| Identification | More | [Name]
Carbon tetrachloride | [CAS]
56-23-5 | [Synonyms]
2-PROPENAL
ACRALDEHYDE
ACROLEIN
ACROLEIN MONOMER
ACRYLALDEHYDE
ACRYLIC ALDEHYDE
AKOS BBS-00004228
ALLYLALDEHYDE
AQUALINE MATRIX K
CARBON TETRACHLORIDE
FIXATIVE 15951
MAGNACIDE
PERCHLOROMETHANE
TETRACHLORKOHLENSTOFF
TETRACHLOROMETHANE
Benzenoform
Benzinoform
Benzinofrm
Carbon chloride
Carbon chloride (CCl4) | [EINECS(EC#)]
203-453-4 | [Molecular Formula]
CCl4 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00006998 | [Molecular Weight]
153.82 | [MOL File]
56-23-5.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
Carbon tetrachloride is a colorless, nonflammable liquid with a characteristic ethereal odor. The Odor
Threshold is 0.52 mg/L in water and 140�548 ppm in
air. | [Melting point ]
-23 °C | [Boiling point ]
76-77 °C(lit.)
| [density ]
1.594 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
| [vapor density ]
5.32 (vs air)
| [vapor pressure ]
4.05 psi ( 20 °C)
| [refractive index ]
n20/D 1.460(lit.)
| [Fp ]
−2 °F
| [storage temp. ]
2-8°C
| [solubility ]
Miscible with ethanol, benzene, chloroform, ether, carbon disulfide (U.S. EPA, 1985), petroleum
ether, solvent naphtha, and volatile oils (Yoshida et al., 1983a). | [form ]
Liquid | [color ]
Clear colorless | [Odor]
Ethereal, sweet, pungent odor detectable at 140 to 584 ppm (mean = 252 ppm) | [Relative polarity]
0.052 | [Odor Threshold]
4.6ppm | [Water Solubility ]
0.8 g/L (20 ºC) | [λmax]
λ: 265 nm Amax: 1.0
λ: 270 nm Amax: 0.30
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.07
λ: 290 nm Amax: 0.02
λ: 300-400 nm Amax: 0.01 | [Merck ]
13,1826 | [BRN ]
1098295 | [Henry's Law Constant]
2.15 at 30 °C (headspace-GC, Sanz et al., 1997) | [Dielectric constant]
2.2(20℃) | [Exposure limits]
NIOSH REL: STEL 1 hour 2 ppm, IDLH 200 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA
10 ppm, C 25 ppm, 5-minute/4-hour peak 200 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 5 ppm. | [InChIKey]
VZGDMQKNWNREIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [LogP]
2.830 | [CAS DataBase Reference]
56-23-5(CAS DataBase Reference) | [IARC]
2B (Vol. 20, Sup 7, 71) 1999 | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
Carbon tetrachloride(56-23-5) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
56-23-5(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
T,N,F | [Risk Statements ]
R23/24/25:Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed .
R40:Limited evidence of a carcinogenic effect.
R48/23:Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation .
R52/53:Harmful to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment .
R59:Dangerous for the ozone layer.
R39/23/24/25:Toxic: danger of very serious irreversible effects through inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed .
R11:Highly Flammable. | [Safety Statements ]
S23:Do not breathe gas/fumes/vapor/spray (appropriate wording to be specified by the manufacturer) .
S36/37:Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves .
S45:In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show label where possible) .
S59:Refer to manufacturer/supplier for information on recovery/recycling .
S61:Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions safety data sheet . | [OEL]
STEL: 2 ppm (12.6 mg/m3) [60-minute] | [RIDADR ]
UN 1846 6.1/PG 2
| [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
FG4900000
| [F ]
8-9 | [HazardClass ]
6.1(a) | [PackingGroup ]
II | [HS Code ]
29031400 | [Safety Profile]
Confirmed carcinogen
with experimental carcinogenic,
neoplastigenic, and tumorigenic data. A
human poison by ingestion and possibly
other routes. Poison by subcutaneous and
intravenous routes. Mildly toxic by
inhalation. Human systemic effects by
inhalation and ingestion: nausea or vomiting,
pupdlary constriction, coma, antipsychotic
effects, tremors, somnolence, anorexia,
unspecified respiratory system and
gastrointestinal system effects. Experimental
teratogenic and reproductive effects. An eye
and skin irritant. Damages liver, kidneys,
and lungs. Mutation data reported. A
narcotic. Individual susceptibility varies
widely. Contact dermatitis can result from
skin contact.
