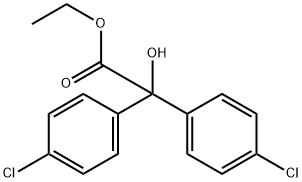
Chlorbenzilat (ISO)
|
|
Chlorbenzilat (ISO) Eigenschaften
- Schmelzpunkt:
- 37-38℃
- Siedepunkt:
- bp0.04 146-148°
- Dichte
- 1.332
- Brechungsindex
- 1.5727
- storage temp.
- 0-6°C
- pka
- 11.11±0.29(Predicted)
- Wasserl?slichkeit
- 13mg/L(20 ºC)
- Merck
- 13,2141
- Stabilit?t:
- Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, alkalies, lime.
- CAS Datenbank
- 510-15-6(CAS DataBase Reference)
- IARC
- 3 (Vol. 30, Sup 7) 1987
- EPA chemische Informationen
- Chlorobenzilate (510-15-6)
Sicherheit
- Risiko- und Sicherheitserkl?rung
- Gefahreninformationscode (GHS)
| Kennzeichnung gef?hrlicher | Xn,N,T | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| R-S?tze: | 22-50/53-63-43-36/37/38-23/24/25-45-67-40 | ||
| S-S?tze: | 60-61-36/37-24/25-23-53 | ||
| RIDADR | UN 1593 6.1/PG 3 | ||
| WGK Germany | 3 | ||
| RTECS-Nr. | DD2275000 | ||
| HS Code | 29181800 | ||
| Giftige Stoffe Daten | 510-15-6(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| Toxizit?t | LD50 in male, female rats (mg/kg): 1040, 1220 orally (Gaines) |
| Bildanzeige (GHS) |
 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alarmwort | Warnung | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gefahrenhinweise |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheit |
|
Chlorbenzilat (ISO) Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
FARBLOSE ODER BLASSGELBE KRISTALLE.CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Zersetzung beim Erhitzen unter Bildung giftiger und ?tzender Rauche. Reagiert mit starken S?uren, Basenund starken Oxidationsmittelnunter Feuergefahr.ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV nicht festgelegt (ACGIH 2005).MAK nicht festgelegt (DFG 2005).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation und durch Verschlucken.INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Verdampfung bei 20°C vernachl?ssigbar; eine gesundheitssch?dliche Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann jedoch beim Dispergieren schnell erreicht werden.WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION:Die Substanz reizt die Augen und die Haut. M?glich sind Auswirkungen auf das Zentralnervensystem mit nachfolgenden Funktionsst?rungen.
LECKAGE
Verschüttetes Material in abgedeckten Beh?ltern sammeln; falls erforderlich durch Anfeuchten Staubentwicklung verhindern. Reste sorgf?ltig sammeln. An sicheren Ort bringen. NICHT in die Umwelt gelangen lassen. Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Atemschutzger?t, P2-Filter für sch?dliche Partikel.R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Verschlucken.R50/53:Sehr giftig für Wasserorganismen, kann in Gew?ssern l?ngerfristig sch?dliche Wirkungen haben.
R63:Kann das Kind im Mutterleib m?glicherweise sch?digen.
R43:Sensibilisierung durch Hautkontakt m?glich.
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
R23/24/25:Giftig beim Einatmen, Verschlucken und Berührung mit der Haut.
R45:Kann Krebs erzeugen.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S60:Dieses Produkt und sein Beh?lter sind als gef?hrlicher Abfall zu entsorgen.S61:Freisetzung in die Umwelt vermeiden. Besondere Anweisungen einholen/Sicherheitsdatenblatt zu Rate ziehen.
S36/37:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzkleidung tragen.
S24/25:Berührung mit den Augen und der Haut vermeiden.
S23:Gas/Rauch/Dampf/Aerosol nicht einatmen(geeignete Bezeichnung(en) vom Hersteller anzugeben).
S53:Exposition vermeiden - vor Gebrauch besondere Anweisungen einholen.
Beschreibung
Chlorobenzilate is an organochlorine pesticide belonging to the same class as dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT). It was originally developed by Ciba–Geigy and introduced in 1952.Chemische Eigenschaften
Ethyl 4,40 -dichlorobenzilate is a yellow solid when pure. The technical product is a brownish liquid.Verwenden
The primary use of chlorobenzilate is as an acaricide for mite control on citrus crops and in beehives. It has a narrow insecticidal action, killing only mites and ticks. Historically, chlorobenzilate was used as a synergist for DDT. Although now banned for use in the United States and Europe, it is believed to be used on crops other than citrus in other countries.Allgemeine Beschreibung
Viscous yellow liquid or pale yellow crystals. Light brown crystalline solid.Air & Water Reaktionen
Insoluble in water.Reaktivit?t anzeigen
CHLOROBENZILATE is hydrolyzed by alkalis and strong acids. Incompatible with lime .Health Hazard
Moderately toxic by oral route; toxic symptoms similar to DDT and Perthane; ingestionof large dose can produce nausea, vomiting,tremor and convulsions; skin or eye contactcan cause irritation; application of 25 mgproduced moderate irritation of eye inrabbits; adequate evidence of carcinogenicityin experimental animals; produced tumors inrats and mice; evidence of carcinogenicity inhumans remains unknown.LD50 oral (rat): 700 mg/kg
LD50 oral (mouse): 729 mg/kg.
