| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
daurisoline | [CAS]
70553-76-3 | [Synonyms]
70553-76-3
Daurisoline
(R,R)-Daurisoline
O7-Demethyldauricine
(1R)-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-1-[[4-hydroxy-3-[4-[[(1R)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-2-methyl-1-isoquinolinyl]methyl]phenoxy]phenyl]methyl]-6-methoxy-2-methyl-7-isoquinolinol | [EINECS(EC#)]
683-239-9 | [Molecular Formula]
C37H42N2O6 | [MDL Number]
29399990 | [MOL File]
70553-76-3.mol | [Molecular Weight]
610.747 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Boiling point ]
724.5±60.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.218±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
?20°C | [solubility ]
DMSO: soluble15mg/mL, clear | [form ]
powder | [pka]
9.31±0.45(Predicted) | [color ]
white to beige | [InChIKey]
BURJAQFYNVMZDV-FIRIVFDPSA-N | [SMILES]
[C@@H]1(CC2=CC=C(O)C(OC3=CC=C(C[C@@H]4C5=C(C=C(OC)C(OC)=C5)CCN4C)C=C3)=C2)C2=C(C=C(OC)C(O)=C2)CCN1C |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Abstract]
Daurisoline is a kind of alkaloid extracted from the rhizome of menispermum dauricum DC, which is the main component of phenolic alkaloids from menispermum dauricum. Experiments show that daurisoline has the function characteristics of class Ⅲ antiarrhythmic drug. And its role in extending the duration of myocardial action potential has the characteristic of use dependence, so it has a broad prospect in the clinical application. | [Physical and chemical properties]
milk yellow powder (cyclohexane), containing 1/3 molecular cyclohexane; melting point 96~102℃, [α] 20D-129°(c = 0.65, methanol). | [Source]
Daurisoline that is belonging to bis benzyltetrahydroi soquinolines is present in the rhizomes of menispermum dauricum DC. | [Rhizoma Menispermi]
Rhizoma menispermi is the rhizome of menispermum dauricurn DC and is mainly produced in Jilin, Liaoning, Hebei, Henan, Shaanxi, Gansu, Shandong and other places. The rhizome is cylindrical, curved and branched, the length of which is up to 50cm and the diameter of which is between 0.3~0.8cm. Its surface is yellow brown to dark brown and many have curved fine roots and vertical wrinkles. Its skin is easy to peel and it has tenacious texture. It is easy to break and the section is not neat. Its texture is fibrous and its xylem is light yellow, which is radial arrangement and the center of which has marrow. It was originally contained in the "Chinese medicinal herbs " and is mainly produced in the northeast, north China, Shaanxi and other places. The property and flavor of rhizoma menispermi is bitter and cold. Rhizoma menispermi has little toxicity and acts on the lungs, stomach and large intestine channel, which has the effect of “clearing heat and removing toxicity”, “dispelling wind and relieving pain” and “regulating Qi and resolving dampness”. It is traditionally used for the treatment of sore throat, enteritis, dysentery, rheumatism and arthralgia spasm pain. Rhizoma menispermi mainly contains alkaloid ingredients and its total alkaloid content is about 1.7%-2.5%, the highest content of which is fat-soluble alkaloids.
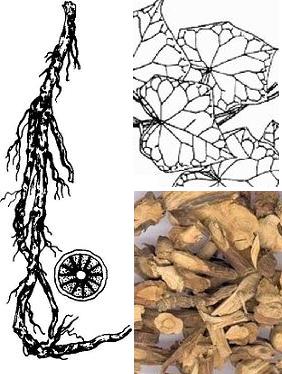
Figure 1 the picture of Rhizoma menispermi rhizomes and leaves | [Analytical method]
Daurisoline is characterized by high performance liquid chromatography. The mobile phase is acetonitrile-water-triethylamine (18: 82: 0.28, adjusted to pH = 3 with phosphoric acid).
The detection wavelength is 284 nm.
The extraction of phenolic alkaloids from menispermum dauricum
1.The extraction of the total alkaloids in the menispermum dauricum:
First pretreated the menispermum dauricum by acid water extraction method and then obtain the crude alkali through alkaline precipitation method according to the propertie that most free alkaloids are insoluble in water. And then extract the fat-soluble part using the method of continuous extraction of benzene reflux. And then use 5% sodium hydroxide to extract the total phenolic alkaloids based on the nature that phenolic alkaloids from menispermum dauricum can be dissolved in a certain amount of lye. The flow chart is as follow:

2.The extraction of phenolic alkaloids from menispermum dauricum:
Extract 1kg of crude alkali (ground) 2 times with benzene (each 2000ml), and then combine the benzene solution and respectively extract 4 times with 5% sodium hydroxide solution (400,300,300, 200 mL). Combine the separated lye and adjust its pH to 4 with 6 mol/L hydrochloric acid. Decolore it with activated charcoal and dropwise add concentrated ammonia to pH=9 to separate out milky white precipitate. Then filter and wash the precipitate with water to neutral. Dry the precipitate in vacuum to obtain 352 g of pale yellow powder (phenolic alkaloids from menispermum dauricum).
