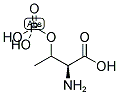
PHOSPHOTHREONINE Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
Verwenden
Mouse monoclonal clone PTR-8 anti-Phosphothreonine antibody reacts with phosphorylated threonine both as a free amino acid or when conjugated to carriers such as BSA or KLH, using ELISA and dot blot. It does not react with nonphosphorylated threonine, phosphorylated tyrosine or serine, AMP or ATP.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Monoclonal Anti-Phosphothreonine (mouse IgG2b isotype) is derived from the hybridoma produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from an immunized mouse.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation are basic mechanisms for the modification of protein function in eukaryotic cells. Phosphorylation is a rare post-translational event in normal tissue. However, the abundance of phosphorylated cellular proteins increases tenfold following various activation processes, which are mediated through phosphotyrosine, phosphoserine or phosphothreonine (p-Tyr/p-Ser/p-Thr). Many different mitogenic systems, such as the EGF, PDGF and insulin receptor systems, contain Tyr/Ser/Thr kinase domains that autophosphorylate specific Tyr/Ser/Thr residues upon binding of their ligands. T cell antigen receptor complex or receptors for some hemopoietic growth factors may stimulate associated kinases, and cells transformed by viral oncogenes contain elevated levels of phosphorylated Tyr/Ser/Thr. An understanding of transformation by oncogenes and mitogenic processes of growth factors depends on the identification of their substrate and a subsequent determination of how phosphorylation affects the properties of these proteins.
PHOSPHOTHREONINE Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte