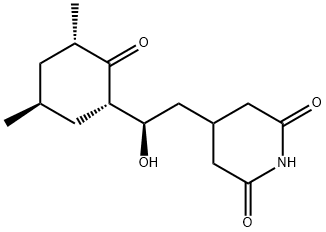
??????? C??? ??, ??, ??
??
Cycloheximide is a glutarimide-type antibiotic produced by Streptomyces
griseus. Colorless crystals, C15H23NO4 (281.4), melting
point: 115.5–117 ?C, weak acidic substance (pKa 11.2),
Soluble in chloroform, isopropanol and methanol; water >
21 g/L (2 ?C). Stable in pH 3–5, but rapidly destroyed in
alkaline solutions.
??? ??
Off-white to light tan powder
??
Cycloheximide is an antibiotic substance isolated from the beers of streptomycin-producing strains of Streptomyces griseus. Cycloheximide is used as fungicide.
?? ??
Colorless crystals. Used as a fungicide and as a anticancer drug.
??? ?? ??
Water soluble.
?? ???
Actidione is an imide. Actidione is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, acid chlorides and acid anhydrides. Actidione decomposes rapidly in alkali at room temperature.
????
Actidione is extremely toxic; the probable oral lethal dose in humans is 5-50 mg/kg, or 7 drops to 1 teaspoonful for a 150-lb. person.
????
When exposed to heat, Actidione emits toxic fumes, including nitrogen oxides.
???
Fungicide; plant growth regulator: A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). Used
as an antibiotic, plant growth regulator, and protein synthesis inhibitor. Inhibits growth of many plant pathogenic
fungi. Effective for control of powdery mildew on roses
and many other ornamentals, rusts and leaf spots on lawn
grasses, and azalea petal blight. Also used as a repellent for
rodents and other animal pests and in cancer therapy. Not
listed for use in EU countries
???
ACTI-AID®[C]; ACTIDIONE®[C];
ACTIDIONE® TGF[C]; ACTIDONE®; ACTIDONE®
PM; ACTIDONE® TGF; ACTISPRAY; HIZAROCIN®;
KAKEN®; NARAMYCIN®; NARAMYCIN A®;
NEOCYCLOHEXIMIDE®; U-4527
???? ??
Selective inhibitor of eukaryotic (over prokaryotic) protein synthesis, blocking tRNA binding and release from ribosomes. Induces apoptosis in a variety of transformed and normal cell lines, including T-cells. Competitively inhibits the PPIase hFKBP12 (K i = 3.4 μ M). Antifungal antibiotic.
Pharmacology
Strongly inhibits the growth of pathogenic fungi but no
effects on bacterial growth, even at 100 mg/ml. Inhibits
protein synthesis by interfering with the translocation
step in eukaryotes, but not in prokaryotes. When
ingested by animals, the agent causes excitement, tremors,
salivation, diarrhea, and melena.
??? ??
A potential danger to those involved
in the manufacture, formulation, or application of this fun-
gicide and pesticide. Used as an antibiotic, plant growth
regulator, and protein synthesis inhibitor. Used on oranges
for processing and to inhibit growth of many pathogenic
plant fungi. Also used as a repellent for rodents and other
animal pests; and in cancer therapy.
Carcinogenicity
Cycloheximide is genotoxic in Escherichia
coli with metabolic activation and in the mouse
sperm morphology assay. Carcinogenicity
bioassays in the mouse and rat are inconclusive.
????
CHX is a potent inhibitor of protein synthesis in animals. It
binds to E-site of 70S ribosome-mRNA complex, blocking the
translational step of protein biosynthesis. It causes an increase
in adrenal RNA and increased production of glucocorticoids.
?? ??
Rapidly inactivated at room temperature by diluted alkali
with the formation of a volatile, fragrant ketone, 2,4-
dimethylcyclohexanone. Hazardous to fish and wildlife.
Purification Methods
It crystallises from H2O /MeOH (4:1), amyl acetate, isopropyl acetate/isopropyl ether or H2O. [Beilstein 21/13 V 434.]
? ???
Incompatible with oxidizers, acid anhy-
drides; strong bases.
??? ??
High-temperature incinerator
with flue gas scrubbing equipment.
??????? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??