| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Polydextrose | [CAS]
68424-04-4 | [Synonyms]
POLYDEXTROSE
Poly-D-glucose
Unii-vh2xou12ie
Polydextrose (200 mg)
Polydextrose solution
POLYDEXTROSE,UNTREATED,FCC
dextrose/ sorbitol condensation polymer | [EINECS(EC#)]
232-536-8 | [Molecular Formula]
(C6H10O5)n | [MDL Number]
MFCD00804499 | [MOL File]
68424-04-4.mol | [Molecular Weight]
342.296 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
>130° | [storage temp. ]
4°C, Hygroscopic | [solubility ]
Completely miscible in water. Sparingly soluble to
insoluble in most organic solvents. Polydextrose has a higher
water solubility than most carbohydrates and polyols, allowing
the preparation of 80% w/w solutions at 20°C. Polydextrose is
soluble in ethanol and only partially soluble in glycerin and
propylene glycol. | [form ]
Solid | [color ]
White to Off-White | [Odor]
at 100.00 %. odorless | [Odor Type]
odorless | [Stability:]
Hygroscopic | [Uses]
Polydextrose is a bulking agent that is a randomly bonded conden-
sation polymer of dextrose containing small amounts of bound sor-
bitol and citric acid. it is a water-soluble powder providing a ph
range of 2.5–3.5. it is partially metabolized which results in a caloric
value of 1 cal/g. as a reduced-calorie bulking agent, it can partially
replace sugars and in some cases fats in reduced-calorie foods. it also
functions as a bodying agent and humectant. applications include
desserts, specific baked goods, frozen dairy desserts, chewing gum,
and candy. usage levels vary according to application, but examples
are frozen dessert, 13–14%; puddings, 8–9%; and cake, 15–16%. |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Polydextrose (PDX) is a randomly bonded polysaccharide produced by the bulk melt polycondensation of glucose and sorbitol in vacu with an average DP of 12, ranging from 2 to 120. The molecule contains all possible combinations of α- and β-linked 1→2, 1→3, 1→4, and 1→6 glycosidic linkages, though the 1→6 (both α and β) predominates. Due to its complex structure, PDX is not hydrolyzed by mammalian digestive enzymes in the small intestine, passing intact into the colon, in which it is gradually and partly fermented by the endogenous microbiota and the remainder, approximately 60%, is excreted in the feces. PDX is not sweet, has a neutral taste, and can be used as a low-calorie bulking agent in a wide range of foods, such as baked goods, confectionery, dairy products, and functional beverages as it is highly soluble in water and results in a non-viscous solution. Polydextrose content could greatly influenced Snack quality. An increase in polydextrose content in the blend from 0 to 10% augmented the product density and decreased its radial and axial expansion ratio and crispness. Moreover, small air cells and thick cell walls were observed in the texture of the product with high polydextrose content[1-2].
| [Chemical Properties]
Polydextrose occurs as an odorless, off-white to light tan powder
with a bland, slightly sweet to slightly tart taste, dependent upon
grade. Polydextrose is also available as a clear, light yellow to
colorless liquid (70% dry substance), which is odorless with a
slightly sweet taste. | [History]
Polydextrose (PDX) was invented at Pfizer Central Research during the late 1960s, and patented in 1973 (Rennhard 1973). It was originally developed as a reduced calorie (1· kcal/g) replacement for sugar, and partial replacer for fat, fl our and starch. PDX is prepared by vacuum thermal polymerisation of glucose, using sorbitol and an approved food acid as catalyst. Random polymerisation and branching yield various types of glycosidic bonds in the structure (1,6 bonds predominate) (Rennhard 1973; Allingham 1982). A representative structure is shown in Fig. 43.1. Improved versions of PDX (Litesse®) have been patented that utilise ion exchange and hydrogenation, and provide even broader utility in foods (Borden et al. 1997; Guzek et al. 1997a, b).