resembling that of chloroform, though not
as strong. Following exposure to high
concentrations, the victim may become
unconscious, and, if exposure is not
terminated, death can follow from
respiratory fdure. The aftereffects following
recovery from narcosis are more serious
than those of delayed chloroform poisoning,
usually taking the form of damage to the
kidneys, liver, and lungs. Exposure to lower
ppd6OM
Carbon tetrachloride has a narcotic action
concentrations, insufficient to produce
unconsciousness, usually results in severe
gastrointestinal upset and may progress to
serious hdney and hepatic damage. The
E kidney lesion is an acute nephrosis; the
liver involvement consists of an acute
degeneration of the central portions of the
lobules. When recovery takes place, there
may be no permanent dsability. Marked
variation in individual susceptibdity to
carbon tetrachloride exists; some persons
appear to be unaffected by exposures that
seriously poison their fellow workers.
Alcoholism and previous liver and kidney
damage seem to render the indwidual more
susceptible. Concentrations on the order of
1000 to 1500 ppm are sufficient to cause
symptoms if exposure continues for several
hours. Repeated ddy exposure to such
concentration may result in poisoning.
Though the common form of poisoning
following industrial exposure is usually one
of gastrointestinal upset, which may be
followed by renal damage, other cases have
been reported in which the central nervous
system has been affected, resulting in the
production of polyneuritis, narrowing of the
visual fields, and other neurologcal changes.
Prolonged exposure to small amounts of
carbon tetrachloride has also been reported
as causing cirrhosis of the liver.
Locally, a dermatitis may be produced
following long or repeated contact with the
liquid. The skin oils are removed and the
skin becomes red, cracked, and dry. The
effect of carbon tetrachloride on the eyes
either as a vapor or as a liquid, is one of
irritation with lachrymation and burning.
Industrial poisoning is usually acute with
malaise, headache, nausea, dminess, and
confusion, which may be followed by stupor
and sometimes loss of consciousness.
Symptoms of liver and kidney damage may
follow later with development of dark urine,
sometimes jaundice and liver enlargement,
followed by scanty urine, albuminuria, and
renal casts; uremia may develop and cause
death. Where exposure has been less acute, the symptoms are usually headache,
dizziness, nausea, vomiting, epigastric
distress, loss of appetite, and fatigue. Visual
disturbances (blind spots, spots before the
eyes, a visual "haze," and restriction of the
visual fields), secondary anemia, and
occasionally a slight jaundice may occur.
Dermatitis may be noticed on the exposed
parts.
with particulates of many metals, e.g.,
aluminum (when ball milled or heated to
152' in a closed container), barium (bulk
metal also reacts violently), beryllium,
potassium (200 times more shock sensitive
than mercury fulminate), potassium-sodium
alloy (more sensitive than potassium),
lithium, sodium, zinc (burns ready). Also
forms explosive mixtures with chlorine
trifluoride, calcium hypochlorite (heatsensitive), calcium dtsllicide (frictionand
pressuresensitive), triethyldialuminum
trichloride (heatsensitive), decaborane(l4)
(impact-sensitive), dinitrogen tetraoxide.
