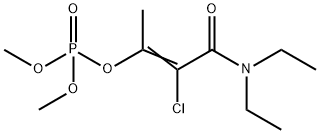
Phosphamidon
|
|
Phosphamidon Eigenschaften
- Schmelzpunkt:
- 120-123℃
- Siedepunkt:
- bp1.5 162°; bp0.001 120°
- Dichte
- 1.2132 g/cm3 (20 ºC)
- Dampfdruck
- 2.2×10-3 Pa (25 °C)
- Brechungsindex
- 1.4718 (589.3 nm 25℃)
- storage temp.
- 2-8°C
- Wasserl?slichkeit
- Totally miscible
- pka
- -1.61±0.70(Predicted)
- Aggregatzustand
- liquid
- Merck
- 13,7423
- BRN
- 8323501
- EPA chemische Informationen
- Phosphamidon (13171-21-6)
Sicherheit
- Risiko- und Sicherheitserkl?rung
- Gefahreninformationscode (GHS)
| Kennzeichnung gef?hrlicher | T+,N | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| R-S?tze: | 24-28-50/53-68 | ||
| S-S?tze: | 23-36/37-45-60-61 | ||
| RIDADR | 3018 | ||
| WGK Germany | 3 | ||
| RTECS-Nr. | TC2800000 | ||
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) | ||
| PackingGroup | II | ||
| HS Code | 29241200 | ||
| Giftige Stoffe Daten | 13171-21-6(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| Toxizit?t | LD50 orally in rats: 24 mg/kg (Gaines) |
| Bildanzeige (GHS) |
  
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alarmwort | Achtung | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Gefahrenhinweise |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheit |
|
Phosphamidon Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
FARBLOSE BIS GELBE, ?LIGE FLüSSIGKEIT.CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Zersetzung beim Erhitzen oder Verbrennen unter Bildung hochgiftiger Rauche mit Phosphoroxiden, Chlorwasserstoff und Stickstoffoxiden. Reagiert mit Basen (Hydrolyse). Greift Metalle wie Eisen, Zinn und Aluminium an.ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV: BEI vorhanden; (ACGIH 2005).MAK nicht festgelegt (DFG 2005).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation des Aerosols, über die Haut und durch Verschlucken.INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Verdampfung bei 20°C vernachl?ssigbar; eine gesundheitssch?dliche Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann jedoch beim Versprühen schnell erreicht werden.WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION:Die Substanz reizt die Augen. M?glich sind Auswirkungen auf das Nervensystem mit nachfolgenden Kr?mpfen, Atemdepression und Tod. Exposition gegenüber hohen Konzentrationen kann zum Tod führen. Cholinesterasehemmer. Die Auswirkungen treten u.U. verz?gert ein. ?rztliche Beobachtung notwendig.
WIRKUNGEN NACH WIEDERHOLTER ODER LANGZEITEXPOSITION
Cholinesterasehemmer. Kumulative Wirkung m?glich (s. AKUTE GEFAHREN/SYMPTOME).LECKAGE
Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Chemikalienschutzanzug mit umgebungsluftunabh?ngigem Atemschutzger?t. NICHT in die Umwelt gelangen lassen. Ausgelaufene Flüssigkeit m?glichst in abdichtbaren, nichtmetallischen Beh?ltern sammeln. Reste mit Sand oder inertem Absorptionsmittel aufnehmen und an einen sicheren Ort bringen.R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R24:Giftig bei Berührung mit der Haut.R28:Sehr giftig beim Verschlucken.
R50/53:Sehr giftig für Wasserorganismen, kann in Gew?ssern l?ngerfristig sch?dliche Wirkungen haben.
R68:Irreversibler Schaden m?glich.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S23:Gas/Rauch/Dampf/Aerosol nicht einatmen(geeignete Bezeichnung(en) vom Hersteller anzugeben).S36/37:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzkleidung tragen.
S45:Bei Unfall oder Unwohlsein sofort Arzt zuziehen (wenn m?glich, dieses Etikett vorzeigen).
S60:Dieses Produkt und sein Beh?lter sind als gef?hrlicher Abfall zu entsorgen.
S61:Freisetzung in die Umwelt vermeiden. Besondere Anweisungen einholen/Sicherheitsdatenblatt zu Rate ziehen.
