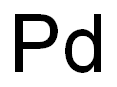
Palladium synthesis
- Product Name:Palladium
- CAS Number:7440-05-3
- Molecular formula:Pd
- Molecular Weight:106.42
The wet method is using the residue of extracted nickel and copper as raw materials, adding aqua for extraction, filtration, adding ammonia and hydrochloric acid to react, thus forming the precipitation of ammonium chloropalladate. After refining, filtration, reduction of ammonium chloropalladate with hydrogen 99.95% finished product of palladium can be obtained.
-, C-(1,1-dimethylethyl) ester (9CI)](/CAS/20240320/GIF/344462-93-7.gif)
344462-93-7
0 suppliers
inquiry
![2-Propanesulfonamide, N-[(2R)-2-(4-iodophenyl)propyl]-](/CAS/20210305/GIF/375345-98-5.gif)
375345-98-5
0 suppliers
inquiry
375345-95-2
43 suppliers
inquiry
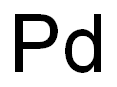
7440-05-3
503 suppliers
$17.69/1G
Yield:375345-95-2 75.7%
Reaction Conditions:
with propan-1-ol;potassium carbonate;palladium diacetate in water at 87; for 20 h;Heating / reflux;
Steps:
2 EXAMPLE 2; Alternative Preparation of {(2R)-2-[4-(4-{2-[(methylsulfonyl)amino]ethyl}phenyl)phenyl]propyl}[(methylethyl)sulfonyl]amine; Preparation of Final Title Compound
EXAMPLE 2 [0094] Alternative Preparation of {(2R)-2-[4-(4-{2-[(methylsulfonyl)amino]ethyl}phenyl)phenyl]propyl}[(methylethyl)sulfonyl]amine. [0095] Preparation of 4-{2-[-(tert-butoxy)N-(methylsulfonyl)carbonylamino]ethyl}benzene Boronic Acid. [CHEMMOL-00021] [0096] Scheme IIIA, step A: To a room temperature solution of (tert-butoxy)-N-(methylsulfonyl)-N-{2-[4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl(1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl))phenyl]ethyl}carboxamide (81.0% potent, 95 g, 0.18 mol, prepared in example 1) in acetone (2 L) was added 1 N ammonium acetate (1L) and sodium periodate (145 g, 0.678 mol) with stirring. The reaction was allowed to proceed overnight. The reaction mixture was concentrated to remove the acetone, and the aqueous phase was decanted away from the oily product. The aqueous phase was extracted with CH2Cl2 (100 mL) and MTBE (2×100 mL). The combined oily product and organic phases were adjusted to pH 12.5 with the addition of 1 N NaOH. The phases were separated, and the organic phase was extracted with 1 N NaOH (100 mL) and water (2×100 mL). HPLC analysis (60% CH3CN/40% H2O, 2 mL/min, Zorbax C-18, 205 nm) of the organic phase indicated that the product had been removed from this phase. The aqueous phases (containing product) were finally combined and washed with CH2Cl2 (100 mL) and MTBE (2×100 mL). The aqueous phase was added to CH2Cl2 (450 mL) and 1 N H2SO4 was added until the aqueous phase was at pH 3.05. The phases were separated and the aqueous phase was extracted with CH2Cl2 (100 mL). The combined organic extracts (containing product) were concentrated to an oil (58.5 g) that crystallized overnight. The resulting solid mass was triturated with 10% MTBE in heptane (100 mL) to afford, after filtration and drying under reduced pressure, the intermediate title compound, 4-{2-[(tert-butoxy)-N-(methylsulfonyl)carbonylamino]ethyl}benzene boronic acid, (47.7 g, 77.2%) as a white powder. [0097] 1H NMR (d6-DMSO, 300 MHz) δ 7.83 (d, 2H, J=4.8), 7.24 (d, 2H, J=5.1), 7.12 (s, 2H), 3.90 (t, 2H, J=3.9), 3.12 (s, 3H), 2.95 (t, 2H, J=4.5), 1.52 (s, 9H). [0098] Preparation of Final Title Compound. [0099] Scheme IIIA, Step B: Run 1. Within a 3-neck, 1000 mL round-bottom flask was placed [(2R)-2-(4-iodophenyl)propyl][(methylethyl)sulfonyl]amine (15.0 g, 0.0408 mol, prepared in example 1), 4-{2-[(tert-butoxy)-N-(methylsulfonyl)carbonylamino]ethyl}benzene boronic acid (19.1 g, 0.0557 mol), K2CO3 (6.8 g, 0.0490 mol) and 1-propanol (300 mL). To this mixture was then added water (42 mL) and finally Pd(OAc)2 (18 mg,-8.17×10-5 mol, 0.2 mol %). The resulting clear, pale amber solution was heated to reflux (87° C.) to become a dark amber, then a clear olive solution with stirring black particulates (Pd°). The reaction was allowed to stir for 20 h and was allowed to cool to room temperature. TLC analysis (1:9 EtOAc/CH2Cl2) of the resulting off-white suspension indicated desired product (Rf 032), complete consumption of [(2R)-2-(4-iodophenyl)propyl][(methylethyl)sulfonyl]amine (Rf 0.60) and only a trace of 4-{2-[(tert-butoxy)-N-(methylsulfonyl)carbonylamino]ethyl}benzene boronic acid (Rf 0.49). The suspension was diluted with EtOAc (300 mL) to give a clear, pale yellow solution that was filtered through Celite (presaturated with EtOAc). [0100] After washing the Celite through with EtOAc, the filtrate was combined with that of an identical Run 2 which was conducted identically as described above. The combined filtrates from both runs were concentrated under reduced pressure to afford white solids that were diluted with EtOAc (1 L) and 10% K2CO3 (300 mL) to form a clear, amber biphasic solution that was agitated. The aqueous phase (light pink) was separated and the organic phase was washed with additional 10% K2CO3 (4×300 mL). The aqueous phase was back extracted with EtOAc (300 mL) and the combined organic phases (1500 mL) were dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated to a volume of about 620 mL within a 3 L round-bottom flask. The clear, pale yellow solution was stirred slowly while heating to 60° C. Heptane (400 mL) was added dropwise from a separatory funnel to the stirring EtOAc solution at 60° C. (17 volumes of EtOAc/11 volumes of heptane). The heptanes were added over a period of 1.5 h and the clear, pale yellow solution was allowed to cool slowly with slow stirring overnight. The resulting white crystalline solids were cooled to 0° C., filtered, and washed with a minimum of 1:1 EtOAc/heptanes to afford the final title compound, {(2R)-2-[4-(4-{2-[(methylsulfonyl)amino]ethyl}phenyl)phenyl]propyl)}[(methylethyl)sulfonyl]amine, (27.1 g, 75.7%) as a white crystalline powder.
References:
US2003/225163,2003,A1 Location in patent:Page 12-13

10025-98-6
208 suppliers
$39.00/250mg
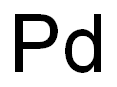
7440-05-3
503 suppliers
$17.69/1G
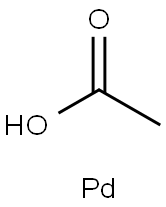
3375-31-3
546 suppliers
$23.00/100mg
7440-05-3
503 suppliers
$17.69/1G