300842-64-2
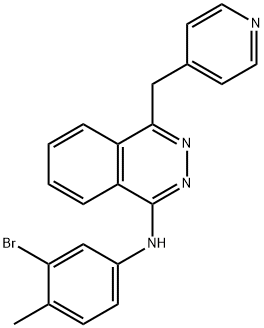 300842-64-2 結(jié)構(gòu)式
300842-64-2 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
N-(3-溴-4-甲基苯基)-4-(4-吡啶甲基)-1-酞嗪胺
ZK 202650
NVP-ACC-789
ACC-789 (NVP-ACC789)
ACC-789
ZK-202650
NVP-ACC-789
ACC789
ACC 789
N-(3-Bromo-4-methylphenyl)-4-(4-pyridinylmethyl)-1-phthalazinamine
N-(3-Bromo-4-methylphenyl)-4-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)phthalazin-1-amine
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
DMF:0.5(Max Conc. mg/mL);1.23(Max Conc. mM)
DMF:PBS (pH 7) (1:10):0.09(Max Conc. mg/mL);0.22(Max Conc. mM)
Ethanol:0.2(Max Conc. mg/mL);0.49(Max Conc. mM)
常見問題列表
|
VEGFR-2 0.02 μM (IC 50 ) |
VEGFR-1 0.38 μM (IC 50 ) |
mVEGFR-2 0.23 μM (IC 50 ) |
VEGFR-3 0.18 μM (IC 50 ) |
PDGFR-β 1.4 μM (IC 50 ) |
The enzymatic kinase assays demonstrate that NVP-ACC789 is an inhibitor of human VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2 (mouse VEGFR-2), VEGFR-3 and PDGFR-β with IC 50 s of 0.38, 0.02 (0.23), 0.18, 1.4 μM, respectively. In VEGF-treated cultures, addition of the VEGFR-2 inhibitor NVP-ACC789 reduces BME cell number to baseline levels from 1 μM. Likewise, bFGF-induced BME cell proliferation is reduced markedly by NVP-ACC789 from 1 to 10 μM, without however reaching basal levels. NVP-ACC789 is found to be a potent inhibitor of VEGF-induced HUVE cell proliferation with an IC 50 of 1.6 nM. NVP-ACC789 also completely inhibits VEGF-induced BME and BAE cell invasion and VEGF-C-induced BAE cell invasion. The inhibition is dose-dependent in both cell types with a maximal effect from 1 μM.
NVP-ACC789 which is given in daily oral doses for 6 days blocks VEGF-induced angiogenesis in a dose-dependent manner. NVP-ACC789 also inhibits the response to bFGF to some extent, but the dose-response curve is not linear for NVP-ACC789.