?? ???
|
|
?? ??? ??
- ???
- 1000 °C
- ??
- 8.35 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
- ???
- 1.964
- ?? ??
- under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2-8°C
- ???
- soluble in concentrated acid solutions
- ??? ??
- ??
- ??
- ???
- Specific Gravity
- 3.864
- ???
- ???
- Crystal Structure
- Sc2O3 type
- crystal system
- Cube
- Merck
- 14,8392
- Space group
- Ia3
- Lattice constant
a/nm b/nm c/nm α/o β/o γ/o V/nm3 0.98459 0.98459 0.98459 90 90 90 0.9545
- InChI
- InChI=1S/3O.2Sc
- InChIKey
- HYXGAEYDKFCVMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
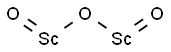
- SMILES
- O([Sc]=O)[Sc]=O
- CAS ??????
- 12060-08-1(CAS DataBase Reference)
??
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ????? | 24/25 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| WGK ?? | 3 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| HS ?? | 28469099 | ||
| ???? ?? | KE-30885 |
?? ??? C??? ??, ??, ??
??? ??
fine white powder(s) or sintered pieces of 3–12mm; used as an evaporation material of 99.99% purity to produce fairly hard coating which is very stable, and is useful for antireflection coating on semiconductors with high index [MER06] [CER91]High-purity scandium oxide (i.e., 99.0 to 99.99 wt.% Sc) is an initial raw material used to produce a metallic scandium.
The growth of scandium oxide produces a smooth surface as evident by the AFM RMS roughness of 0.5 to 0.8 nm.The growth rate of the scandium oxide was 0.67nm/min for Tsc=1130℃ and 1.25nm/min for Tsc=1170℃.
??
Scandium oxide (Sc2O3): 2Sc3+ + 3O2- → Sc2O3. Scandium oxide is used to prepare scandium fluoride (ScF3), which is also used as an electrolyte to produce scandium metal.?? ??
Scandium Oxide, SC2O3: It is obtained readily by heating the salts such as scandium carbonate and scandium nitrate.Sc2(CO3)3-Heat->Sc2O3+3CO2
4Sc(NO3)3-->2Sc2O3+12NO2+3O2
Scandium oxide is a white powder. It is more basic than aluminium oxide but less basic than calcium oxide. It absorbs carbon dioxide from the air.
It has the MnO3 structure.The crystal structure of scandium oxide is Bixbyite , which is an FCC array of scandium atoms with oxygen occupying 44 of the tetrahedral sites.
??
Scandium oxide has an extremely high melting point and is therefore likely to be an ionic compound, meaning its particles are joined by ionic bonds.?? ??? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??
?? ??? ?? ??
???( 308)?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHENGDU BEYOND CHEMICAL CO.,LTD. | +86-2886084545 +86-18608044545 |
info@beyondchem.com | China | 54 | 58 |
| Zhuoer Chemical Co., Ltd | 02120970332; +8613524231522 |
sales@zhuoerchem.com | China | 2904 | 58 |
| LEAPCHEM CO., LTD. | +86-852-30606658 |
market18@leapchem.com | China | 43340 | 58 |
| Shanghai MaiNo material technology Co.Ltd | +86-13862580743 +86-13862580743 |
shirleyzhang04@hotmail.com | China | 71 | 58 |
| SHANGHAI KEAN TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. | +8613817748580 |
cooperation@kean-chem.com | China | 40066 | 58 |
| Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12827 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 |
sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5879 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531151365 |
mina@chuanghaibio.com | China | 18143 | 58 |
| Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd | +8613343047651 |
admin@zlchemi.com | China | 3692 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21632 | 55 |