Glycine derivative
Glycine derivatives,Scientific name:aminoacetic acid, the simplest and the only α-amino acid without any optical isomer. In 1820, chemist Braconnot treated with gelatin with hydrochloric acid and found a sweet substance. At first, he wrongly thought that is a saccharides. After analysis, he discovered that is a nitrogen-containing compound with a carboxyl group. The compound can be used to produce ammonia and given a name of glycine. Glycine often has four sides columnar. It is a colorless monoclinic crystal with a density of 1.1607 g / cm, melting point 232 ~ 236 ℃(decomposition), and soluble in water while insoluble in organic solvents such as ether. Glycine has a sweet flavor. It is a neutral amino acids, and its isoelectric point pH is 6. In aqueous solution, it will be oxidized to formaldehyde by ninhydrin. Glycine is soluble in acid or alkali, amphoteric, and can be precipitated by alcohol. Glycine synthesizes many important compounds in vivo. It can generate purine compounds with ammonia, formic acid and carbon dioxide and synthesize porphyrins with succinic acid. It plays the role of detoxification in the human body. For instance, when the aromatic substances get into the body, glycine combines them into non-toxic substances and then excreted them by the liver oxidation, such as react with benzoic acid (preservative) to generate hippuric acid to excrete from the body. Under the catalysis of hydroxymethylase, it can be transformed into serine. In recent years, glycine can act as an amino acid pesticide. For example, aerial spraying 85% glycine solution of 2.5 kg in every10000 square metres (15 acres) sugar cane can kill weeds. Glycine can also be used to produce some anti-cancer drugs. For instance, the series of anti-cancer drugs made by glycine and diazocompound have a significant effect on gastric cancer. Now glycine is in a large number of production.
Click on the specific product, view the latest prices of the products, information, serving information
| Structure |
Chemical Name |
CAS |
MF |
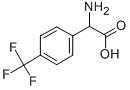 |
4-(Trifluoromethyl)-DL-phenylglycine |
142012-65-5 |
C9H8F3NO2 |
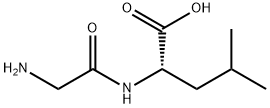 |
GLYCYL-DL-LEUCINE |
688-14-2 |
C8H16N2O3 |
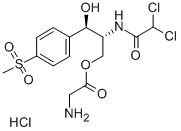 |
Thiamphenicol glycinate hydrochloride |
2611-61-2 |
C14H18Cl2N2O6S.ClH |
![(R)-(+)-alpha-[(3-Methoxy-1-methyl-3-oxo-1-propenyl)amino]-1,4-cyclohexadiene-1-acetic acid sodium salt](/CAS/GIF/26774-89-0.gif) |
(R)-(+)-alpha-[(3-Methoxy-1-methyl-3-oxo-1-propenyl)amino]-1,4-cyclohexadiene-1-acetic acid sodium salt |
26774-89-0 |
C13H18NNaO4 |
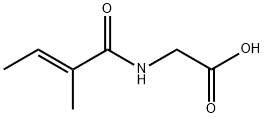 |
N-Tigloylglycine |
35842-45-6 |
C7H11NO3 |
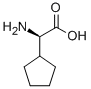 |
D-Cyclopentylglycine |
2521-86-0 |
C7H13NO2 |
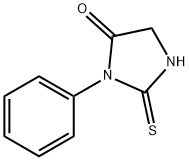 |
PTH-GLYCINE |
2010-15-3 |
C9H8N2OS |
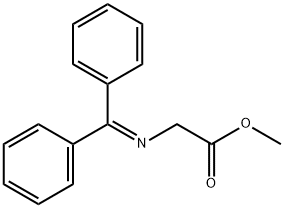 |
N-(DIPHENYLMETHYLENE)GLYCINE METHYL ESTER |
81167-39-7 |
C16H15NO2 |
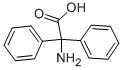 |
2,2-Diphenylglycine |
3060-50-2 |
C14H13NO2 |
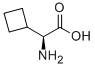 |
L-Cyclobutylglycine |
49607-08-1 |
C6H11NO2 |
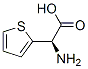 |
(R)-2-THIENYLGLYCINE |
65058-23-3 |
C6H7NO2S |
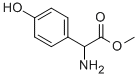 |
Methyl D-(-)-4-hydroxy-phenylglycinate |
37763-23-8 |
C9H11NO3 |
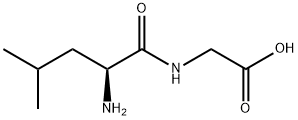 |
DL-LEUCYL-GLYCINE |
615-82-7 |
C8H16N2O3 |
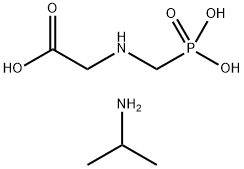 |
N-(Phosphonomethyl)glycine 2-propylamine (1:1) |
38641-94-0 |
C6H17N2O5P |
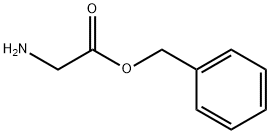 |
H-Gly-OBzl |
1738-68-7 |
C9H11NO2 |
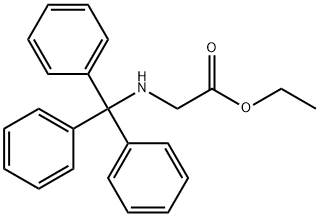 |
N-(TRIPHENYLMETHYL)GLYCINE ETHYL ESTER |
18514-46-0 |
C23H23NO2 |
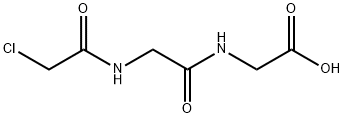 |
CHLOROACETYL-GLYCYL-GLYCINE |
15474-96-1 |
C6H9ClN2O4 |
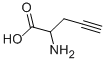 |
DL-PROPARGYLGLYCINE |
64165-64-6 |
C5H7NO2 |
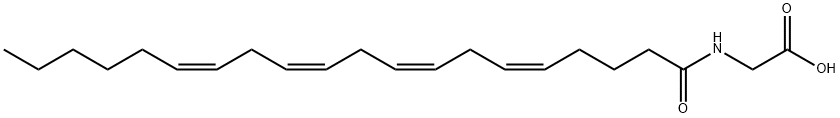 |
NAGLY |
179113-91-8 |
C22H35NO3 |
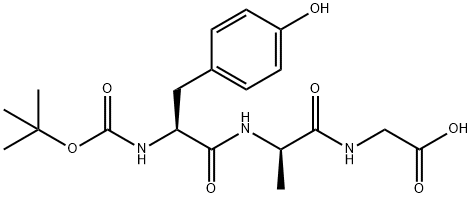 |
BOC-TYR-D-ALA-GLY-OH |
64410-47-5 |
C19H27N3O7 |
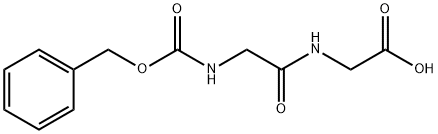 |
Cbz-Gly-Gly |
2566-19-0 |
C12H14N2O5 |
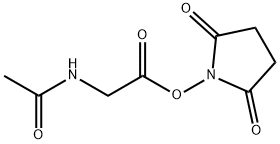 |
AC-GLY-OSU |
24715-24-0 |
C8H10N2O5 |
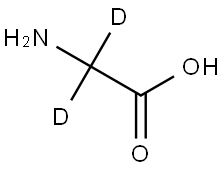 |
GLYCINE-2,2-D2 |
4896-75-7 |
C2H3D2NO2 |
![Glycine, N-acetyl-N-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]valyl-](/CAS/20200119/GIF/379685-96-8.gif) |
Glycine, N-acetyl-N-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]valyl- |
379685-96-8 |
C16H19F3N2O4 |
 |
L-P-HYDROXYPHENYLGLYCINE METHYL EST |
127369-30-6 |
C9H12ClNO3 |
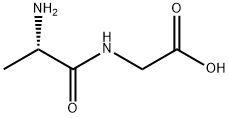 |
H-ALA-GLY-OH |
687-69-4 |
C5H10N2O3 |
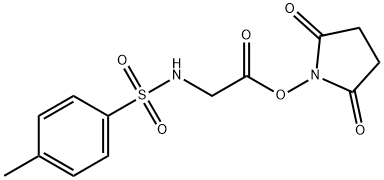 |
TOS-GLY-OSU |
68385-26-2 |
C13H14N2O6S |
![diaquatetrachloro[mu-[N-ethyl-N-[(tridecafluorohexyl)sulphonyl]glycinato-O1:O1']]-mu-hydroxybis(propan-2-ol)dichromium](/CAS/20211123/GIF/68891-98-5.gif) |
diaquatetrachloro[mu-[N-ethyl-N-[(tridecafluorohexyl)sulphonyl]glycinato-O1:O1']]-mu-hydroxybis(propan-2-ol)dichromium |
68891-98-5 |
C16H23Cl4Cr2F13NO9S |
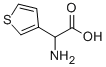 |
DL-ALPHA-(3-THIENYL)GLYCINE |
38150-49-1 |
C6H7NO2S |
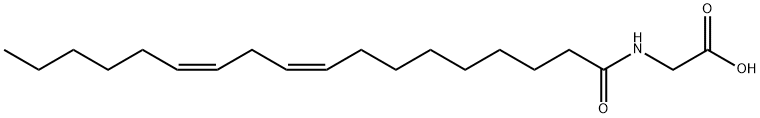 |
glycine linoleamide |
2764-03-6 |
C20H35NO3 |
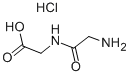 |
GLYCYLGLYCINE HYDROCHLORIDE |
13059-60-4 |
C4H9ClN2O3 |
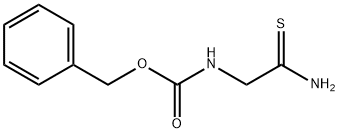 |
N-BENZYLOXYCARBONYLGLYCINE THIOAMIDE |
49548-40-5 |
C10H12N2O2S |
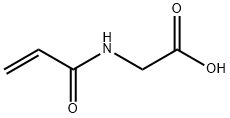 |
ACRYLAMIDO BUFFER |
24599-25-5 |
C5H7NO3 |
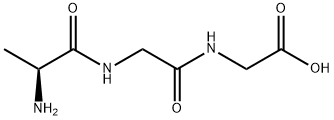 |
DL-ALANYL-GLYCYL-GLYCINE |
927-21-9 |
C7H13N3O4 |
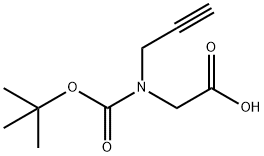 |
N-Boc-N-2-propyn-1-yl-glycine |
158979-29-4 |
C10H15NO4 |
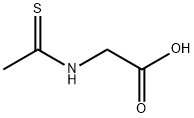 |
N-(1-Thioxoethyl)glycine |
412307-34-7 |
C4H7NO2S |
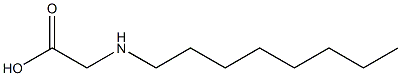 |
Glycine,N-octyl- |
52478-47-4 |
C10H21NO2 |
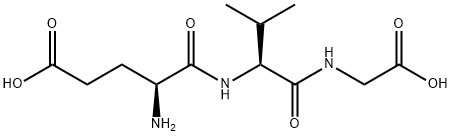 |
GLUTAMYL-VALYL-GLYCINE |
38837-70-6 |
C12H21N3O6 |
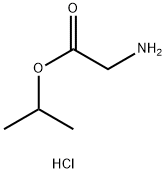 |
H-GLY-OIPR HCL |
14019-62-6 |
C5H12ClNO2 |
![ETHYL [2-(BOC-AMINO)ETHYLAMINO]ACETATE HYDROCHLORIDE](/CAS/GIF/72648-80-7.gif) |
ETHYL [2-(BOC-AMINO)ETHYLAMINO]ACETATE HYDROCHLORIDE |
72648-80-7 |
C11H22N2O4 |
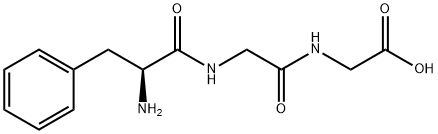 |
PHE-GLY-GLY |
23576-42-3 |
C13H17N3O4 |
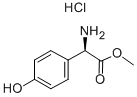 |
D-4-Hydroxyphenylglycine Methyl ester hydrochloride |
57591-61-4 |
C9H12ClNO3 |
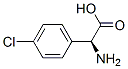 |
DL-2-(4-CHLOROPHENYL)GLYCINE |
7292-70-8 |
C8H8ClNO2 |
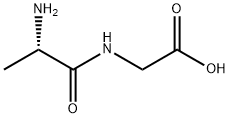 |
DL-ALANYL-GLYCINE |
1188-01-8 |
C5H10N2O3 |
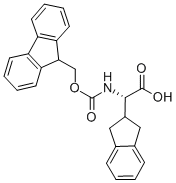 |
FMOC-(2-INDA)GLY-OH |
205526-39-2 |
C26H23NO4 |
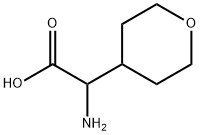 |
AMINO-(TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-YL)-ACETIC ACID |
53284-84-7 |
C7H13NO3 |
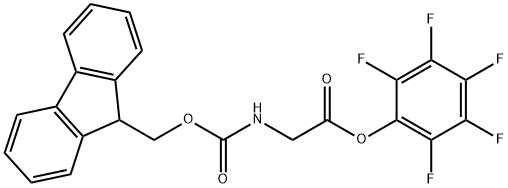 |
FMOC-GLY-OPFP |
86060-85-7 |
C23H14F5NO4 |
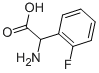 |
(2-FLUOROPHENYL)GLYCINE |
2343-27-3 |
C8H8FNO2 |
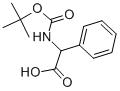 |
TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYLAMINO-PHENYL-ACETIC ACID |
3601-66-9 |
C13H17NO4 |
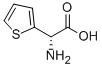 |
(R)-2-THIENYLGLYCINE |
43189-45-3 |
C6H7NO2S |
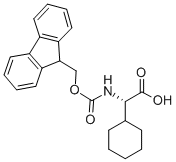 |
FMOC-CHG-OH |
161321-36-4 |
C23H25NO4 |
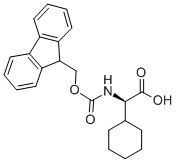 |
FMOC-D-CHG-OH |
198543-96-3 |
C23H25NO4 |
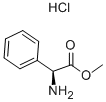 |
H-PHG-OME HCL |
13226-98-7 |
C9H12ClNO2 |
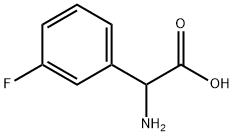 |
AMINO-(3-FLUORO-PHENYL)-ACETIC ACID |
7292-74-2 |
C8H8FNO2 |
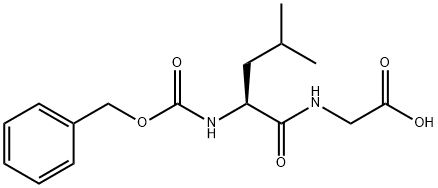 |
Z-LEU-GLY-OH |
2706-38-9 |
C16H22N2O5 |
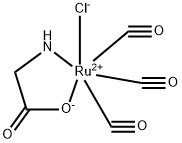 |
(OC-6-44)-Tricarbonylchloro(glycinato)ruthenium |
475473-26-8 |
C5H3ClNO5Ru |
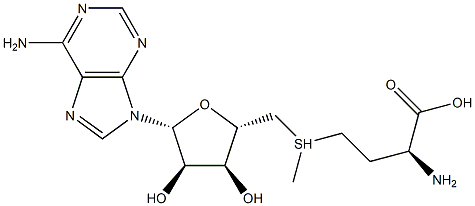 |
S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine Impurity 1 |
1334162-51-4 |
C15H24N6O5S |
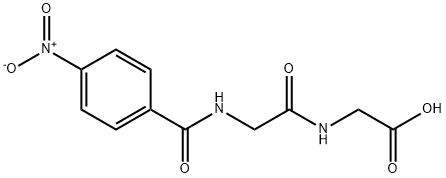 |
4-NITROBENZOYL-GLYCYL-GLYCINE |
78196-53-9 |
C11H11N3O6 |
![2-[4-CHLORO(PHENYLSULFONYL)ANILINO]ACETIC ACID](/CAS/GIF/117309-41-8.gif) |
2-[4-CHLORO(PHENYLSULFONYL)ANILINO]ACETIC ACID |
117309-41-8 |
C14H12ClNO4S |
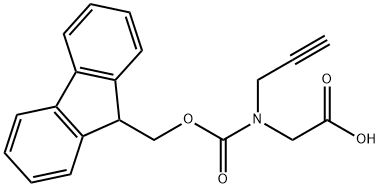 |
Fmoc-d-propargylglycine |
1033622-38-6 |
C20H17NO4 |
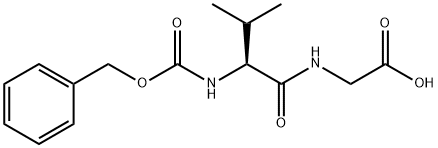 |
Z-VAL-GLY-OH |
2790-84-3 |
C15H20N2O5 |
![N-[1-Oxo-2-(phenylmethyl)-2-propenyl]glycine Ethyl Ester](/CAS/20200331/GIF/CB15323581.gif) |
N-[1-Oxo-2-(phenylmethyl)-2-propenyl]glycine Ethyl Ester |
660848-81-7 |
C14H17NO3 |
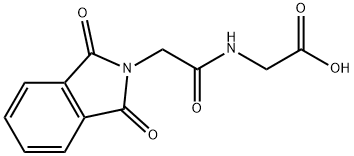 |
Phthaloylgly Cylglycine |
3916-40-3 |
C12H10N2O5 |
 |
ABG 3168|AVG|Aviglycine |
|
|
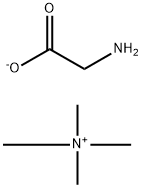 |
tetramethylammomium glycinate |
55378-67-1 |
C6H16N2O2 |
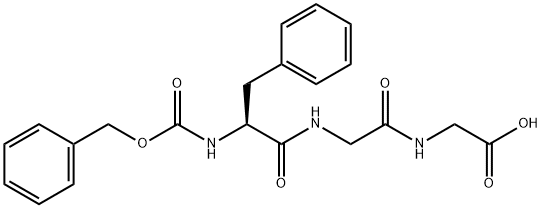 |
Z-PHE-GLY-GLY-OH |
37700-64-4 |
C21H23N3O6 |