Brandgefahr
Flash point data for CHLOROBENZILATE are not available; however, CHLOROBENZILATE is probably combustible.Sicherheitsprofil
Suspected carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, and tumorigenic data. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A skin and eye irritant. A pesticide. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-.m?gliche Exposition
It is a buffer in many chemical intermediates; an organochlorine miticide; to kill mites, ticks, and other insects; as a synergist for DDT. Incompatibilities: Strong acids, strong bases; lime.Environmental Fate
Biological. Rhodotorula gracilis, a yeast isolated from an insecticide-treated soil, degraded chlorobenzilate in a basal medium supplemented by sucrose. Metabolites identified by this decarboxylation process were 4,4′-dichlorobenzilic acid, 4,4′-dichlorobenzophenone and carbon dioxide (Miyazaki et al., 1969, 1970).Soil. Though no products were identified, the half-life of chlorobenzilate in two fine sandy soils was estimated to be 1.5–5 weeks (Wheeler, 1973).
Photolytic. Chlorobenzilate should not undergo direct photolysis since it does not absorb UV light at wavelengths greater than 290 nm (Gore et al., 1971).
Versand/Shipping
UN2996 Organochlorine pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.UN2761 Organochlorine pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.Waste disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.Chlorbenzilat (ISO) Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
Chlorbenzilat (ISO) Anbieter Lieferant Produzent Hersteller Vertrieb H?ndler.
Global( 60)Lieferanten
| Firmenname | Telefon | Land | Produktkatalog | Edge Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28172 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22963 | 58 |
| Chongqing Chemdad Co., Ltd | +86-023-6139-8061 +86-86-13650506873 |
sales@chemdad.com | China | 39894 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8617732866630 |
bess@weibangbio.com | China | 18148 | 58 |
| SUZHOU SENFEIDA CHEMICAL CO.,LTD | +86-0512-83500002 +8615195660023 |
sales@senfeida.com | China | 23046 | 58 |
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-+1(833)-552-7181 |
sales@aladdinsci.com | United States | 57505 | 58 |
| XIAMEN AMITY INDUSTRY AND TRADE CO., LTD. | +8618950047208 |
ellena@amitychem.com | China | 43416 | 58 |
| Mainchem Co., Ltd. | +86-0592-6210733 |
sale@mainchem.com | China | 32343 | 55 |
| Shaanxi Didu New Materials Co. Ltd | +86-89586680 +86-13289823923 |
1026@dideu.com | China | 8670 | 58 |
| Syntechem Co.,Ltd | |
info@syntechem.com | China | 12984 | 57 |
510-15-6(Chlorbenzilat (ISO))Verwandte Suche:
4-Chlorbenzhydrylalkohol
Chlorbenzilat (ISO)
Methylbenzilat
Ethyl-(S)-2-hydroxypropionat
Methyl-(R)-lactat
Ethyldiphenylglykolat
4-Chlormandelsaeure
L-2-Hydroxy-2-phenylessigsure
Bis(p-chlorphenyl)essigsure
Chloropropylat
4,4'-dichlor-α-phenylbenzylalkohol
2,2-Bis(p-chlorphenyl)ethanol
Ethylglykolat
Benzilsure
Chlorfenethol (ISO)
Ethylphenylacetat
DL-2-Phenylpropan-1,2-diol
2-Phenylmilchsure
- WOPROSILAN
- ACARBEN(R)
- AKAR(R)
- ETHYL 4,4'-DICHLOROBENZILATE
- Ethyl-2-hydroxy-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)acetate
- ethyl2-hydroxy-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)acetate
- ethyl2-hydroxy-2,2-di(p-chlorophenyl)acetate
- ethyl4,4’-dichlorobenilate
- ethyl4,4’-dichlorodiphenylglycollate
- ethyl4,4’-dichlorophenylglycollate
- ethyl-4,4’-diphenylglycollate
- ethyl4-chloro-a-(4-chlorophenyl)-a-hydroxybenzeneethanoate
- folbexsmoke-strips
- G 338
- g338
- Geigy 338
- geigy338
- NCI-C00408
- NCI-C60413
- Rcra waste number U038
- rcrawastenumberu038
- G23922
- CHLORBENZILAT PESTANAL (ETHYL 4,4'-DICHL
- CHLOROBENZILATE, 250MG, NEAT
- CHLOROBENZILATE, 1X1ML, CH2CL2, 200UG/ML
- chlorobenzilate solution
- ETHYL44DICHLOROBENZYLATE
- CHLOROBENZILLATE
- Chorobenzilate
- Benzeneacetic acid, 4-chloro-alpha-(4-chlorophenyl)-(4-chlorophenyl)-alpha-hydroxy, ethyl ester
- chlorobenzilate (ISO) ethyl 2,2-di(4-chlorophenyl)-2-hydroxyacetate ethyl 4,4'-dichlorobenzilate
- CHLORBENZILAT
- CHLOROBENZILATE
- KOP-MITE
- FOLBEX(R)
- G 23992
- 4,4’-dichlorbenzilsaeureaethylester
- 4,4’-dichlorobenzilate
- 4,4’-dichlorobenzilicacidethylester
- 4,4’-dichloro-benzilicaciethylester
- 4,4'-Dichlorbenzilsaeureaethylester
- 4,4'-Dichlorobenzilate
- 4,4'-Dichlorobenzilic Acid ethyl ester
- 4-chloro-alpha-(4-chlorophenyl)-alpha-hydroxybenzeneaceticacidethylester
- 4-chloro-alpha-(4-chlorophenyl)-alpha-hydroxy-benzeneaceticaciethylest
- 4-chloro-alpha-(4-chlorophenyl)-alpha-hydroxy-benzeneaceticaciethylester
- Acar
- Acaraben
- Acaraben 4E
- acaraben4e
- acarben4e
- Akar
- Akar 338
- Akar 50
- akar338
- akar50
- Benzeneacetic acid, 4-chloro-alpha-(4-chlorophenyl)-alpha-hydroxy-, ethyl ester
- Benzilan