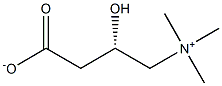
| Identification | More | [Name]
L(-)-Carnitine | [CAS]
541-15-1 | [Synonyms]
3-CARBOXY-N,N,N-TRIMETHYL-2-PROPEN-1-AMINIUM CHLORIDE
3-HYDROXY-4-(TRIMETHYLAMMONIO)-BUTANOAT
3-HYDROXY-4-(TRIMETHYLAMMONIO)BUTANOATE
3-HYDROXY-GAMMA-(TRIMETHYLAMMONIO)-BUTYRATE
BETA-HYDROXY-GAMMA-TRIMETHYLAMINOBUTYRIC ACID
(-)-BETA-HYDROXY-GAMMA-TRIMETHYLAMINOBUTYRIC ACID INNER SALT
[(-)-BETA-HYDROXY-GAMMA-TRIMETHYLAMMONIO]BUTYRATE
B-HYDROXY-GAMMA-TRIMETHYLAMINOBUTYRIC ACID
BICARNESINE
CARNIFEED(R)
CARNIKING(R)
CARNITINE, L-
CAR-OH
D(+)-CARNITINE
D-CARNITINE
GAMMA-AMINO-BETA-HYDROXYBUTYRIC ACID TRIMETHYL BETAINE
L-CARNITHINE
L-CARNITIN
L(-)-CARNITINE
L-CARNITINE | [EINECS(EC#)]
208-768-0 | [Molecular Formula]
C7H15NO3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00038747 | [Molecular Weight]
161.2 | [MOL File]
541-15-1.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
White crystalline | [Melting point ]
197-212 °C(lit.)
| [alpha ]
-31 º (c=10, H2O) | [Boiling point ]
287.5°C (rough estimate) | [bulk density]
636kg/m3 | [density ]
0.64 g/cm3 | [refractive index ]
-32 ° (C=1, H2O) | [storage temp. ]
2-8°C
| [solubility ]
H2O: 0.1 g/mL at 20 °C, clear, colorless
| [form ]
Crystals or Crystalline Powder | [pka]
3.80(at 25℃) | [color ]
White | [PH]
6.5-8.5 (50g/l, H2O) | [biological source]
synthetic | [optical activity]
L -23.930 (c 0.86, H2O)D +30.9 | [Water Solubility ]
2500 g/L (20 ºC) | [Usage]
Essential cofactor of fatty acid metabolism; required for the transport of fatty acids through the inner mitochondrial membrane. Synthetized primarily in the liver and kidney; highest concentrations found in heart and skeletal muscle. Dietary source | [Merck ]
14,1849 | [BRN ]
4292315 | [Stability:]
Hygroscopic | [InChIKey]
PHIQHXFUZVPYII-ZCFIWIBFSA-N | [LogP]
-5.48 at 20℃ | [CAS DataBase Reference]
541-15-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing .
S37/39:Wear suitable gloves and eye/face protection . | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
BP2980000
| [F ]
3-10 | [Autoignition Temperature]
>365 °C | [Hazard Note ]
Irritant | [HS Code ]
29239000 | [Hazardous Substances Data]
541-15-1(Hazardous Substances Data) | [Toxicity]
LD50 orally in Rabbit: > 5000 mg/kg |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
L-carnitine, also known as L-carnitine and vitamin BT, the chemical formula is C7H15NO3, the chemical name is (R)-3-carboxyl-2-hydroxy-n, N, n-trimethylammonium propionate hydroxide internal salt, and the representative drug is L-carnitine. It is a kind of amino acid that promotes the conversion of fat into energy. The pure product is white crystal or white transparent fine powder. It is very soluble in water, ethanol and methanol, slightly soluble in acetone, and insoluble in ether, benzene, chloroform and ethyl acetate. L-carnitine is easy to absorb moisture, has good water solubility and water absorption, and can withstand high temperatures above 200 ℃. It has no toxic and side effects on human body. Red meat is the main source of L-carnitine, which can also be synthesized by human body to meet physiological needs. It is not a real vitamin, but a substance similar to vitamins. It has many physiological functions such as fat oxidative decomposition, weight loss and anti fatigue. As a food additive, it is widely used in infant food, weight loss food, athlete food, nutritional supplements for the middle-aged and elderly, nutritional fortifiers for vegetarians and animal feed additives. | [Chemical Properties]
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, hygroscopic. | [Physical properties]
The appearance is white lens or white transparent fine powder, with a slight special fishy smell. Very soluble in water, ethanol and methanol, slightly soluble in acetone, insoluble in ether, benzene, chloroform and ethyl acetate. It is easy to absorb moisture, and will deliquesce or even liquefy when exposed to air. It can be placed in the solution with pH value of 3 ~ 6 for more than 1 year, and can withstand the high temperature of more than 200 ℃. Its combined bond and binding group have good water solubility and water absorption. The specific rotation is - 30 ± 1 °. | [Originator]
Carnitene,Sigma Tau Industrie,Italy | [Occurrence]
Synthetic. It is found in its natural state in food | [Uses]
antimethemoglobinemic, cyanide antidote | [Uses]
Carniking(R) is a product for premix- and feed industry. It is particularly recommended for the enrichment of compound feed. | [Uses]
Essential cofactor of fatty acid metabolism; required for the transport of fatty acids through the inner mitochondrial membrane. Synthetized primarily in the liver and kidney; highest concentrations f
ound in heart and skeletal muscle. Dietary sources include red meat, dairy products, beans, avocado. | [Uses]
L-Carnitine is a natural, vitamin-like nutrient wich plays an important role inhuman metabolism. It is essential in the utilization of fatty acids and in transporting metabolic energy | [Uses]
Natrulon(R) RC-100 is 100% L-Carnitine. This white crystalline powder, highly hygroscopic and amino acid like material brings not only the exfoliation but also, an additional benefit of a high level of moisturization capability. | [Uses]
Natrulon(R) RC-50DG is a 50% solution of L-Carnitine in decaglycerol/water. Natrulon(R) RC-50DG to provide a truly multi-functional product: an exfoliating product with excellent moisturization capability. | [Definition]
ChEBI: The (R)-enantiomer of carnitine. | [Manufacturing Process]
9.3 g of epichlorohydrin was added at a temperature of 40°-50°C under
stirring to 9.6 g of trimethylamine hydrochloride dissolved in 10 cc of water.
Continuing the reaction for an hour at the above temperature, the reaction
product was concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain the crystals of 3-
chloro-2-oxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride which were recrystallized
with 25 cc of ethanol. The crystals obtained by concentrating the mother
liquor were also recrystallized. The yield was 17.4 g (MP 190°C, yield 91.5%).
This substance occurs as white, somewhat hygroscopic crystals and is readily
soluble in water or alcohol, but insoluble in benzene, toluene, ether, acetone
or chloroform.
The result of analysis assuming (C6H15C10N)+Cl--calculated value: N, 7.45%;
total Cl, 37.7%; Cl-, 18.88%. Observed value: N, 7.36%; total Cl, 37.54%;
Cl-, 18.98%.
18.8 g of 3-chloro-2-oxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride was dissolved in
a mixed solvent composed of 19 cc of methanol and 1 cc of water. 5.1 g of
sodium cyanide dissolved in 8 cc of water was dropped into the solution at
50°C under stirring. After dropping, the mixture was held at this temperature
for 30 minutes under stirring. The reaction product was then neutralized with
6 N hydrochloric acid toward pH 5, and, after cooling, sodium chloride
separated out and was filtered. The filtrate was concentrated to dryness under
reduced pressure, and the residue was washed with small quantity of ethanol.
Drying the residue, dissolving in hot methanol, filtering off insoluble matters,
and cooling mother liquor, the crystals of 3-cyano-2-axypropyl trimethyl
ammonium chloride which deposited out were filtered and dried. Yield 16.7 g
[MP (decomposition) 220°-223°C, yield 93.4%].
