PERFLUOROOCTANOHYDROXAMIC ACID Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
synthetische
With suitable safety precautions, to 300 ml of methanol (in which 24.45 g (0.45 mol) of sodium methoxide has been dissolved) is added, portionwise, 31.45 g (0.45 mol) of hydroxylamine hydrochloride. The precipitating sodium chloride is filtered off. To the methanolic solution of hydroxylamine is added dropwise, with stirring, 200 g (0.45 mol) of ethyl perfluorooctanoate. Stirring is continued overnight. The product is isolated by evaporating the solution to dryness. Yield: 168.28 g (87%). The product may be recrystallized from acetoni-trile: m.p. 115-116°C; IR (KBr) 1690 cm-1 (CO).
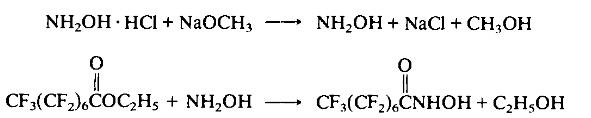
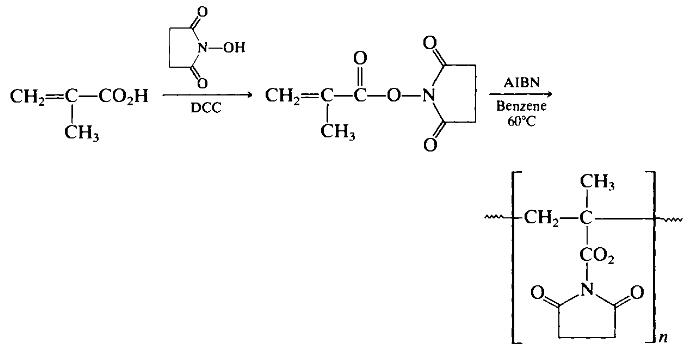
Polymeric methacrylic ester derivatives have been converted to polymeric hydroxamic acids by reaction with hydroxylamine derivatives. For example, the N-hydroxysuccinimide ester of N-methacryloyl β-alanine was polymerized and treated with methylhydroxylamine-DMF solution for 7 h to produce the corresponding hydroxamic acid polymer. Preparation 2-8 illustrates the methodology with a slightly simpler polymer structure. For this preparation, the initial polymer, poly(TV-methacryloxysuccini-mide) was prepared according to Eq. 24, using 2,2-azo-bisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) as initiator. Note the use of a carbodiimide (DCC) to form the TV-hydroxysuccinimide derivative of methacrylic acid.
PERFLUOROOCTANOHYDROXAMIC ACID Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