Beschreibung
Types of phosphamidon formulations include soluble liquid, suspension concentrate and emulsifiable concentrate, ULV liquid, and 10% granules Phosphamidon is a pale yellow to colourless oily liquid with a faint odour. It is miscible with water and is soluble in aromatic hydrocarbons. Technical phosphamidon is a pale yellow to colourless oily liquid with a faint odour. It consists of a mixture of (Z)-isomer and (E)-isomer in the approximate proportion of 70:30. It decomposes on heating and releases highly toxic fumes such as phosphorus oxides, hydrogen chloride, and nitrogen oxides. Phosphamidon reacts and gets rapidly hydrolysed by alkalis and decomposes on heating or on burning, producing highly toxic fumes. It attacks metals such as iron, tin, and aluminium. It is used as a broad-spectrum insecticide and acaricide for the control of pests and vectors on crops like sugarcane, rice, citrus orchards, and cotton.Chemische Eigenschaften
Phosphamidon is a pale yellow to colorless oily liquid with a faint odor. It is miscible with water and is soluble in aromatic hydrocarbons. Phosphamidon decomposes on heating and releases highly toxic fumes, such as phosphorus oxides, hydrogen chloride, and nitrogen oxides. It reacts with bases (hydrolysis) and attacks metals such as iron, tin, and aluminium. Phosphamidon should be handled by trained personnel wearing protective clothing. Phosphamidon is used as a broad-spectrum insecticide and acaricide for the control of pests and vectors on crops like sugar cane, rice, citrus orchards, and cotton. Occupational exposures to phosphamidon occur among factory workers involved in synthesizing formulation and dispensing spray operations. Human exposures also occur among crop harvesters and in vector control operations.Verwenden
Phosphamidon is used to control sucking and boring insects and mites in a very wide range of crops and in forestry applications.Allgemeine Beschreibung
Pale yellow oily liquid with a faint odor. Used as an insecticide for citrus, cotton, and deciduous fruit and nuts. and as an acaricide.Air & Water Reaktionen
Water soluble. Hydrolyzed by alkali with a half-life at 73°F of 13.8 days at pH 7 and 2.2 days at pH 10 .Reaktivit?t anzeigen
PHOSPHAMIDON is corrosive to iron, tin and aluminum. Incompatible with alkaline preparations and should not be mixed with copper oxychloride, captan, folpet or sulfur.Health Hazard
PHOSPHAMIDON is extremely toxic; the probable oral lethal dose for humans is 5-50 mg/kg, or between 7 drops and 1 teaspoonful for a 150-lb person. It is a cholinesterase inhibitor.Brandgefahr
(Non-Specific -- Organophosphorus Pesticide, Liquid, n.o.s.) Container may explode in heat of fire. Heat above 320F may cause decomposition and evolution of highly toxic fumes of phosphorus oxides and chlorides. Hydrolyzes in alkali. Stable in neutral and acid media. Hydrolyzes in alkali.m?gliche Exposition
This material is used as an insecticide on citrus, cotton, and deciduous fruit and nuts. It is also an acaricide.Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. Emits toxic fumes of chlorine, phosphorus and nitrogen oxides when heated to decomposition (Sax and Lewis, 1987)Stoffwechselwegen
The metabolism of phosphamidon has been reviewed by Geissbuhler et al. (1971) and Beynon et al. (1973). Technical phosphamidon consists of two stereochemical isomers in the E:Z ratio of ca. 3:7. The Z-isomer has the greater insecticidal activity. It is important to note that in the case of phosphamidon the isomer with the phosphate ester function trans to the amide group is assigned the Z configuration due to the priority of chlorine, whereas in the case of mevinphos, monocrotophos and dicrotophos it is assigned the E configuration. In all four compounds, the isomers with this configuration (also referred to as the cis-crotonamide or crotonate structure) have the greater insecticidal activities. It is a systemic insecticide which is rapidly translocated in the plant via the xylem. Phosphamidon is rapidly degraded in the environment, the major routes being via N-de-ethylation and cleavage of the P-O-vinyl function. The resultant N,N-diethyl-2-chloroacetoacetamide or N-ethyl-2-chloroacetoacetamide are then degraded via dechlorination and hydrolysis, ultimately to give acetone, diethylamine and ethylamine. Conjugated metabolites have not been identified.Stoffwechsel
