| Identification | More | [Name]
2,3-Diaminobenzoic acid | [CAS]
603-81-6 | [Synonyms]
2,3-DIAMINOBENZOIC ACID
3-carboxy-1,2-diaminobenzene
2,3-Diaminobenzonicacid | [Molecular Formula]
C7H8N2O2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00137818 | [Molecular Weight]
152.15 | [MOL File]
603-81-6.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
198-204 °C | [Boiling point ]
274.61°C (rough estimate) | [density ]
1.2804 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.5200 (estimate) | [storage temp. ]
Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature | [form ]
solid | [pka]
5.10±0.10(Predicted) | [color ]
Brown to dark brown | [CAS DataBase Reference]
603-81-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
2,3-Diaminobenzoic acid (23DBA) is an important organic reagent mainly used in scientific research and laboratory experiments. 23DBA can undergo polycondensation with terephthalic acid dichloro anhydride[1]. 23DBA isomer is also used in the study of luminescence mechanism of red luminescent carbon dots (RCDs)[2]. In addition, 2,3-Diaminobenzoic acid also possesses antioxidant properties that help reduce the formation of free radicals in the body. It is also used as a chelating agent that effectively binds to metal ions and prevents them from forming insoluble complexes. | [Synthesis]
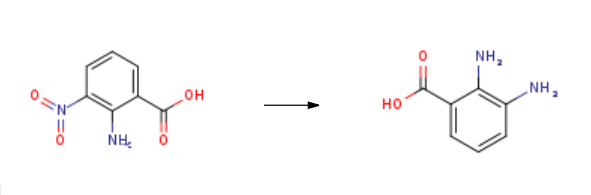
2,3-Diaminobenzoic acid is synthesised using 3-nitroanthranilic acid as a raw material by chemical reaction. The specific synthesis steps are as follows:
2-amino-3-nitrobenzoic acid (9.36 g, 51.4 mmol) was dissolved in MeOH (100 mL) and there was added 10% Pd/C (2.0g). The reaction was stirred under H2-atmosphere (ambient pressure) until absorption ceased. The reaction was filtered through a pad of Celite and the filtrate was evaporated under reduced pressure. The product was purified by flash chromatography (CH2Cl2/MeOH 5:1) and the collected fractions were evaporated to give 2,3-Diaminobenzoic acid (5.40 g, 69%) as a dark brown solid. mp. 199 °C dec. (Litt4. 201 °C dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.09 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (dd, J = 7.4, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 6.34 (dd, J = 8.0, 7.4 Hz, 2H), 6.32 (br s, 4H). 13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 170.5, 139.6, 135.6, 119.4, 117.0, 114.9, 110.3.
 | [References]
[1] V. N. ODNORALOVA. The polycondensation reaction of 2,4-diaminobenzoic acid with dichloroanhydride of terephthalic acid[J]. Fibre Chemistry, 1974. DOI:10.1007/BF00542946.
[2] LIU Y, DING H, ZHANG S, et al. Photoluminescence mechanism of red emissive carbon dots from a diaminobenzoic acid isomer?[J]. Materials Advances, 2023. DOI:10.1039/D3MA00836C.
|
|
|