Violent or explosive reaction on contact
with fluorine. Forms explosive mixtures
with ethylene between 25' and 105' and
between 30 and 80 bar. Potentially explosive
reaction on contact with boranes. 9:l
mixtures of methanol and cCl4 react
exothermically with aluminum, magnesium,
or zinc. Potentially dangerous reaction with
dimethyl formamide, 1,2,3,4,5,6
hexachlorocyclohexane, or
dtmethylacetamide when iron is present as a
catalyst. CCh has caused explosions when
used as a fire extingusher on wax and
uranium fires. Incompatible with aluminum
trichloride, dtbenzoyl peroxide, potassiumtert-butoxide. Vigorous exothermic reaction
with allyl alcohol, Al(C2H5)3, (benzoyl
peroxide + C2H4), BrF3, diborane, dsilane,
liquid O2, Pu, (AgClO4 + HCl), potassiumtert-butoxide, tetraethylenepentamine,
tetrasilane, trisilane, Zr. When heated to
decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl
and phosgene. It has been banned from
household use by the FDA. See also
Forms impact-sensitive explosive mixtures
CHLORINATED HYDROCARBONS,
ALIPHATIC. | [Hazardous Substances Data]
56-23-5(Hazardous Substances Data) | [Toxicity]
LC50 for mice: 9528 ppm (Svirbely); LD50 in rats, mice, dogs (g/kg): 2.92, 12.1-14.4, 2.3 orally; LD50 in mice (g/kg): 4.1 i.p., 30.4 s.c. (IARC, 1979) | [IDLA]
200 ppm |
| Raw materials And Preparation Products | Back Directory | [Raw materials]
Ethanol-->Sodium hydroxide-->Hydrochloric acid-->Methanol-->Chloroform-->Chlorine-->Carbon disulfide-->METHANE-->Tetrachloroethylene | [Preparation Products]
6-BROMOMETHYL-2-PYRIDINECARBOXYLIC ACID-->DIMETHYL 4-CHLOROPYRIDINE-2,6-DICARBOXYLATE-->IMIDAZO[1,2-A]PYRIDINE-2-CARBOXYLIC ACID ETHYL ESTER-->METHYL 4-(BROMOMETHYL)-3-METHOXYBENZOATE-->5-BROMO-2-(METHYLTHIO)PYRIMIDINE-->2-(AMINOCARBONYL)NICOTINIC ACID-->5-IODOCYTOSINE-->2,6-Dibromopyridin-3-amine-->1-(4-BROMO-2-THIENYL)ETHAN-1-ONE-->Chlorinated rubber-->2-(Chloromethyl)pyridine-->2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone-->Atropine sulfate monohydrate-->1-Bromo-2,4-difluorobenzene-->2,5-DICHLOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE-->trans-Methyl crotonate-->Ethyl 2-amino-4-phenyl-5-thiazolecarboxylate-->5-BROMO-2-METHANESULFONYL-PYRIMIDINE-->2-(2-BROMOACETYL)THIOPHENE-->2-(Bromomethyl)pyridine hydrobromide-->2,4-Dichlorobenzotrifluoride-->2-Nitrobenzyl bromide-->Salicylanilide-->9,10-Dibromoanthracene-->Dimethylthiocarbamoyl chloride-->2,5-Dimethylthiophene-->1-(BROMOMETHYL)-4-(METHYLSULFONYL)BENZENE-->CARBON TETRAIODIDE-->N-Chloromethyl-N-phenylaminoformyl chloride-->4-Bromo-2,6-dichlorophenol-->3-Bromonitrobenzene-->2,3-Dibromo-1-propanol-->Bromotrichloromethane-->1,2,3,4-Tetrachloro-5,6-Dimethylbenzylene-->3,5-DI-T-BUTYL-4-METHOXYBENZALDEHYDE-->Diphenyldichloromethane-->3,4-DIBROMO-4-PHENYL-2-BUTANONE-->Butyl benzoate-->2-Nitrobenzenesulfenyl chloride-->Diacetone acrylamide |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [General Description]
A clear colorless liquid with a characteristic odor. Denser than water (13.2 lb/gal) and insoluble in water. Noncombustible. May cause illness by inhalation, skin absorption and/or ingestion. Used as a solvent, in the manufacture of other chemicals, as an agricultural fumigant, and for many other uses. | [Reactivity Profile]
CARBON TETRACHLORIDE(56-23-5) is a commonly used liquid in fire extinguishers to combat small fires. CARBON TETRACHLORIDE(56-23-5) has no flash point, CARBON TETRACHLORIDE(56-23-5) is not flammable. However, when heated to decomposition, CARBON TETRACHLORIDE(56-23-5) will emit fumes of extremely toxic phosgene and of hydrogen chloride. Forms explosive mixtures with chlorine trifluoride, calcium hypochlorite, decaborane, dinitrogen tetraoxide, fluorine. Forms impact-sensitive explosive mixtures with particles of many metals: lithium, sodium, potassium, beryllium, zinc, aluminum, barium. Vigorous exothermic reaction with allyl alcohol, boron trifluoride, diborane, disilane, aluminum chloride, dibenzoyl peroxide, potassium tert-butoxide, liquid oxygen, zirconium. [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 666]. Potentially dangerous reaction with dimethylformamide or dimethylacetamide in presence of iron [Cardillo, P. et al., Ann. Chim. (Rome), 1984, 74, p. 129]. | [Air & Water Reactions]
Insoluble in water. | [Hazard]
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin
absorption. Do not use to extinguish fire. Narcotic.