12.5 cc of concentrated hydrochloric acid was added to 17.9 g of 3-cyano-2-
oxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride. Gradually heating the mixture on a
water bath under stirring, so bringing the temperature up to 98°C at the end
of about 3 hours, 9 cc of water was added. After cooling, free hydrochloric
acid was neutralized with 3 cc of 6 N sodium hydroxide, and then by adding 1
g of active charcoal, the reaction product was decolorized and filtered. The
filtrate was concentrated to almost dryness under reduced pressure. Then,
this concentrate was, after washing with 10 cc of ethanol, dried. Yield 24.7 g.
The dried product was dissolved in 46.5 cc of glacial acetic acid by heating on
a boiling water bath. The insoluble matter is removed by filtering hot, and on
cooling the mother liquor, crystals of carnitine hydrochloride separated out.
The crystals were filtered, washed with 10 cc of ethanol, and dried.
Recrystallizing 19.7 g of the crude carnitine with methanol, 17 g of the refined
carnitine was obtained [MP 195°-198°C (decomposing point), yield 86%], The
overall yield of the refined carnitine through whole steps was about 74%.
Carnitine thus prepared was an odorless, white, crystalline powder, having a
strong acid taste. | [Brand name]
Carni tor (Sigma-Tau). | [Therapeutic Function]
Appetite stimulant | [General Description]
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Levocarnitine is a naturally available compound that plays a significant role in fatty acid oxidation and energy production in the human body. It is majorly found in skeletal and cardiac muscles of mammals and facilitates the transport of long chain fatty acids into mitochondria. | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
Carnitine is a quaternary amine that occurs naturally in most mammalian tissue. It is present in relatively high concentrations in skeletal muscle and heart where it is involved in regulating energy metabolism. It shifts glucose metabolism from glycolysis to glycogen storage and enhances the transport of long chain fatty acids into the mitochondria where they are oxidized for energy production. | [Purification Methods]
The S(L) isomer is levocarnitine, Vitamin B7. The R or S isomers crystallise from EtOH/Me2CO (hygroscopic). The R or S hydrochlorides crystallise from hot EtOH or EtOH/Et2O and have m 142o(dec). The RS-isomer crystallises from hot EtOH (hygroscopic). The RS hydrochloride crystallises in needles from hot EtOH and has m 196o(dec). [(±) Mazzetti & Lemmon J Org Chem 22 228 1957, Beilstein 4 H 513, 4 I 548, 4 II 937-8, 4 III 1632-5, 4 IV 3185.] |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Indications and Usage]
Carnitine is a type of vitamin B, and its structure is similar to that of amino acids. It is mainly used to help transport long-chain fatty acids to provide energy and to prevent fat from collecting in the heart, liver, and skeletal muscles. Carnitine can prevent disordered fat metabolism due to diabetes, fatty liver disease and heart disease, and it can reduce heart damage, lower blood triglyceride, aid in weight loss, and increase the antioxidant effects of vitamin E and C. Meats and giblets are high in carnitine. Artificially synthesized carnitine includes L-carnitine, D-carnitine, and DL-carnitine, and only L-carnitine has physiological activities. On the other hand, D-carnitine and DL-carnitine competitively inhibit the activity of carnitine acetyltransferase (CAT) and carnitine palmitoyltransferase (PTC) to prevent cells’ fat metabolism, thus harming human nutrition. L-carnitine was first discovered in 1905 by Russian chemists Gulewitsch and Krimberg in infusion broth, and its chemical structure was determined in 1927 by Tomita and Senju. L-carnitine is a white crystalline or transparent powder, and its melting point is 200℃ (decompose). It is easily soluble in water, lye, methanol and ethanol, barely soluble in acetone and acetate, and insoluble in chloroform. It is hygroscopic.
