| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Zaltoprofen | [CAS]
89482-00-8 | [Synonyms]
Peon
CN-100
Soreton
Zaltoprofen
Zaltoprofene
Zaltoprofeno
Zaltoprofenum
Unii-H8635ng3py
CN 100 (antiphlogistic)
Zaltoprofene [inn-french]
Zaltoprofeno [inn-spanish]
10,11-Dihydro-a-methyl-10-oxodibenzo[b,f]thiepin-2-acetic Acid
2-(10,11-Dihydro-10-oxodibenzo[b,f]thiepin-2-yl)propionic Acid
(±)-10,11-Dihydro-α-methyl-10-oxodibenzo[b��,f]thiepin-2-acetic acid
Dibenzo[b,f]thiepin-2-acetic acid, 10,11-dihydro-a-methyl-10-oxo-(9CI) | [EINECS(EC#)]
277-973-5 | [Molecular Formula]
C17H14O3S | [MDL Number]
MFCD00864323 | [MOL File]
89482-00-8.mol | [Molecular Weight]
298.36 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
Off-White to Pale Yellow Crystalline Solid | [Usage]
Anti-inflammatory activity resides in (S)-enantiomer | [Description]
Zaltoprofen is a potent non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic
activity. In rats and mice, zaltoprofen is reported to be equipotent or superior to other NSAlDs
in bradykinin-induced pain, acetic acid-induced writhing, carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia,
and in several other experimental models of analgesia. It acts by selectively suppressing the
production of prostaglandins at the inflammatory site and not in other organs such as stomach
and kidney, therefore, has remarkably low gastric side effects that are associated with
conventional antiinflammatory agents. | [Originator]
Nippon Chemiphar (Japan) | [Uses]
Anti-inflammatory activity resides in (S)-enantiomer | [Definition]
ChEBI: Zaltoprofen is an organic molecular entity. | [Manufacturing Process]
Zaltoprofen may be prepared in 4 steps:
1. Preparation of 2-(3-carboxymethyl-4-nitrophenyl)propionic acid:
Dimethyl malonate (4.04 g, 30.6 mmol), potassium t-butoxide (3.43 g, 30.6
mmol) and anhydrous N,N-dimethylformamide (15 ml) were mixed and stirred
for 10 minutes in a nitrogen atmosphere at 90°C. The mixture was then
cooled to room temperature, and to the cooled mixture was added a solution
of diethyl 2-(3-chloro-4-nitrophenyl)-2-methylmalonate (5.04 g, 15.3 mmol)
prepared in the manner as described in Japanese Patent Publication No. 47-
45, 746) in anhydrous N,N-dimethylformamide (15 ml). The resulting mixture
was stirred at 90°C for 3 hours, and then poured into 1 N hydrochloric acid
(30 ml). The mixture was subjected to extraction using two portions of diethyl
ether. The ether extracts were combined, washed successively with water and
an aqueous saturated sodium chloride solution, and dried over anhydrous
sodium sulfate. The dried extract was placed under reduced pressure to give
7.97 g of yellow oil. The oil was adsorbed on silica gel (16 g) and subjected to moderate pressure silica gel column chromatography. The adsorbed oil was
eluted using a mixture of ethyl acetate/hexane (1/3, v/v) to give 4.33 g
(yield: 66.7%) of diethyl 2-[3-bis(methoxycarbonyl)methyl-4-nitrophenyl]-2-
methylmalonate as a yellow oil.
The diethyl 2-[3-bis(methoxycarbonyl)methyl-4-nitrophenyl]-2-
methylmalonate obtained above,(4.13 g, 9.71 mmol) was dissolved in acetic
acid (40 ml). To the solution were added water (16 ml) and concentrated
sulfuric acid (4 ml), and the resulting mixture was heated for 15 hours under
reflux. The acetic acid was distilled off under reduced pressure. The residue
was concentrated under reduced pressure after addition of toluene. The
precipitated crystals were collected by filtration and washed with water to give
2.06 g of the desired compound as a pale brown crystalline product. The
filtrate and washing were combined and subjected to extraction using ethyl
acetate. The ethyl acetate portion was washed successively with water and an
aqueous saturated sodium chloride solution, and dried over anhydrous sodium
sulfate. The solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to leave 0.32 g of
2-(3-carboxymethyl-4-nitrophenyl)propionic acid as a yellow crystalline
product. The total amount was 2.38 g (yield: 96.8%).
