| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Neotuberostemonine | [CAS]
143120-46-1 | [Synonyms]
Neotuberostemonine
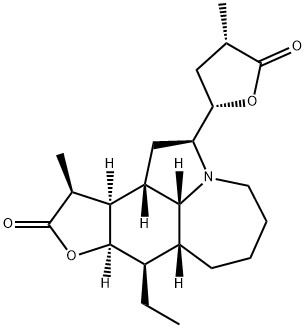
(2S,7aR,8R,8aR,11S,11aR,11bS,11cR)-8-Ethyl-11-methyl-2-[(2S,4S)-4 -methyl-5-oxotetrahydro-2-furanyl]dodecahydroazepino[3,2,1-hi]fur o[3,2-e]indol-10(2H)-one
Furo[2,3-h]pyrrolo[3,2,1-jk][1]benzazepin-10(2H)-one,8-ethyldodecahydro-11-methyl-2-[(2S,4S)-tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-furanyl]-,(2S,7aR,8R,8aR,11S,11aR,11bS,11cR)- | [EINECS(EC#)]
200-158-5 | [Molecular Formula]
C22H33NO4 | [MDL Number]
MFCD17214798 | [MOL File]
143120-46-1.mol | [Molecular Weight]
375.5 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Boiling point ]
554.2±50.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.19±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) | [solubility ]
DMSO: 10 mM | [form ]
A crystalline solid | [pka]
8.90±0.70(Predicted) | [color ]
White to off-white |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Neotuberostemonine (NTS) is one of the main antitussive alkaloids in the root of Stemona tuberosa Lour, it has a significant protective effect on bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis through suppressing the recruitment and M2 polarization of macrophages. Neotuberostemonine demonstrates antitussive properties in guinea pigs. | [Uses]
Neotuberostemonine is a major bioactive alkaloid of Stemona tuberosa. It can also be used to treat pulmonary fibrosis. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Neotuberostemonine is an alkaloid. It has a role as a metabolite. | [Biological Functions]
Neotuberostemonine is an alkaloid originally isolated from S. tuberosa that has diverse biological activities. It inhibits LPS-induced increases in inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) protein levels and NO production in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 100 μM. Neotuberostemonine (50 μM) inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation of RAW 264.7 cells. It reduces the citric acid-induced cough reflex in conscious guinea pigs when administered at a dose of 133 μmol/kg. Neotuberostemonine (40 mg/kg) inhibits pulmonary collagen deposition and fibrosis, as well as bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) monocyte and lymphocyte infiltration in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. | [Biological Activity]
Neotuberostemonine, one of the main antitussive alkaloids in the root of Stemona tuberosa Lour, attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing the recruitment and activation of macrophages. |
|
|