| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Linaclotide | [CAS]
851199-59-2 | [Synonyms]
CY-14
Liclotide
Argpessin
Linaclotide
Linaelotide
Linacllotide
Linaelotide Acetate
Rinalodipine Acetate
Linaclotide USP/EP/BP
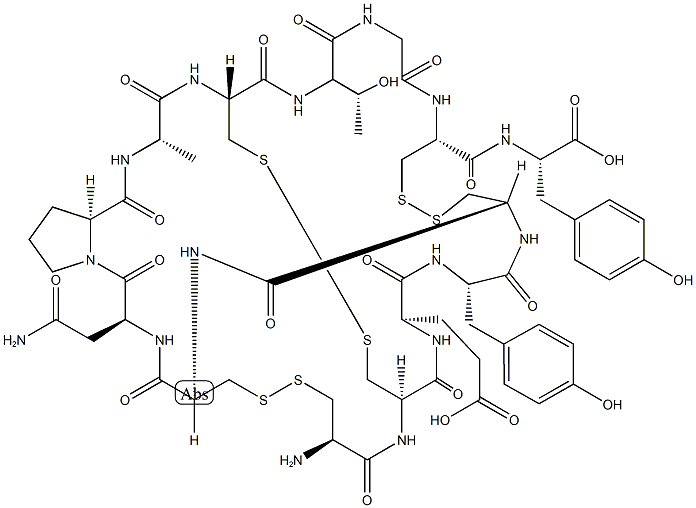
L-Tyrosine, L-cysteinyl-L-cysteinyl-L-α-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-L-cysteinyl-L-cysteinyl-L-asparaginyl-L-prolyl-L-alanyl-L-cysteinyl-L-threonylglycyl-L-cysteinyl-, cyclic (1→6),(2→10),(5→13)-tris(disulfide) | [EINECS(EC#)]
251-228-4 | [Molecular Formula]
C59H79N15O21S6 | [MDL Number]
MFCD20526656 | [MOL File]
851199-59-2.mol | [Molecular Weight]
1526.74 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
231-235°C (dec.) | [Boiling point ]
2045.0±65.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.60 | [storage temp. ]
Hygroscopic, Refrigerator, under inert atmosphere | [solubility ]
DMSO (Slightly, Heated), Methanol ((Slightly, Heated)), Water (Slightly, Heated) | [form ]
Solid | [pka]
3.05±0.10(Predicted) | [color ]
White | [Stability:]
Hygroscopic | [InChIKey]
KXGCNMMJRFDFNR-VRMHCMCOSA-N |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
In August 2012, the US FDA approved linaclotide (also referred to as
MD-1100), a first-in-class, orally administered 14-amino acid peptide as a
therapy for patients suffering from chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C).
Linaclotide and its active metabolite MM-419447, which results from the
cleavage of the C-terminal tyrosine residue by carboxypeptidase A, mimic
the actions of the endogenous intestinal peptides guanylin (15 amino acids) and uroguanylin (16 amino acids) by activating guanylyl cyclase C (GC-C) on the intestinal epithelium. Activation of GC-C leads to increased intra- and extracellular levels of cGMP and activation of the CFTR ion channel, resulting in increased levels of HCO3-, Cl-, and water in the intestinal lumen and accelerated gastrointestinal transit. Based on an in vitro assaymeasuring the accumulation of cGMP in T84 cell exposed to an agonist, the EC50 of linaclotide at pH 7.0 was 99±17.5 nM. In preclinical studies in mice using the transit of activated charcoal as ameasure of efficacy, linaclotide at 100 μg/kg significantly accelerated transit compared to wild-type mice treated with charcoal only or
GC-Cnullmice treatedwith and without linaclotide.118 Efficacy was also seen
in rats treatedwith linaclotide atdoses of 5, 10, and 20 μg/kg. Linaclotide has been synthesized using conventional solid-phase peptide technology. | [Originator]
Ironwood Pharmaceuticals and Forest
Pharmaceuticals (United States) | [Uses]
Linaclotide is a guanylate cyclase-C agonist currently being studied in Phase 3 trials for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Linaclotide is a fourteen-membered heterodetic cyclic peptide consisting of Cys, Cys, Glu, Tyr, Cys, Cys, Asn, Pro, Ala, Cys, Thr, Gly, Cys and Tyr residues joined in sequence and cyclised by three disulfide bonds: between Cys(1) and Cys(6), between Cys(2) and Cys(10), and between Cys(5) and Cys(13). Used for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome accompanied by constipation. It has a role as a guanylate cyclase 2C agonist. | [Brand name]
Linzess | [Biological Functions]
Linaclotide works by increasing fluid in your intestines and helping speed up movement of food through the gut. Linaclotide may improve stool texture and lessen symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain/discomfort, straining, and feelings of incomplete bowel movements. | [Side effects]
Side effects include:Diarrhea, abdominal pain, flatulence, abdominal distension, viral gastroenteritis, headache, upper respiratory tract infection, sinusitis |
|
|