L-carnitine can be used as an animal nutrition enhancer, and it is mainly used to enhance protein-based food additives to promote fat absorption and utilization. L-carnitine also is a nutrition enhancer that is mainly used in soy-based infant foods, sports nutritional foods and weight loss foods to promote fat absorption and utilization. According to China’s regulations, the permitted amount in biscuits, drinks, and dairy beverages is 600-3000mg/kg; in solid beverages, liquids, and gel capsules, 250-600mg/kg; in formula, 300-400mg/kg; in infant foods, 70-90mg/kg (1g tartrate is equivalent to 0.68g l-carnitine). L-carnitine can also be used as an appetite booster. L-carnitine affects the elimination and utilization of ketone bodies, so it can be used as a biological antioxidant to eliminate free radicals, maintain membrane stability, increase animal immunity and resistance to disease and stress. Oral L-carnitine can increase the speed of sperm maturation and sperm vitality, it can increase the number of forward-moving sperm and motile sperm in oligospermia and asthenospermia patients, thus increasing the women’s clinical pregnancy rate, and it does so safely and effectively. L-carnitine can bind with organic acids and the large amounts of acyl coenzyme derivatives produced in children with fatty acid metabolism disorder and turn them into water soluble acylcarnitine to be excreted through urine. This not only aids in controlling acute acidosis occurrences, but also effectively improves long-term prognosis.
| [Mechanisms of Action]
L-carnitine cannot participate in protein biosynthesis, but it promotes ketone body utilization and nitrogen generation to an extent. Its main function is to promote fatty acid beta oxidation, which occurs in the liver and the mitochondria of other tissue cells. It is known that free fatty acids and acyl coenzyme A cannot penetrate the inner mitochondrial membrane, but acylcarnitine can do so swiftly. Thus, it is determined that L-carnitine is the carrier that transports fatty acid and acyl forms into the mitochondrial membrane. The mechanisms of this transporting process are still unknown, but it is certain that carnitine acyl-CoA transferase is the key enzyme in this process. It has two isoenzymes, one of which is carnitine acyl-CoA transferase I, positioned on the outer side of the membrane. When fatty acid is catalyzed by acyl-CoA-synthatase to produce acyl-CoA, it is transported by carnitine acyl-CoA transferase I into the membrane. After it has entered the membrane, it is catalyzed by the second isoenzyme - carnitine acyl-CoA transferase II – to turned into a form of acyl-CoA that can be directly utilized by fatty acid catabolic enzymes. Afterwards, it releases energy through processes such as dehydrogenation and deoxygenation.
L-carnitine can also adjust the acyl ratio in mitochondria, thus affecting energy metabolism. L-carnitine can participate in the transportation of branched chain amino acid metabolites, which encourages the regular metabolism of branched chain amino acid.
| [Pharmacokinetics]
L-Carnitine is very easily soluble in water, and can be entirely absorbed by the human body when consumed through food. It is known that the small intestine absorbs L-carnitine, but there is little known about the specific absorption process of carnitine (free or esterified) through intestine mucosa and about the specific absorption area. Besides external food sources of carnitine, humans can also synthesize carnitine with their own bodies. The liver and kidneys are mainly responsible for synthesizing carnitine. They progress from lysine into epsilon beta hydroxy three methyl lysine, and use aldolase and aldehyde oxidase to transform it into L-carnitine. Besides lysine, the body’s biosynthesis of L-carnitine also requires methionine, vitamin C, nicotinic acid and vitamin B6.
A rat dissection showed that carnitine is most concentrated in the adrenal gland, followed by the heart, bones, muscles, fat tissue, and liver, and the carnitine concentration in the kidneys and brain are 40 times that in blood. Human carnitine concentration has varied greatly due to inconsistencies in measuring method and test subject. The biological method of testing human blood carnitine content placed it between 0.86-2.87mg/100ml, and the enzymology method of testing muscle carnitine content placed it between 0.457-2.479μg/g. The absorbed carnitine is metabolized by the human body and excreted in urine as free carnitine.
|
|
|