The major routes of degradation are oxidative dealkylation of the amide group and hydrolysis of the vinyl phosphate ester bond. Dechlorination also occurs. In soils, DT50 is 7–25 d depending upon the soil type.Versand/Shipping
UN3018 Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.Inkompatibilit?ten
Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides (releasing heat, toxic and possibly flammable gases), thiosulfates and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur). Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Strong oxidizers may cause release of toxic phosphorus oxides. Organophosphates, in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides, may form highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas. Keep away from alkaline materials. Attacks metals, such as aluminum, iron, tin.Waste disposal
Small quantities may be treated with alkali followed by landfill disposal. Large quantities should be incinerated with effluent gas scrubbing. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.Phosphamidon Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
4-Methylen-2-oxetanon
Petroleum crude oil
Acetoacetamid
Diethylamin, in w?ssriger L?sung
Trimethylphosphit
Downstream Produkte
13171-21-6(Phosphamidon)Verwandte Suche:
Dimethylphosphinsure
Dimethylhydrogenphosphat
Schradan (ISO)
Triamiphos (ISO)
Hexamethylphosphorsaeuretriamid
Monocrotophos (ISO)
Trofosfamid
Propetamphos
2-Chlor-N,N-diethylacetamid
2-Chlor-N,N-dimethylacetamid
Phosphamidon
Triethylammoniumdihydrogenphosphat
Diethylaminphosphat
- 2-chloro-n,n-diethyl-3-hydroxycrotonamidedimethylphosphate
- Aphidamon
- 2-CHLORO-2-DIETHYLCARBAMOYL-1-METHYLVINYL DIMETHYL PHOSPHATE
- 2-CHLORODIETHYL-CARBAMOYL METHYL VINYL DIMETHYL PHOSPHATE
- 2-CHLORO-N,N-DIETHYL-3-(DIMETHYLPHOSPHONO)CROTONIC AMIDE
- AIMPHON
- ALFAMIDON
- PHOSRON
- PHOSPHAMIDON
- Phosphamidon emulsion(content0.5%-30%)
- RIMDON
- RILAN
- (2-chlor-3-diaethylamino-1-methyl-3-oxo-prop-1-en-yl)-dimethyl-phosphat[german
- (2-Cloro-3-dietilamino-1-metil-3-oxo-prop-1-en-il)-dimetil-fosfato
- (2-cloro-3-dietilamino-1-metil-3-oxo-prop-1-en-il)-dimetil-fosfato[italian]
- (O,O-Dimethyl-O-(1-methyl-2-chloro-2-diethylcarbamoyl-vinyl) phosphate)
- (o,o-dimethyl-o-(1-methyl-2-chloro-2-diethylcarbamoyl-vinyl)phosphate
- (o,o-dimethyl-o-(1-methyl-2-chloro-2-diethylcarbamoyl-vinyl)phosphate)
- 1-Chloro-diethylcarbamoyl-1-propen-2-yl dimethyl phosphate
- 1-chloro-diethylcarbamoyl-1-propen-2-yldimethylphosphate
- 2-chloro-2-diethylcarbamyl-1-methylvinyl-dimethylphosphate
- 2-chloro-2-dimethylcarbamoyl-1-methylvinyldimethylphosphate
- Apamidon
- C 570
- c570
- Crotonamide, 2-chloro-N,N-diethyl-3-hydroxy-, dimethyl phosphate
- Dimecron 100
- Dimecron 50
- dimecron100
- Dimecron-20
- fosfamidon[dutch]
- Fosfamidone
- fosfamidone[italian]
- Foszfamidon
- foszfamidon[hungarian]
- Merkon
- ML 97
- ml97
- n,n-diethyl2-chloro-3-dimethylphosphatecrotonamide
- nch]
- NCI-C00588
- O,O-Dimethyl O-(2-chloro-2-(N,N-diethylcarbamoyl)-1-methylvinyl) phosphate
- O,O-Dimethyl-O-(1-methyl-2-chlor-2-N,N-diaethyl-carbamoyl)-vinyl-phosphat
- Phosphoric acid, 2-chloro-3-(diethylamino)-1-methyl-3-oxo-1-propenyl dimethyl ester
- Phosphoric acid, dimethyl ester, ester with 2-chloro-N,N-diethyl-3-hydroxycrotonamide
- phosphoricacid,2-chloro-3-(diethylamino)-1-methyl-3-oxo-1-propenyldimethyle
- phosphoricacid,dimethylester,esterwith2-chloro-n,n-diethyl-3-hydroxycroto
- Sundaram 1975
- sundaram1975
- CIBA 570
- Dixon emulsion
- DIMECRON
- Dimecron emulsion
- DIMECRON(R)
- KINADON
- Dimetcron
- Dimethyl 2-chloro-2-diethylcarbamoyl-1-methylvinyl phosphate
- Dimethyl diethylamido-1-chlorocrotonyl (2) phosphate