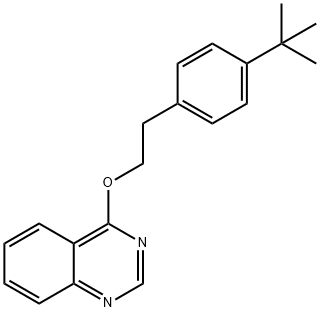
Fenazaquin
|
|
Fenazaquin Eigenschaften
- Schmelzpunkt:
- 70-71° (Dreikorn); mp 77.5-80.0° (Gambie)
- Siedepunkt:
- 447.01°C (rough estimate)
- Dichte
- 1.0970 (rough estimate)
- Dampfdruck
- 3.4 x l0-6 Pa (25 °C)
- Brechungsindex
- 1.5700 (estimate)
- storage temp.
- Sealed in dry,Room Temperature
- L?slichkeit
- Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly)
- Wasserl?slichkeit
- 0.102 mg l-1 (20 °C, pH 7)
- pka
- 2.88±0.30(Predicted)
- Aggregatzustand
- solid
- Farbe
- White to off-white
- BRN
- 8331263
- LogP
- 5.510
- CAS Datenbank
- 120928-09-8(CAS DataBase Reference)
- EPA chemische Informationen
- Fenazaquin (120928-09-8)
Sicherheit
- Risiko- und Sicherheitserkl?rung
- Gefahreninformationscode (GHS)
| Kennzeichnung gef?hrlicher | T,N | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| R-S?tze: | 20-25-50/53 | ||
| S-S?tze: | 37-45-60-61 | ||
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 | ||
| WGK Germany | 3 | ||
| RTECS-Nr. | VA1382000 | ||
| Giftige Stoffe Daten | 120928-09-8(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| Toxizit?t | LD50 orally in rats, mice (mg/kg): 134, 1480; dermally in rabbits (mg/kg): >5000; LC50 (96 hr) in bluegill, trout (mg/l): 34.1, 3.8 (Longhurst) |
| Bildanzeige (GHS) |
 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alarmwort | Achtung | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gefahrenhinweise |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheit |
|
Fenazaquin Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R20:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Einatmen.R25:Giftig beim Verschlucken.
R50/53:Sehr giftig für Wasserorganismen, kann in Gew?ssern l?ngerfristig sch?dliche Wirkungen haben.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S37:Geeignete Schutzhandschuhe tragen.S45:Bei Unfall oder Unwohlsein sofort Arzt zuziehen (wenn m?glich, dieses Etikett vorzeigen).
S60:Dieses Produkt und sein Beh?lter sind als gef?hrlicher Abfall zu entsorgen.
S61:Freisetzung in die Umwelt vermeiden. Besondere Anweisungen einholen/Sicherheitsdatenblatt zu Rate ziehen.
Verwenden
Fenazaquin is a non-systemic acaricide/insecticide used widely in controlling mites and other related pests in fruits, vegetables and tea.Stoffwechselwegen
Fenazaquin is a lipophilic compound and hence is immobile in soils and is not translocated in plants. The main pathways of metabolism involve cleavage of the bridging group between the quinazoline and phenyl rings, oxidation of the tert-butyl sustituent and of the heterocyclic portion of the quinazoline ring and cleavage of that ring. Most of the information is taken from a pamphlet produced by the manufacturer of the compound in which full experimental details were not given (DowElanco, 1993).Degradation
Fenazaquin is hydrolysed under acidic conditions but the rate is slow under neutral and alkaline conditions. Half-lives were 8,442 and 584 days (22 °C) at pH values of 5, 7 and 9, respectively. Hydrolysis occurs by cleavage of the ether linkage to form quinazolin-2-ol (2) and an alcohol (3) as shown in Scheme 1. The major route of degradation in aquatic environments is by photolysis, the main products (2 and 3) being formed by cleavage of the ether lmkage and include the alkene (4) (DowElanco, 1993).Fenazaquin Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
Fenazaquin Anbieter Lieferant Produzent Hersteller Vertrieb H?ndler.
Global( 148)Lieferanten
| Firmenname | Telefon | Land | Produktkatalog | Edge Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qingdao Trust Agri Chemical Co.,Ltd | +8613573296305 |
aroma@qdtrustagri.com | China | 301 | 58 |
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28172 | 58 |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 |
sales@conier.com | China | 49732 | 58 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 |
factory@coreychem.com | China | 29807 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-29-87569266 15319487004 |
1015@dideu.com | China | 3974 | 58 |
| TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | +1-781-999-5354 +1-00000000000 |
marketing@targetmol.com | United States | 32268 | 58 |
| Hubei Ipure Biology Co., Ltd | +8613367258412 |
ada@ipurechemical.com | China | 10244 | 58 |
| Longyan Tianhua Biological Technology Co., Ltd | 0086 18039857276 18039857276 |
CHINA | 2783 | 58 | |
| InvivoChem | +1-708-310-1919 +1-13798911105 |
sales@invivochem.cn | United States | 6391 | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418684 +8618949823763 |
sales@tnjchem.com | China | 25356 | 58 |
120928-09-8()Verwandte Suche:
Phenylvalerat
Diphenylether
Ethoxychin
Phenylsalicylat
3,6-Bis(o-chlorphenyl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazin
Azocyclotin
Sulfachinoralin
PHENYL RESIN
Phenylessigsure
Ethoxy
- 4-((4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenyl)ethoxy)-quinazolin
- Fenazaquin 0.1
- 4-(4-(tert-Butyl)phenethoxy)quinazoline
- 4-(4-(tert-Butyl)
- phenethoxy)
- 4-((4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenyl)ethoxy)quinazoline
- 4-(2-(4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenyl)ethoxy)quinazoline
- 4-tert-butylphenethylquinazolin-4-ylether
- el436
- MAGISTER
- FENAZAQUIN PESTANAL, 100 MG
- FENAZAQUIN ANALYTICAL STANDARD
- Quinazoline, 4-2-4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenylethoxy-
- FENAZAQUIN
- 4-tert-Butyl phenylethyl quinazolin-4-yl ether
- 4-[2-(4-tert-butylphenyl)ethoxy]quinazoline
- AFenazaquin
- Quetiapine mite ether
- Fenazaquin@100 μg/mL in Hexane
- Fenazaquin@1000 μg/mL in Acetone
- FenazaquinSolution,100mg/L,1ml
- Fenazaquin (EL436
- XDE 436)
- C13441000 Fenazaquin
- Fenazaquin 10.0 μg/ml Acetonitrile
- Fenazaquin 10.0 μg/ml Ethyl acetate
- L13441000ALFenazaquin 10μg/mLin Acetonitrile
- L13441000CY Fenazaquin 10μg/mLin Cyclohexane
- XA13441000CY Fenazaquin 100μg/mLin Cyclohexane
- Fenazaquin in Acetonitrile
- Pioglitazone Impurity 37
- 120928-09-8
- 20928-09-8
- AcaricidesPesticides&Metabolites
- Alpha sort
- E-GAlphabetic
- F
- FA - FL
- Pesticides
- Pesticides&Metabolites