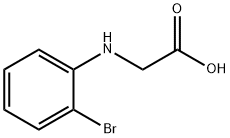 |
(2-BroMo-phenylaMino)-acetic acid |
40789-38-6 |
C8H8BrNO2 |
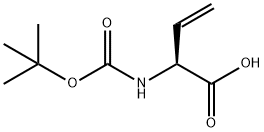 |
Boc-L-vinylglycine |
91028-39-6 |
C9H15NO4 |
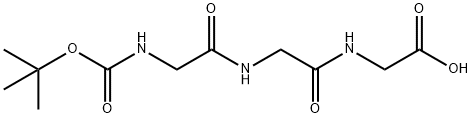 |
BOC-GLY-GLY-GLY-OH |
28320-73-2 |
C11H19N3O6 |
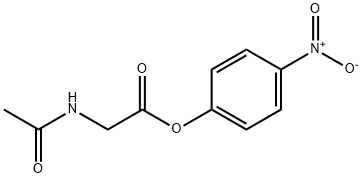 |
AC-GLY-ONP |
3304-61-8 |
C10H10N2O5 |
 |
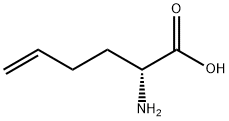
(R)-4-methoxyphenylglycine |
24593-49-5 |
C9H11NO3 |
 |
Fmoc-D-phenylglycine(4-OtBu) |
1270295-28-7 |
C27H27NO5 |
![N-[N′-FMoc-(2′-aMinoethyl)]glycine](/CAS/20180808/GIF/172405-45-7.gif) |
N-[N′-FMoc-(2′-aMinoethyl)]glycine |
172405-45-7 |
C19H20N2O4 |
 |
(R)- 2-(3'-butenyl) glycine |
103067-78-3 |
C6H11NO2 |
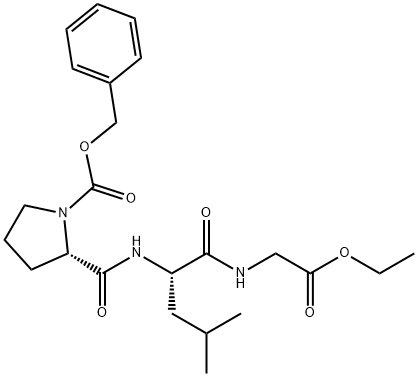 |
Z-PRO-LEU-GLY-OET |
7784-82-9 |
C23H33N3O6 |
 |
GLYCYLGLYCINE ETHYL ESTER HYDROCHLORIDE |
2087-41-4 |
C6H13ClN2O3 |
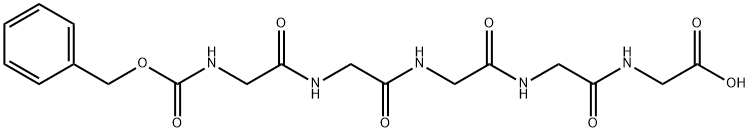 |
Z-GLY-GLY-GLY-GLY-GLY-OH |
20228-72-2 |
C18H23N5O8 |
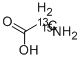 |
GLYCINE-2-13C-15N |
91795-59-4 |
C2H5NO2 |
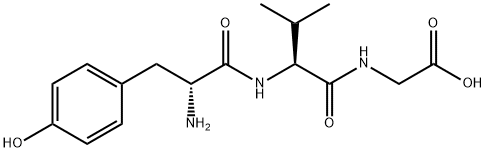 |
H-D-TYR-VAL-GLY-OH |
86030-52-6 |
C16H23N3O5 |
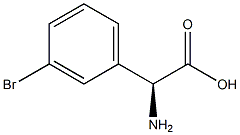 |
(2S)-2-AMINO-2-(3-BROMOPHENYL)ACETIC ACID |
2088419-03-6 |
C8H8BrNO2 |
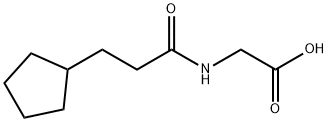 |
Glycine, N-(3-cyclopentyl-1-oxopropyl)- |
954272-16-3 |
C10H17NO3 |
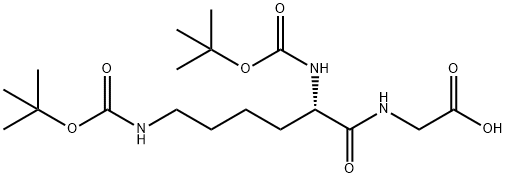 |
BOC-LYS(BOC)-GLY-OH |
120893-72-3 |
C18H33N3O7 |
![9-Thia-1,6-diazabicyclo[8.2.1]trideca-10(13),11-diene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-[[(carboxymethyl)amino]carbonyl]-5-oxo-, (2S,7R)-](/CAS/20210111/GIF/877614-95-4.gif) |
9-Thia-1,6-diazabicyclo[8.2.1]trideca-10(13),11-diene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-[[(carboxymethyl)amino]carbonyl]-5-oxo-, (2S,7R)- |
877614-95-4 |
C14H17N3O6S |
![trisodium [N,N-bis[2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl]glycinato(5-)]manganate(3-)](/CAS/20180808/GIF/11065-74-0.gif) |
trisodium [N,N-bis[2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl]glycinato(5-)]manganate(3-) |
11065-74-0 |
C14H18MnN3O10.3Na |
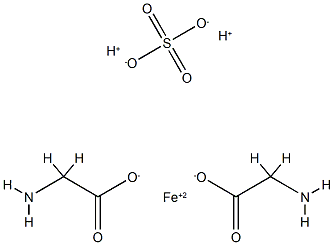 |
Ferrous Glycine Sulphate |
14729-84-1 |
C2H5NO2.1/2Fe.1/2H2O4S |
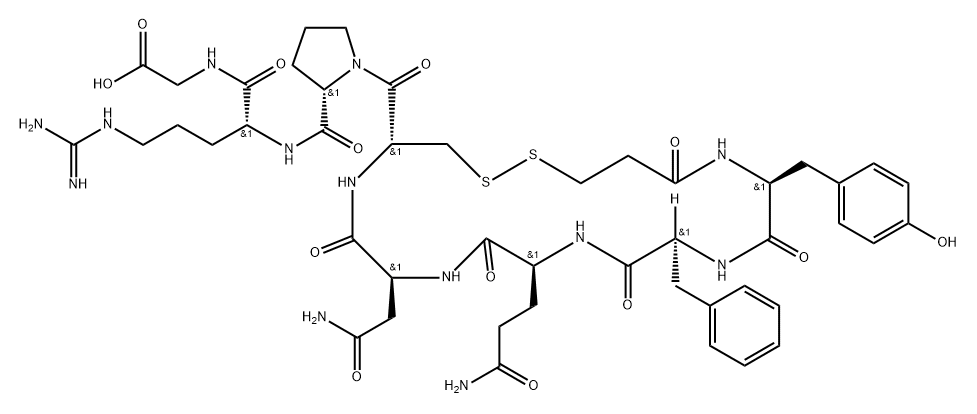 |
DesmopressinEPImpurityC |
160848-60-2 |
C46H63N13O13S2 |
 |
NA |
|
|
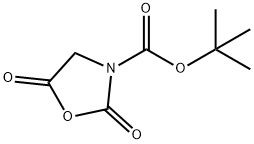 |
BOC-GLY-NCA |
142955-50-8 |
C8H11NO5 |
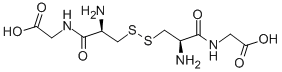 |
(H-CYS-GLY-OH)2 |
7729-20-6 |
C10H18N4O6S2 |
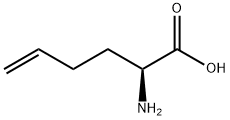 |
(2S)-2-AMINO-5-HEXENOIC ACID |
90989-12-1 |
C6H11NO2 |
![HEXAHYDROPYRROLO[1,2-A]PYRAZINE-1,4-DIONE](/CAS/GIF/19179-12-5.gif) |
HEXAHYDROPYRROLO[1,2-A]PYRAZINE-1,4-DIONE |
19179-12-5 |
C7H10N2O2 |
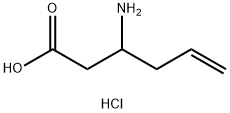 |
3-aminohex-5-enoic acid hydrochloride |
1335042-10-8 |
C6H12ClNO2 |
 |
N-DODECYL-N,N-DIMETHYLGLYCINE |
66455-29-6 |
C16H33NO2 |
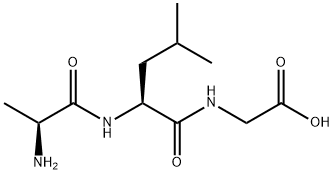 |
DL-ALA-DL-LEU-GLY |
82267-71-8 |
C11H21N3O4 |
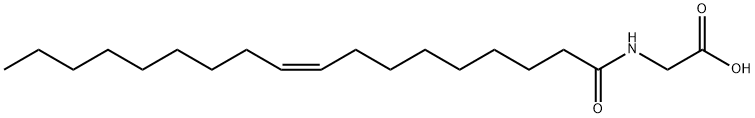 |
N-OLEOYLGLYCINE |
2601-90-3 |
C20H37NO3 |
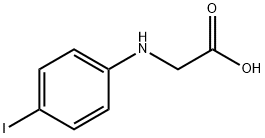 |
DL-4-Iodophenylglycine |
13370-63-3 |
C8H8INO2 |
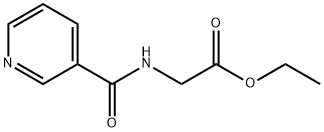 |
(PYRIDINE-3-CARBONYL)-AMINO-ACETIC ACID ETHYL ESTER |
54466-74-9 |
C10H12N2O3 |
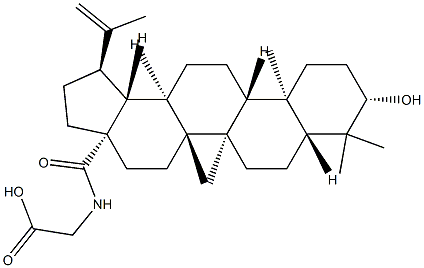 |
Betulinic acid gly deriv. |
174740-40-0 |
C32H51NO4 |
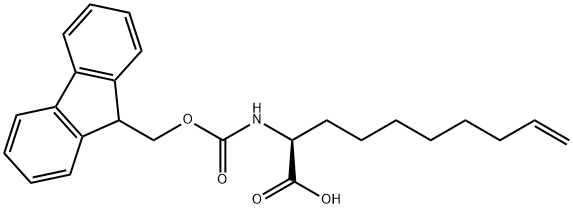 |
(S)-N-Fmoc-2-(7'-octenyl)glycine |
1262886-64-5 |
C25H29NO4 |
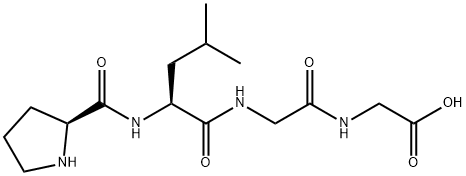 |
H-PRO-LEU-GLY-GLY-OH |
75188-89-5 |
C15H26N4O5 |