| Chemical Properties |
Chemical properties of sulfur hexafluoride are very stable. And compared to selenium hexafluoride, the hydrolysis rate of sulfur hexafluoride is extremely low, this is due to the small radius sulfur atom, which resulting in six fluorine atoms form a larger steric hindrance around. However, the fluorine atom radius is not big, so the repulsive force between the six fluorine atoms is not too large, S-F bond is not easy to dissociate. Enthalpy of formation of sulfur hexafluoride is-1220 kJ/mol, but enthalpy of formation of sulfur hexafluoride is-74 kJ/mol. Thus, the radius of fluorine atom and sulfur atom radius cause the very stable of sulfur hexafluoride molecule together---the molecules themselves are difficult to disconnect bond and break down and the attack group is difficult to approach to the central atom, in the thermodynamics and kinetics, they are both stable. Studies have said sulfur hexafluoride can be stably present in the atmosphere for thousands of years. |
| Molecular Structure |
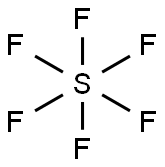
In VSEPR theory, sulfur hexafluoride molecular configuration is regular octahedron, which shows in Figure 1, the yellow is sulfur atom, the blue is fluorine atom. The hybrid orbital type of sulfur atom in sulfur hexafluoride is generally considered sp3d2. The angles between adjacent S-F bond are all 90 °. S-F bond length is 1.55 Å. The dipole moment is 0, and therefore they are non-polar molecules.
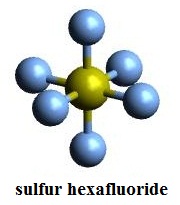
Figure 1 is a sulfur hexafluoride stick model. |
| Uses |
| Industry |
Application |
Role/benefit |
| Medicine |
Anesthesia |
Anesthetic/better anesthesia effect than nitric oxide |
| Retinal detachment repair operations |
Provide a tamponade or plug of a retinal hole in the form of a gas bubble |
| Ultrasound imaging |
Contrast agent/enhance the visibility of blood vessels to ultrasound |
| Semiconductor |
Plasma etching |
Etchant/breaking down product fluorine plasma can perform the etching |
| Metal casting |
Magnesium and aluminum casting |
Oxygen asphyxiant/inert and not corrosive and toxic |
| High-power microwave systems |
Pressurizes waveguides |
Insulates the waveguide, preventing internal arcing |
| Chemical weapon |
Production of disulfur decafluoride |
Feedstock |
| Magic show |
Object floating show |
Be colorless, tasteless and has greater density than air |
| Electrical equipment |
High-voltage circuit breakers and gas insulated switchgear |
Gaseous dielectric medium/has much higher dielectric strength than air or dry nitrogen |
| Others |
Tennis, insoles filling |
Gas filler/much lower capacity to pass through rubber membrane than air |
| Monitor the flow of the water and the diffusion of the air pollutants |
Tracer agent/ stably exists in water and air |
| Zanyism |
Performers breathe a little sulfur hexafluoride gas to make the voice become low and deep |
| Refrigerant |
Good chemical stability and no corrosion on the equipment |
|
| Impact on the environment |
Since the high intensity of infrared absorption, sulfur hexafluoride has been identified as a greenhouse gas, and it is the strongest greenhouse gases. 《Kyoto Protocol》indicate human must make great efforts to reduce the emissions of sulfur hexafluoride. Although sulfur hexafluoride in the atmosphere is very stable, when it once dissociate, it will generate S2F10, SF4 and HF and other fluorine-containing molecules, and these are corrosive and toxic substances, some of which are also greenhouse gases. |
| Acute intravenous toxicity |
Rabbit LD50: 5790 mg/kg |
| Storage characteristics |
Treasury ventilation low-temperature drying; Handle gently. |
| Chemical Properties |
Colorless gas; odorless. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and ether. Noncombustible. |
| Uses |
In electrical circuit interrupters. In electronic ultra-high frequency piping. |
| Brand name |
SonoVue (for the microbubble formulation) (Ausimont). |
| Reactivity Profile |
This substance undergoes chemical reactions only under relatively severe circumstances. They are resistant to ignition, although they may become flammable at very high temperatures. They may be resistant to oxidation reduction, except in the most severe conditions. These materials may be nontoxic. They can asphyxiate. Contact of very cold liquefied gas with water may result in vigorous or violent boiling of the product and extremely rapid vaporization due to the large temperature differences involved. If the water is hot, there is the possibility that a liquid "superheat" explosion may occur. Pressures may build to dangerous levels if liquid gas contacts water in a closed container [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980]. |
| Hazard |
Asphyxiant. |
| Health Hazard |
Vapors may cause dizziness or asphyxiation without warning. Vapors from liquefied gas are initially heavier than air and spread along ground. Contact with gas or liquefied gas may cause burns, severe injury and/or frostbite. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. |
| Fire Hazard |
Some may burn but none ignite readily. Containers may explode when heated. Ruptured cylinders may rocket. |






 China
China