| Identification | More | [Name]
Tri-tert-butylphosphine tetrafluoroborate | [CAS]
131274-22-1 | [Synonyms]
TRI-(T-BUTYL)PHOSPHONIUM HYDROGEN HBF4 SALT
TRI-T-BUTYLPHOSPHONIUM TETRAFLUOROBORATE
TRI-TERT-BUTYLPHOSPHINE TETRAFLUOROBORATE
TRI-TERT-BUTYLPHOSPHINE TETRAFLUOROBORIC ACID ADDUCT
TRI-TERT-BUTYLPHOSPHONIUM TETRAFLUOROBORATE
TRI-TERT-BUTYLPHOSPHINE TETRAFLUOROBORA&
Tri-t-butylphosphoniumtetrafluoroborate,99%
fluoroboric acid tri-tert-butylphosphine adduct
tri-tert-butylphosphine fluoroboric acid adduct
Tri-tert-butylphosphonium tetrafluoroborate, 97+%
Tri-tert-butylphosphonium tetrafluoroborate,99% | [EINECS(EC#)]
672-603-2 | [Molecular Formula]
C12H27BF4P- | [MDL Number]
MFCD07189501 | [Molecular Weight]
289.12 | [MOL File]
131274-22-1.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white to light yellow crystal powde | [Melting point ]
261 °C(lit.)
| [storage temp. ]
Inert atmosphere,2-8°C | [solubility ]
Chloroform (Slightly), Dichloromethane (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) | [form ]
Crystals and Chunks | [color ]
White | [Water Solubility ]
Soluble in methylene chloride and chloroform. Slightly soluble in terahydro furan. Insoluble in hexane, toluene and water. | [Sensitive ]
Hygroscopic | [BRN ]
8813613 | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C12H28P.BF4/c1-10(2,3)13(11(4,5)6)12(7,8)9;2-1(3,4)5/h13H,1-9H3;/q2*-1 | [InChIKey]
YSTLBJVHZMEEAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [SMILES]
[P-](C(C)(C)C)(C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)C.[B-](F)(F)(F)F | [CAS DataBase Reference]
131274-22-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xn | [Risk Statements ]
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin .
R20/21/22:Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed . | [Safety Statements ]
S22:Do not breathe dust .
S24/25:Avoid contact with skin and eyes .
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection .
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice . | [RIDADR ]
UN 1759 8/PG III | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [TSCA ]
No | [HazardClass ]
8 | [PackingGroup ]
III | [HS Code ]
29319090 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
white to light yellow crystal powde | [Uses]
suzuki reaction | [Application]
Tri-tert-butylphosphonium tetrafluoroborate is a ligand used in the palladium-catalyzed enantioselective alfa-arylation of N-boc-pyrrolidine. It is also used with a palladium(0)-15-membered, triolefinic, macrocyle in Suzuki cross-coupling reactions of aryl bromides and chlorides. Further, it is used in the Heck coupling of vinyl tosylates with olefins. | [Preparation]
Addition of HBF4 to a solution of tri-tert-butylphosphine in methylene chloride. Separation of the organic layer and removal of the solvent gives analytically pure Tri-tert-butylphosphine tetrafluoroborate.
| [reaction suitability]
reaction type: Cross Couplings
reagent type: ligand
reaction type: Addition Reactions
reagent type: ligand
reaction type: Buchwald-Hartwig Cross Coupling Reaction
reagent type: ligand
reaction type: Carbonylations
reagent type: ligand
reaction type: Heck Reaction
reagent type: ligand
reaction type: Negishi Coupling
reagent type: ligand
reaction type: Sonogashira Coupling
reagent type: ligand
reaction type: Stille Coupling
reagent type: ligand
reaction type: Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling | [storage]
Tri-tert-butylphosphine tetrafluoroborate is indefinitely stable as a solid and in solution and requires no special handling. This compound is considered non-hazardous. Protection from oxygen is required in the presence of the base, as the highly air-sensitive tri-tert-butylphosphine will be formed.
|
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Reaction]
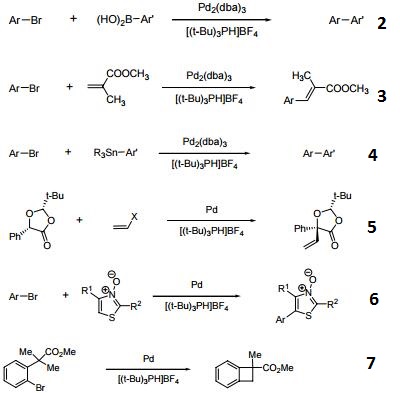
- Air-stable, non-pyrophoric precursor of the Tri-t-butylphosphine ligand which is used in a variety of catalytic processes.
- Ligand for Suzuki cross-couplings.
- Ligand for Heck Reactions.
- Ligand for Stille Cross-couplings.
- Ligand for α-Arylation and vinylation of arylmandelic acid derivatives.
- Ligand for direct arylation of hetercycles
- Synthesis of benzocyclobutenes by C-H activation.
- Cross-coupling of Grignard reagents and aryl bromides.
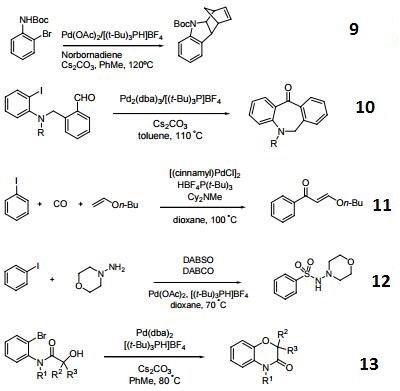
- Palladium catalyzed annulation of haloanilines.
- Palladium-Catalyzed Acylation.
- Palladium Catalyzed Carbonylative Heck Reaction.
- Palladium-catalyzed aminosulfonylation.
- Palladium-catalyzed intramolecular C–O bond formation.
- Ruthenium-catalyzed cross-coupling of aldehydes with arylboronic acid.
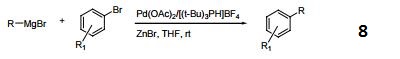
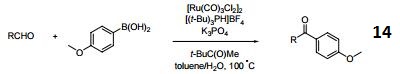
|
|
|