A possible carcinogen. Liver damage. Decomposes
to phosgene at high temperatures.
| [Health Hazard]
Dizziness, incoordination, anesthesia; may be accompanied by nausea and liver damage. Kidney damage also occurs, often producing decrease or stopping of urinary output. | [Potential Exposure]
Carbon tetrachloride, and organochlorine, is used as a solvent for oils, fats, lacquers, varnishes,
rubber, waxes, and resins. Fluorocarbons are chemically
synthesized from it. It is also used as an azeotropic drying
agent for spark plugs; a dry-cleaning agent; a fire extinguishing agent; a fumigant, and an anthelmintic agent. The
use of this solvent is widespread, and substitution of less
toxic solvents when technically possible is recommended. | [First aid]
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any
contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least
15 minutes, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek
medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the
skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately
with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately.
If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,
begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if
heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical
facility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce
vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. | [Shipping]
UN1846 Carbon tetrachloride, Hazard Class:
6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. | [Incompatibilities]
Oxidative decomposition on contact with
hot surfaces, flames, or welding arcs. Carbon tetrachloride
decomposes forming toxic phosgene fumes and hydrogen
chloride. Decomposes violently (producing heat) on contact
with chemically active metals, such as aluminum, barium,
magnesium, potassium, sodium, fluorine gas, allyl alcohol,
and other substances, causing fire and explosion hazard.
Attacks copper, lead, and zinc. Attacks some coatings, plastics, and rubber. Becomes corrosive when in contact with
water; corrosive to metals in the presence of moisture. | [Description]
Carbon tetrachloride is a manufactured chemical and does not
occur naturally in the environment. It is produced by chlorination
of a variety of low molecular weight hydrocarbons such
as carbon disulfide, methane, ethane, propane, or ethylene
dichloride and also by thermal chlorination of methyl chloride.
Carbon tetrachloride is a precursor for chlorofluorocarbon
(CFC) gases that have been used as aerosol propellant. A
decrease in this use is occurring due to the agreement reached
in the Montreal Protocol for the reduction of environmental
concentrations of ozone-depleting chemicals, including carbon
tetrachloride. | [Waste Disposal]
Incineration, preferably after
mixing with another combustible fuel; care must be exercised to assure complete combustion to prevent the formation of phosgene; an acid scrubber is necessary to remove
the halo acids produced. Recover and purify by distillation where possible. | [Physical properties]
Carbon tetrachloride is a volatile colourless clear heavy liquid with a characteristic sweet non-irritant odour. The odour threshold in water is 0.52 mg/litre and in air is > 10 ppm. Carbon tetrachloride is miscible with most aliphatic solvents and it is a solvent for benzyl resins, bitumen, chlorinated rubber, rubber-based gums, oils and fats.The solubility in water is low. Carbon tetrachloride is non-flammable and is stable in the presence of air and light. Decomposition may produce phosgene, carbon dioxide and hydrochloric acid.
| [History]
In the 1890s, commercial manufacturing processes were being investigated by the United Alkali Co. in England. At the same time it was also produced in Germany, exported to the United States, and retailed as a spotting agent under the trade name Carbona. Large-scale production of carbon tetrachloride in the United States commenced in the early 1900s. By 1914, annual production fell just short of 4500 metric tons and was used primarily for dry cleaning and for charging fire extinguishers. During World War I, U.S. production of carbon tetrachloride expanded greatly; its use was extended to grain fumigation and the rubber industry. In 1934 it was supplanted as the predominant dry-cleaning agent in the United States by perchloroethylene, which is much less toxic and more stable. During the years immediately preceding World War II, trichloroethylene began to displace carbon tetrachloride from its then extensive market in the United States as a metal degreasing solvent. Carbon tetrachloride is more difficult to recover from degreasing operations, more readily hydrolyzed, and more toxic than trichloroethylene C2HCl3. The demands of World War II stimulated production and marked the beginning of its use as the starting material for chlorofluoromethanes, by far the most important application for carbon tetrachloride. | [Definition]
ChEBI: A chlorocarbon that is methane in which all the hydrogens have been replaced by chloro groups. | [Production Methods]
Carbon tetrachloride is made by the reaction of carbon disulfide and chlorine in the presence of a catalyst, such as iron or antimony pentachloride:
CS2 + 3Cl2 → CCl4 + S2Cl2
Sulfur chloride is removed by treatment with caustic soda solution. The product is purified by distillation.
Alternatively, CCl4 may be prepared by heating a mixture of chlorine and methane at 250 to 400°C.
CH4 + 4Cl2 → CCl4 + 4HCl
| [Flammability and Explosibility]
Carbon tetrachloride is noncombustible. Exposure to fire or high temperatures may
lead to formation of phosgene, a highly toxic gas. | [Chemical Reactivity]
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reactions; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent. | [Industrial uses]
Carbon tetrachloride is a clear, heavy liquid with a strong, aromatic odor. Its formula is CC14. It is produced in large quantities for use in the manufacturing of refrigerants and propellants for aerosol cans. It is also used as a feedstock in the synthesis of chlorofluorocarbons and other chemicals, in petroleum refining, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and general solvent use. Until the mid- 1960s, it was also widely used as a cleaning fluid, both in industry, where it served as a degreasing agent, and in the home, where it was used as a spot remover and in fire extinguishers.
Carbon tetrachloride is a highly volatile liquid with a strong etherial odor similar to chloroform. It mixes sparingly with water and is not flammable. When heated to decomposition, it emits highly toxic fumes of phosgene and hydrogen chloride. There is strong evidence that the toxicity of carbon tetrachloride is dramatically increased by its interaction with alcohols, ketones, and a range of other chemicals.
Carbon tetrachloride is known to deplete the ozone layer, where it is responsible for 17% of the ozone-destroying chlorine now in the stratosphere due to human activities. Carbon tetrachloride has a half-life of between 30 and 100 years.Its DOT Label is Poison, and its UN number is 1846. | [Carcinogenicity]
Carbon tetrachloride is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals. | [Source]
Carbon tetrachloride is used in fumigant mixtures such as 1,2-dichloroethane (Granosan)
because it reduces the fire hazard (Worthing and Hance, 1991). | [Environmental Fate]
Biological. Carbon tetrachloride was degraded by denitrifying bacteria forming chloroform (Smith and Dragun, 1984). An anaerobic species of Clostridium biodegraded
carbon tetrachloride by reductive dechlorination yielding trichloromethane, dichloromethane and unidentified products (G?lli and McCarty, 1989). Chloroform also formed
by microbial degradation of carbon tetrachloride using denitrifying bacteria (Smith and
Dragun, 1984).
Carbon tetrachloride (5 and 10 mg/L) showed significant degradation with rapid
adaptation in a static-culture flask-screening test (settled domestic wastewater inoculum)
conducted at 25°C. Complete degradation was observed after 14 days of incubation (Tabak
et al., 1981).
Chemical/Physical. Under laboratory conditions, carbon tetrachloride partially hydrolyzed to chloroform and carbon dioxide (Smith and Dragun, 1984). Complete hydrolysis
yielded carbon dioxide and hydrochloric acid (Kollig, 1993). Carbon tetrachloride slowly
reacts with hydrogen sulfide in aqueous solution yielding carbon dioxide via the intermediate carbon disulfide. However, in the presence of two micaceous minerals (biotite and
vermiculite) and amorphous silica, the rate of transformation increased. At 25°C and a
hydrogen sulfide concentration of 1 mM, the half-lives for carbon tetrachloride were
calculated to be 2,600, 160 and 50 days for the silica, vermiculite and biotite studies,
respectively. In all three studies, the major transformation pathway is the formation of
carbon disulfide which undergoes hydrolysis yielding carbon dioxide (81–86% yield) and
hydrogen sulfide ions. Minor intermediates detected include chloroform (5–15% yield),carbon monoxide (1–2% yield) and a nonvolatile compound tentatively identified as formic
acid (3–6% yield) (Kriegman-King and Reinhard, 1992).