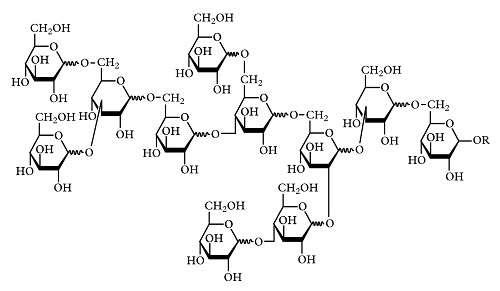
The structural compactness and complexity of PDX prevents mammalian enzymes from hydrolysing the molecule. This imparts reduced caloric content, as the majority of PDX passes through the stomach and enters the large intestine, whereupon it behaves as a dietary fi bre (Craig et al. 1998). This chapter discusses the physiological benefi ts and analytical measurement of PDX.
| [Production Methods]
Polydextrose is prepared by the bulk melt polycondensation of
glucose and sorbitol in conjunction with small amounts of foodgrade
acid in vacuo. Further purification steps are then involved to
generate a range of products with improved organoleptic properties
by the removal of acidity and flavor notes generated during the
condensation reaction. A partially hydrogenated version of polydextrose,
which is suited for high inclusion rates, for sugar-free applications, and where Maillard reactions are not required, is also
available. | [Pharmaceutical Applications]
Polydextrose is used in pharmaceutical formulations and food
products. In food products it is used as a bulking agent; it also has
texturizing and humectant properties.
Although polydextrose can be used in a wide range of
pharmaceutical formulations, its primary use is in solid-dosage
forms.
In tableting, polydextrose solutions are used as binders in wetgranulation
processes. Polydextrose is also used in the manufacture
of directly compressible tableting excipients. Polydextrose solutions
may also be used, in conjunction with other materials, as a film and
tablet coating agent.
Polydextrose acts as a bulking agent in the formulation of ‘sugarfree’
confectionery-type dosage forms. In conjunction with isomalt,
lactitol, or maltitol, polydextrose can be used in the manufacture of
‘sugar-free’ hard-boiled candies and acacia lozenges or pastilles as a
base for medicated confectionery.
The combination of high water solubility and high viscosity of
polydextrose facilitates the processing of sugar-free candies of
excellent quality. Polydextrose is amorphous and does not crystallize
at low temperatures or high concentrations, so it can be used to
control the crystallization of polyols and sugars and therefore the
structure and texture of the final product. | [Side effects]
Polydextrose is POSSIBLY SAFE when taken by mouth in doses of less than 50 grams per day. Polydextrose can cause intestinal gas (flatulence), bloating, stomach cramps, and diarrhea. Polydextrose is POSSIBLY UNSAFE when taken by mouth in single doses of more than 50 grams or in daily doses of more than 90 grams. | [Safety]
Polydextrose is used in oral pharmaceutical applications, food
products, and confectionery, and is generally regarded as a
relatively nontoxic and nonirritant material.
However, excessive consumption of non-digestible carbohydrates,
such as polydextrose, can lead to gastrointestinal distress.
After evaluating a series of clinical studies, the Joint FAO/WHO
Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) and the European
Commission Scientific Committee for Food (EC/SCF) concluded
that polydextrose was better tolerated than other digestible
carbohydrates such as polyols. The committee concluded that
polydextrose has a mean laxative threshold of approximately
90g/day (1.3 g/kg body-weight) or 50g as a single dose.
(mouse, oral): >30 g/kg
(rat, oral): >15 g/kg | [storage]
Polydextrose powder is hygroscopic and absorbs significant
amounts of moisture at relative humidities greater than 60%.
Under dry storage conditions, and in original sealed packaging,
polydextrose powders can be expected to retain stability for at least
3 years. Solution grades have a shorter shelf-life of 3 to 6 months
(dependent upon grade) at an ambient temperature of 25°C,
although this can be extended to 12 months through the use of
refrigeration.
The bulk material should be stored in a cool, dry place in wellclosed
containers. | [Incompatibilities]
Incompatible with oxidizing agents, strong acids, and alkalis,
forming a brown coloration and depolymerizing. | [Regulatory Status]
Approved as a food additive in over 60 countries worldwide,
including Europe and the USA. Included in the FDA Inactive
Ingredients Database (oral tablets). Included in non-parenteral
medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of
Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. | [References]
[1] Auerbach M, et al. Caloric availability of polydextrose. Nutrition Reviews, 2008; 65: 544–549.
[2] Yang J, et al. Use of corn flour and polydextrose in fried extrudate making: Effects of polydextrose content in the blend and extrusion temperature on the product quality. Journal of Food Process Engineering , 2020; 43: e13438. |
|
|