Separation of dauricine and daurisoline
Dissolve 100 g of phenolic alkaloids in about 250 ml of chloroform. After dissolved completely, pour them into separatory funnel and extract three times with 3% sodium hydroxide solution (200, 100, 100 mL) to separate the chloroform solution (monophenol) and lye (bisphenol and trisphenol). First wash the chloroform solution containing the monophenol portion with 150 mL of water, and then remove the aqueous layer and extracte four times with 1% hydrochloric acid (200, 200, 100, 100 mL). Combine the acid water and decolor it with activated carbon. Adjust the pH to 9 with concentrated ammonia water to separate out white precipitate. Then filter and wash them to neutral. Dry in vacuum to obtain white powder dauricine 45g, a yield that is 45 % of the total phenolic alkaloid.
Decolor the lye containing bisphenol and triphenol with activated carbon and adjust the pH to 8 with concentrated ammonia water to precipitate milky white polyphenols precipitation.
Dissolve the precipitation with about 200mL of chloroform, and wash them with 0.5% sodium hydroxide 3 times (100ml×3). Then wash them with 1% sodium hydroxide solution (150mL) and combine all the lye (including tricelles, etc.). Extract the chloroform solution (containing bisphenol) with 1% hydrochloric acid 3 times (150mL × 3) and combine the acid water. Decolor them with activated carbon and adjust the pH to 8 with concentrated ammonia water to precipitate milky white precipitation. Filter and wash them to neutral. Dry in vacuum to obtain light grayish yellow powder daurisoline, a yield that is 11.5% of the total phenolic alkaloid. | [Pharmacological activity]
Daurisoline is a strong Ca ion antagonist, which has potential antihypertensive and antiarrhythmic activity.
Daurisoline is a pure alkaloid isolated from the total alkaloids in Tonkin Sophora root. Daurisoline pretreated with methyl bromide was used in the nutation test and the in vivo neuromuscular block test. The result showed that daurisoline had the effect of muscle relaxation. It has been used in the clinical practice of spinal anaesthesia surgery. The observation of 35 times drug use in 19 cases confirmed that daurisoline was added when the spinal anaesthesia was shallow and muscle loose was not enough, which made the surgical operation difficult (peritoneal exploration, peritoneal suture), thus overcoming the muscle loose deficiency to successfully complete the operation. The animal experiments and clinical practice all verified the daurisoline does have muscle relaxation effect.
There are many examples, such as the died chicks are relaxation paralysis, daurisoline has obvious synergistic effect with tubocurarine and has antagonism effect with neostigmine and calcium gluconate, clinical observations in the electromyography find the facilitation phenomenon after strong stimulation, etc., which all can demonstrate that the drug is non-depolarizing type muscle relaxant. | [Toxicology]
In the toxicity test, the amount of respiratory paralysis in rabbits was 3.71mg/kg, while the amount of daurisoline that made S-T segment begin to show depression was 43.7mg/kg.
The ratio between the two doses reached 1: 11.2. In the acute toxicity test, when the intravenous injection of daurisoline was 4mg/kg, the rabbit’s breathing changed difficult and gradually stopped. After 40 seconds, the rabbit finally died. The important organs of the died rabbit was checked by tissue section and no abnormalities was found. The above examples all demonstrated that this drug has no obvious damage to the physical organs and has a larger safety range. | [Metabolism]
Pharmacokinetic studies showed that the dynamic behavior in the rabbit body was consistent with the two-compartment open model when three doses of the daurisoline were injected. It has the advantages of rapid dispersion, faster elimination and extensive distribution. | [Storage method]
2-8 °C; protected from light | [Characterization spectrogram]
UV λKBrmax cm-1: 3420, 3350 (OH), 2850 (OCH3), 1590, 1500 (aromatic ring), 1015, 1155 (ether chain). 1H-NMR (CDCl3): 2144 (3H, s, N2-CH3), 2150 (3H, s, N'2-CH3), 3.60, 3.75, 3.82 (3H, s, OCH3) to 5.00 (2H, s, 2×OH, disappeared after adding H2O), 6.10~7.14 (11H, m, aromatic hydrogen).
MS m/z: 610(M+, 25), 206 (92.5), 192 (100), 177 (5.35).
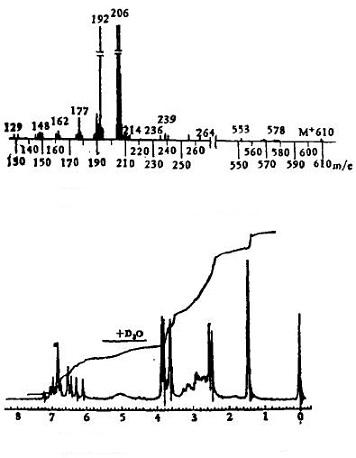
Figure 2: the mass spectrum and nuclear magnetic resonance diagram of daurisoline | [References]
1. Quantitative analysis of the components in natural drugs of daurisoline
2. Deng S W, Ming Z D, et al. New alkaloids from menispermum dauricum-daurisoline [J]. Science Bulletin, No.6, 1979 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
Daurisoline is a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid isolated from Menispermum dauricum and displays antiarrythmic effects. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Daurisoline is a member of isoquinolines. |
|
|