Anticipated products from the reaction of carbon tetrachloride with ozone or hydroxyl
radicals in the atmosphere are phosgene and chloride radicals (Cupitt, 1980). Phosgene is
hydrolyzed readily to hydrochloric acid and carbon dioxide (Morrison and Boyd, 1971).
Matheson and Tratnyek (1994) studied the reaction of fine-grained iron metal in an
anaerobic aqueous solution (15°C) containing carbon tetrachloride (151 μM). Initially,
carbon tetrachloride underwent rapid dehydrochlorination forming chloroform, which
further degraded to methylene chloride and chloride ions. The rate of reaction decreased
with each dehydrochlorination step. However, after 1 hour of mixing, the concentration
of carbon tetrachloride decreased from 151 to approximately 15 μM. No additional products were identified although the authors concluded that environmental circumstances may
exist where degradation of methylene chloride may occur. They also reported that reductive
dehalogenation of carbon tetrachloride and other chlorinated hydrocarbons used in this
study appears to take place in conjunction with the oxidative dissolution or corrosion of
the iron metal through a diffusion-limited surface reaction.
The evaporation half-life of carbon tetrachloride (1 mg/L) from water at 25°C using
a shallow-pitch propeller stirrer at 200 rpm at an average depth of 6.5 cm is 29 minutes
(Dilling, 1977).
| [storage]
Carbon tetrachloride should be handled in the laboratory using the "basic prudent
practices". | [Purification Methods]
For many purposes, careful fractional distillation gives adequate purification. Carbon disulfide, if present, can be removed by shaking vigorously for several hours with saturated KOH, separating, and washing with water: this treatment is repeated. The CCl4 is shaken with conc H2SO4 until there is no further coloration, then washed with water, dried with CaCl2 or MgSO4 and distilled (from P2O5 if desired). It must not be dried with sodium. An initial refluxing with mercury for 2hours removes sulfides. Other purification steps include passage of dry CCl4 through activated alumina, and distillation from KMnO4. Carbonyl containing impurities can be removed by percolation through a Celite column impregnated with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH), H3PO4 and water. (Prepared by dissolving 0.5g DNPH in 6mL of 85% H3PO4 by grinding together, then mixing with 4mL of distilled water and 10g Celite.) [Schwartz & Parks Anal Chem 33 1396 1961]. Photochlorination of CCl4 has also been used: CCl4 to which a small amount of chlorine has been added is illuminated in a glass bottle (e.g. for 24hours with a 200W tungsten lamp near it), and, after washing out the excess chlorine with 0.02M Na2SO3, the CCl4 is washed with distilled water and distilled from P2O5. It can be dried by passing through 4A molecular sieves and distilled. Another purification procedure is to wash CCl4 with aqueous NaOH, then repeatedly with water and N2 gas is bubbled through the liquid for several hours. After drying over CaCl2 it is percolated through silica gel and distilled under dry N2 before use [Klassen & Ross J Phys Chem 91 3664 1987]. [Beilstein 1 IV 56.] | [Toxicity evaluation]
Most of the carbon tetrachloride produced is released to the
atmosphere. In the atmosphere, photodegradation by shorter
wavelength ultraviolet radiation appears to be the primary
removal process although it is very stable in the environment
remaining in the air for several years before breaking down, so
a significant global transport is expected. The estimated half-life
of atmospheric carbon tetrachloride is 30–100 years. Small
amounts can be released to the water but due to the relatively
high rate of volatilization from water, carbon tetrachloride
tends to evaporate in a short time. It is stable to hydrolysis in
water. Most of the amount released to soil evaporates rapidly
due to its high vapor pressure but a small proportion could
remain associated to the soil organic matter. Carbon tetrachloride
is mobile in most soils depending on the organic
carbon content and can reach groundwater where it remains for
long periods before it is broken down to other chemicals. | [Toxics Screening Level]
The initial threshold screening level (ITSL) for carbon tetrachloride is 480 μg/m3 based on an annual averaging time. |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Organic solvents]
Carbon tetrachloride, also known as tetrachloromethane, has its molecule formula being CCl4. It appears as colorless liquid with the melting point of-23 ° C, boiling point of 76.8 ° C and the relative density of 1.5867. It can dissolve grease, paint, resin, rubber and many other substances, being commonly used organic solvent and extractant. It can also be used as dry cleaning agent. However, long-term exposure to carbon tetrachloride will irritate the skin, inhibit the central nervous system and cause damage to the liver and kidney. Therefore, the operator should pay special attention. Carbon tetrachloride is volatile with its vapor being heavier than air, being non-conductive and inflammable. When the carbon tetrachloride is heat to be evaporated to become heavy steam, the gas will cover the combustion products, so that the firing product is isolated from the air and the fire is extinguished. It is especially suitable for extinguishing oil fire and fire near the power. However, carbon tetrachloride, at high temperature (500 ℃ above), can react with water to produce highly toxic phosgene, so we should pay attention to ventilation for extinguishing fire.
