| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
POLY(METHYL ACRYLATE) | [CAS]
9003-21-8 | [Synonyms]
Polymethacrylates
METHYL ACRYLATE LATEX
METHYL ACRYLATE RESIN
POLY(METHYL ACRYLATE)
Poly(methyleacrylate)
Polymethyl-acrylate paste
Methylacrylatehomopolymer
Microparticles based on PMAA
Polymethyl methacrylate,color
poly(methyl acrylate) solution
Polymethyl methacrylate,aero grade
poly(methyl acrylate) macromolecule
2-Propenoicacid,methylester,homopolymer
solutionintolueneaveragemwca.40000(gpc)
Polymethyl methacrylate,industrial grade
Microparticles based on poly(methacrylic acid)
POLY(METHYL ACRYLATE), SECONDARY STANDAR D (TOLUENE)
Poly(methyl acrylate) solution average Mw ~40,000 by GPC
POLY(METHYL ACRYLATE), SOLUTION IN TOLUE NE, AVERAGE MW CA. 40,000 (GPC | [EINECS(EC#)]
203-625-9 | [Molecular Formula]
(C4H6O2)x | [MDL Number]
MFCD00084441 | [MOL File]
9003-21-8.mol | [Molecular Weight]
86.09 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
clear liquid | [Definition]
ChEBI: An acrylate macromolecule composed of repeating methoxycarbonylethylene units. | [Uses]
PMA/methylamine borane (MeAB) composites, prepared by solution blending process finds uses as a hydrogen storage material with better dehydrogenation property compared to MeAB. | [Preparation]
The structure of methyl acrylate is H2C=CH-COOCH3. The monomer used to prepare poly(methyl acrylate) is produced by the oxidation of propylene. The resin is made by free-radical polymerization initiated by peroxide catalysts and has the following formula:
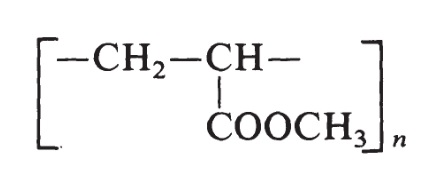
Poly(methyl acrylate) resins vary from soft, elastic, film-forming materials to hard plastics. | [Production Methods]
Prepared by the polymerization of acrylic and methacrylic acids or
their esters, e.g. butyl ester or dimethylaminoethyl ester | [Pharmaceutical Applications]
Polymethacrylates are primarily used in oral capsule and tablet
formulations as film-coating agents.(1–21) Depending on the type of
polymer used, films of different solubility characteristics can be
produced;
Eudragit E is used as a plain or insulating film former. It is
soluble in gastric fluid below pH 5. In contrast, Eudragit L, S and
FS types are used as enteric coating agents because they are resistant
to gastric fluid. Different types of enteric coatings are soluble at
different pH values: e.g. Eudragit L is soluble at pH > 6 whereas
Eudragit S and FS are soluble at pH > 7. The S grade is generally
used for coating tablets, while the flexible FS 30 D dispersion is
preferred for coating particles.
Eudragit RL, RS, NE 30D, NE 40D, andNM30D are used to
form water-insoluble film coats for sustained-release products.
Eudragit RL films are more permeable than those of Eudragit RS,
and films of varying permeability can be obtained by mixing the two
types together. The neutral Eudragit NE/NM grades do not have functional ionic groups. They swell in aqueous media independently
of pH without dissolving.
Eudragit L 30 D-55 is used as an enteric coating film former for
solid-dosage forms. The coating is resistant to gastric juice but
dissolves readily at above pH 5.5.
Eudragit L 100-55 is an alternative to Eudragit L 30 D-55. It is
commercially available as a redispersible powder.
Kollicoat MAE 100 P, Acryl-EZE and Acryl-EZE MP are also
commercially available as redispersible powder forms, which are
designed for enteric coating of tablets or beads.
Eastacryl 30 D and Kollicoat MAE 30 DP are aqueous
dispersions of methacrylic acid–ethyl acrylate copolymers. They
are also used as enteric coatings for solid-dosage forms.
Polymethacrylates are also used as binders in both aqueous and
organic wet-granulation processes. Larger quantities (5–20%) of
dry polymer are used to control the release of an active substance
from a tablet matrix. Solid polymers may be used in directcompression
processes in quantities of 10–50%.
Polymethacrylate polymers may additionally be used to form the
matrix layers of transdermal delivery systems and have also been
used to prepare novel gel formulations for rectal administration. | [Safety]
Polymethacrylate copolymers are widely used as film-coating
materials in oral pharmaceutical formulations. They are also used
in topical formulations and are generally regarded as nontoxic and
nonirritant materials.
Based on relevant chronic oral toxicity studies in rats and
conventionally calculated with a safety factor of 100, a daily intake
of 2–200 mg/kg body-weight depending on the grade of Eudragit
may be regarded as essentially safe in humans. | [Solubility in organics]
Aromatic hydrocarbons, esters, ketones, THF | [storage]
Dry powder polymer forms are stable at temperatures less than
30°C. Above this temperature, powders tend to form clumps,
although this does not affect the quality of the substance and the
clumps can be readily broken up. Dry powders are stable for at least
3 years if stored in a tightly closed container at less than 30°C.
Dispersions are sensitive to extreme temperatures and phase
separation occurs below 0°C. Dispersions should therefore be
stored at temperatures between 5 and 25°C and are stable for at
least 18 months after shipping from the manufacturer’s warehouse
if stored in a tightly closed container at the above conditions. | [Purification Methods]
Precipitate it from a 2% solution in acetone by addition of water. | [Incompatibilities]
Incompatibilities occur with certain polymethacrylate dispersions
depending upon the ionic and physical properties of the polymer
and solvent. For example, coagulation may be caused by soluble
electrolytes, pH changes, some organic solvents, and extremes of
temperature. For example, dispersions of Eudragit L 30
D, RL 30 D, L 100-55, and RS 30 D are incompatible with
magnesium stearate. Eastacryl 30 D, Kollicoat MAE 100 P, and
Kollicoat MAE 30 DP are also incompatible with magnesium
stearate.
Interactions between polymethacrylates and some drugs can
occur, although solid polymethacrylates and organic solutions are
generally more compatible than aqueous dispersions. | [Regulatory Status]
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral capsules
and tablets). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the
UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal
Ingredients. |
|
| Company Name: |
Sigma-Aldrich
|
| Tel: |
021-61415566 800-8193336 |
| Website: |
https://www.sigmaaldrich.cn |
|