobocertinib displayed activity against 14 EGFR mutations with IC50 values ranging from 2.7 to 22.5 nM, vs. 34.5 nM for wt EGFR. More specifically, mobocertinib inhibited all five variants of EGFRex20ins mutations with IC50 ranging from 4.3 nM to 22.5 nM. | [target]
EGFR, HER2-4 | [Metabolism]
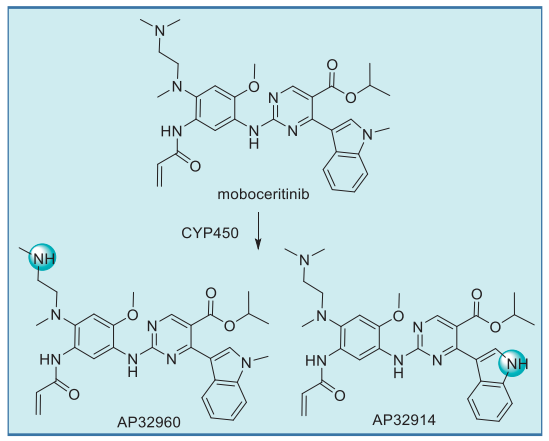
Moboceritinib undergoes CYP450-mediated metabolism to give two primary N-demethylated metabolites, AP32914 and AP32960, whose IC50 values are within 2-fold of mobocertinib for both wt and mutant EGFR. It is likely that these metabolites also contribute to the pharmacologic activity of mobocertinib. Interestingly, the typically labile isopropyl ester appears resistant to esterase-induced hydrolysis.
 |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Binding Mode]
In the co-crystal structure of moboceritinib in complex with EGFRT790M+V948R, the aminopyrimidine scaffold occupies the ATP-binding site, forming two critical hydrogen bonds with Met793 of the hinge, and the isopropyl ester occupies a selectivity pocket in the vicinity of αC helix. The ester carbonyl group interacts with Gln791 backbone carbonyl via a bound water molecule. Most importantly, the inhibitor forms the expected covalent bond with Cys797 at the edge of the active site cleft and the acrylamide Michael--acceptor group, making binding irreversible. The co-crystal structure of wt EGFR kinase in complex with moboceritinib shows that the ester group is slightly tilted to enable a hydrogen bond between the Thr790 gatekeeper side chain hydroxyl group and the ester carbonyl oxygen. However, a comparison of the wt and mutant proteins with moboceritinib reveals that the binding pockets are similar despite differences in overall kinase conformation. |
|
|