| Identification | More | [Name]
Grepafloxacin | [CAS]
119914-60-2 | [Synonyms]
GREPAFLOXACIN
GREPAFLOXACIN HYDROCHLORIDE
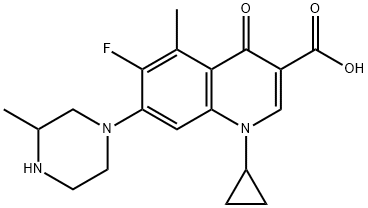
1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(3-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-5-methyl-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid | [EINECS(EC#)]
631-454-3 | [Molecular Formula]
C19H22FN3O3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00865116 | [Molecular Weight]
359.39 | [MOL File]
119914-60-2.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
189-192 ºC | [Boiling point ]
610.0±55.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.366 | [storage temp. ]
under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2–8 °C | [solubility ]
DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) | [form ]
Solid | [pka]
6.44±0.50(Predicted) | [color ]
Pale Beige to Pale Yellow | [Stability:]
Hygroscopic | [CAS DataBase Reference]
119914-60-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
dl-Grepafloxacin is an antibacterial compound used to treat various respirator infections. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Grepafloxacin is a member of quinolines, a quinolone antibiotic and a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. | [in vivo]
Grepafloxacin (OPC-17116; 200 mg/kg; p.o.; Balb/c mice) displays good safety profile in terms of phototoxicity[2].
Grepafloxacin (25-200 mg/kg; p.o.; 5 days/week for 4 weeks; female C57BL6/J-Lyst bg-J/ mice/beige mice) has modest activities in both intranasal (IN) infection and intravenous (IV) Mycobacterium aviuminfection models[3]. | Animal Model: | Female Balb/c mice (5-6 weeks)[2] | | Dosage: | 200 mg/kg | | Administration: | Oral administration; once | | Result: | Had mild and short-lived erythema and no changed auricular thickness. |
| Animal Model: | Female C57BL6/J-Lyst bg-J/ mice/beige mice with mycobacterium avium infection[3] | | Dosage: | 25, 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg | | Administration: | Oral administration; 5 days/week for 4 weeks | | Result: | Had bactericidal activity and limited the growth of the bacteria. |
| [IC 50]
Quinolone |
|
|