??????
|
|
?????? ??
- ???
- 65-70 °C
- ?? ?
- 460.1±40.0 °C(Predicted)
- ??
- 1.2486 (rough estimate)
- ???
- 1.6070 (estimate)
- ?? ??
- 2-8°C
- ???
- ??? ?? ?? ???, ???? ???(96%)?? ? ????.
- ?? ?? (pKa)
- pKa ~1.3(H2O) (Uncertain)
- ??? ??
- Solid
- ??
- ???? ?? ???
- ???
- 22&C?? <0.01g/100mL
- ?? ??(λmax)
- 588nm(DMSO aq.)(lit.)
- Merck
- 14,2073
- BRN
- 999011
- BCS Class
- 3/1
- ???
- ?????? ?? ??? ? ????. ??? ?????. ?? ???? ???? ????.
- InChIKey
- JCKYGMPEJWAADB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- CAS ??????
- 305-03-3(CAS DataBase Reference)
- IARC
- 1 (Vol. 26, Sup 7, 100A) 2012
??
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ??? ?? | T | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ???? ?? | 45-25-36/37/38 | ||
| ????? | 53-26-45 | ||
| ????(UN No.) | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 | ||
| WGK ?? | 3 | ||
| RTECS ?? | ES7525000 | ||
| ?? ?? | 6.1(b) | ||
| ???? | III | ||
| HS ?? | 29224999 | ||
| ?? ?? ??? | 305-03-3(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| ?? | LD50 i.p. in rats: 58.2 mmole/kg (Ross) |
?????? C??? ??, ??, ??
??
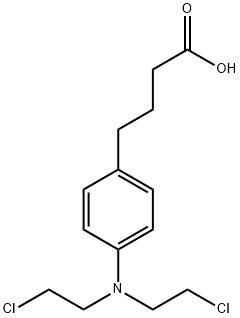
Chlorambucil, approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1957, is an antineoplastic/alkylating agent with a broad spectrum of antitumor activity used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas.??? ??
Chlorambucil is a crystalline solid??
Chlorambucil is a alkylating agent that is used as an chemotherapy drug in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Chlorambucil is also used to treat non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) and Hodgkin's disease.??
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid that is butanoic acid substituted at position 4 by a 4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenyl group. A chemotherapy drug that can be used in combination with the antibody obinutuzumab for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Indications
Chlorambucil (Leukeran) is an aromatic nitrogen mustard that is intermediate in chemical reactivity between mechlorethamine and melphalan. Its mechanisms of action and range of antitumor activity are similar to theirs. It is well absorbed orally, but detailed information concerning its metabolic fate in humans is lacking.Chlorambucil is used primarily as daily palliative therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Waldenstr?om’s macroglobulinemia, myeloma, and other lymphomas.
Bone marrow toxicity is the major side effect of chlorambucil. Nausea is uncommon or mild, and hair loss does not occur. Chlorambucil shares the immunosuppressive, teratogenic, and carcinogenic properties of the nitrogen mustards.
?? ??
Chlorambucil is available as 2-mg tablets for oral administrationin the treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma, andchronic lymphocytic leukemia in combination with prednisoneand as a single agent. The mechanisms of resistanceare the same as those seen for other agents of the class suchas mechlorethamine. The agent is well absorbed (75%) uponoral administration and highly protein bound. Metabolism ismediated by CYP and occurs extensively to give severalmetabolites, including the active phenylacetic acid–nitrogenmustard. The drug is eliminated via the kidneys with a terminalelimination half-life of 1.5 hours. Adverse effects includedose-limiting myelosuppression, which are seen asboth leucopenia and thrombocytopenia. Nausea and vomitingoccur less often than for mechlorethamine. Additionaladverse effects include hyperuricemia, azoospermia, amenorrhea,seizures, pulmonary fibrosis, and skin rash.??? ?? ??
Insoluble in water.?? ???
Chloroambucil is an alkylating agent. Reacts with proteins and a variety of nucleophilic compounds .????