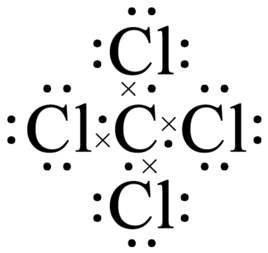
carbon tetrachloride lewis structure
| [Chemical Properties]
Carbon tetrachloride is a clear, colorless liquid with a distinctive, sweet ether-like odor. It is toxic and forms phosgene, hydrogen chloride, and chlorine when heated. It has a water solubility of 1160 mg/l and is miscible with various organic solvents. It is mildly reactive with lead and copper and can be reduced to chloroform in the presence of zinc and an acid. | [Uses]
Most of the carbon tetrachloride produced is used in the production of CFCs, which were primarily used as refrigerants, propellants, foam-blowing agents and solvents and in the production of other chlorinated hydrocarbons.
Carbon tetrachloride has been used as a grain fumigant, pesticide, solvent for oils and fats, metal degreaser, fire extinguisher and flame retardant, and in the production of paint, ink, plastics, semi-conductors and petrol additives. It was previously also widely used as a cleaning agent. All these uses have tended to be phased-out as production has dropped (ECDIN, 1992; ATSDR, 1994).
| [Chemical reaction]
Carbon tetrachloride molecule exhibits tetrahedral structure, belonging to non-polar molecule. It chemical reactivity was inert, but being more active than chloroform. At 250 ℃ with the presence of water, it can react with some metals to produce carbon dioxide; Upon anhydrous condition, the reaction between carbon tetrachloride and metal is very slow.
CCl4 + 2H2O→CO2 + 4HCl
Carbon tetrachloride is decomposed by water in the presence of metals such as aluminum and iron (catalyzed). If it is superheated steam, even without the presence of metal catalyst, carbon tetrachloride can also be decomposed to produce phosgene.
CCl4 + H2O →COCl2 + 2HCl
In the case of heating, carbon tetrachloride can have reaction with halogen salt, generating other kinds of tetrahalide. For example, its reaction with silver fluoride can generate carbon tetrafluoride; its reaction with aluminum bromide and calcium iodide can generate carbon tetrabromide and tetra-iodide.
In the presence of trace amount of hydrogen chloride, the product can react with silver perchlorate, generating explosive compounds Cl3CClO4:
CCl4 + AgClO4 → Cl3CClO4 + AgCl
In the presence of antimony pentachloride catalyst, this product can react with hydrogen fluoride to generate fluoride methyl chloride, such as monofluorotrichloromethane, difluorodichloromethane, namely, Freon refrigerant.
CCl4 + HF→CCl3F + HCl
CCl4 + 2HF→CCl2F2 + HCl
Carbon tetrachloride can react with sulfur at high temperatures (above 200 ° C) to produce carbon disulfide.
CCl4 + 6S → CS2 + 2S2Cl2
Under the catalysis of anhydrous aluminum chloride, carbon tetrachloride can react with benzene, generating triphenyl methane.
Under the catalysis of iron or iron salt, heating to 330 ℃ can promote the oxidation of carbon tetrachloride decomposition, generating phosgene.
2CCl4 + O2 →2COCl2 + 2Cl2 | [Preparation]
Carbon tetrachloride, CCl4 (i.e., tetrachloromethane) is prepared by the action of chlorine on carbon disulphide in the presence of iodine, which acts as a catalyst.
CS2 + Cl2= CCl4 + S2Cl2
Carbon tetrachloride may also be prepared by the free radical substitution of the hydrogen atoms of methane by chlorine.
CH4 + 4Cl2 = CCl4 + 4HCl
The bonding in carbon tetrachloride is covalent, as in methane.
|
|