2. Preparation of 2-(4-amino-3-carboxymethylphenyl)propionic acid disodium
salt:
In 0.5 N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (0.8 ml) was dissolved 2-(3-
carboxymethyl-4-nitrophenyl)propionic acid (50 mg, 0.2 mmol). The solution
was stirred for 18 hours at room temperature in a hydrogen gas atmosphere,
after addition of 10% palladium/carbon (10 mg). Insolubles were removed by
filtration, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to give 55
mg (yield: quantitative amount) of the desired compound as a colorless oil.
3. Preparation of 2-(3-carboxymethyl-4-phenylthiophenyl)propionic acid:
In 2 N hydrochloric acid (0.5 ml) was dissolved 2-(4-amino-3-
carboxymethylphenyl)propionic acid disodium salt, 53 mg, 0.2 mmol). Sodium
nitrite (14 mg, 0.2 mmol) was added to the resulting solution under stirring
and chilling with ice. The mixture was stirred for 30 minutes under chilling
with ice. The mixture was then neutralized with a chilled aqueous saturated
sodium acetate solution. To the neutralized mixture was added a solution of
thiophenol (0.02 ml, 0.2 mmol) in 6 N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution
(0.1 ml), and the mixture was stirred for 2 hours at room temperature. The
reaction mixture was then made acidic by addition of 2 N hydrochloric acid,
and extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate portion was extracted with
an aqueous saturated sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. The aqueous
portion was then made acidic by addition of 6 N hydrochloric acid and
extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate portion was washed
successively with water and an aqueous saturated sodium chloride solution,
and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was distilled off under
reduced pressure to give 28 mg (yield: 45%) of the 2-(3-carboxymethyl-4-
phenylthiophenyl)propionic acid.
4. Preparation of 2-(10,11-dihydro-10-oxodibenzo[b,f]thiepin-2-yl)propionic
acid [i.e., Zaltoprofen]:
2-(3-Carboxymethyl-4-phenylthiophenyl)propionic acid prepared above (174mg, 0.55 mmol) was mixed with polyphosphoric acid (3.5 g). The mixture was
stirred at 60°-70°C for 3 hours. The reaction mixture was then extracted with
ethyl acetate after addition of chilled water. The ethyl acetate portion was
washed successively with water and an aqueous saturated sodium chloride
solution, and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was distilled
off under reduced pressure to leave a brown crystalline residue. The residue
was recrystallized from benzene-hexane, to give 123 mg (yield: 75%) of the
desired compound as a pale yellow crystalline product. MP: 130.5°-131.5°C.
The structure of compounds was confirmed with 1 H-NMR spectrum. | [Brand name]
Soleton; Peon | [Therapeutic Function]
Antiinflammatory, Analgesic | [Clinical Use]
Zaltoprofen is a non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory drug originated by Nippon
Chemiphar and jointly developed with Zeria.
It has been available on the market in Japan
since 1993 for the relief of pain and inflammation
resulting from arthritis deformations, periarthritis
of the shoulder, neck-shoulder-arm
syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, lumbago, postsurgery
pain, trauma, and tooth extraction and
used in oral doses of 80 mg . According to
studies, the analgesic effects of zaltoprofen may
involve the inhibition of bradykinin-2 receptormediated
responses in primary afferent neurons
. Although zaltoprofen is marketed as
a racemate the anti-inflammatory activity resides
in the (S)-enantiomer. | [Synthesis]
The cyclization of 5-(1- cyanoethyl)-2-(phenylthio)phenylacetic acid in presence of polyphosphoric acid at 120 ℃ gives 2-(10-oxo-10,11-dihydrodibenzo[b,f ]thiepin- 2-yl)propionitrile, which is then hydrolyzed with KOH in refluxing ethanol – water to zaltoprofen.
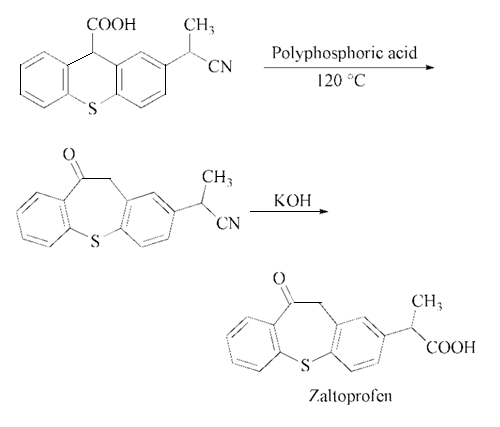
|
|
|