Literature sources indicate that Chloroambucil is nonflammable.Clinical Use
It is used in the palliative treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, malignant lymphoma, and Hodgkin's disease.Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen producing leukemia. Experimental carcinogenic and neoplastigenic data. Poison by ingestion, intravenous, intraperitoneal, and subcutaneous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: convulsions, cough, dyspnea, and interstitial fibrosis. Human reproductive effects by ingestion and possibly other routes: changes in spermatogenesis, menstrual cycle changes or disorders, and teratogenic effects of the fetal urogenital system. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. An anti-neoplastic agent. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Cland NOx.??? ??
Chlorambucil, an anticancer drug, is a derivative of nitrogen mustard. This drug is primarily used as an antineoplastic agent for treating lymphocytic leukemia; malignant lymphomas; follicular lymphoma; and Hodgkin’s disease. The treatments are not curative but do produce some marked remissions. Chlorambucil has also been tested for treatment of chronic hepatitis, rheumatoid arthritis; and as an insect chemosterilant. All of the chemical used in this country is imported from the United Kingdom. Work exposure in the United States would be limited to workers formulating the tablets, or to those patients receiving the drug.Carcinogenicity
Chlorambucil is known to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in humans.????
The mechanism of action of chlorambucil is thought to be an alkylating agent and an aromatic nitrogen mustard derivative; it interferes with DNA replication and RNA transcription by alkylation and cross-linking the strands of DNA.?? ??
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.Purification Methods
Chlorambucil is recrystallised from pet ether (flat needles) and has a solubility at 20o of 66% in EtOH, 40% in CHCl3, 50% in Me2CO but is insoluble in H2O [Everett et al. J Chem Soc 2386 1953]. [Beilstein 14 IV 1715.] CARCINOGEN.? ???
Moisture. Chlorambucil is an alkylating agent. Reacts with proteins and a variety of nucleophilic compounds. Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water, and a salt that may beharmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, sulfides (releasing heat, toxic, and possibly flammable gases), thiosulfates, and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur).??? ??
It is inappropriate and possibly dangerous to the environment to dispose of expired or waste drugs and pharmaceuticals by flushing them down the toilet or discarding them to the trash. Household quantities of expired or waste pharmaceuticals may be mixed with wet cat litter or coffee grounds, double-bagged in plastic, discard in trash. Larger quantities shall carefully take into consideration applicable DEA, EPA, and FDA regulations. If possible return the pharmaceutical to the manufacturer for proper disposal being careful to properlylabel and securely package the material. Alternatively, the waste pharmaceutical shall be labeled, securely packaged, and transported by a state licensed medical waste contractor to dispose by burial in a licensed hazardous or toxic waste landfill or incinerator. Permanganate oxidation, high temperature incineration with scrubbing equipment, or microwave plasma treatment.?????? ?? ?? ? ???
???
4-Phenylbutyric acid
????????????
Hydrogen chloride methanol solution
???????
??
Phosphorus oxychloride
?? ??
?????? ?? ??
???( 258)?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capot Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-(0)57185586718 +86-13336195806 |
sales@capot.com | China | 29685 | 60 |
| Shanghai Daken Advanced Materials Co.,Ltd | +86-371-66670886 |
info@dakenam.com | China | 19885 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21632 | 55 |
| Hangzhou FandaChem Co.,Ltd. | 008657128800458; +8615858145714 |
FandaChem@Gmail.com | China | 7433 | 55 |
| ATK CHEMICAL COMPANY LIMITED | +undefined-21-51877795 |
ivan@atkchemical.com | China | 32965 | 60 |
| Biochempartner | 0086-13720134139 |
candy@biochempartner.com | CHINA | 965 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22963 | 58 |
| Shanghai Longyu Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | +8619521488211 |
info@longyupharma.com | China | 2558 | 58 |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 |
sales@conier.com | China | 49732 | 58 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 |
factory@coreychem.com | China | 29809 | 58 |