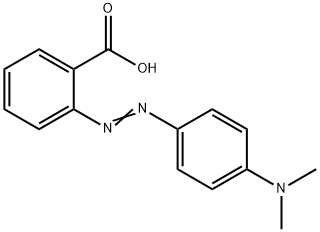
| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Methyl Red | [CAS]
493-52-7 | [Synonyms]
ACID RED
S NO 250
Nsc 9597
Nsc 34729
Nsc 215212
ACID RED 2
METHYL RED
ciacidred2
C.I. 13020
o-methylred
CI NO 13020
c.i.acidred2
o-Methyl red
cervenkysela2
cervenmethylova
C.I. Acid Red 2
methyl red, acs
ORTHO-METHYLRED
Cerven kysela 2
Methyl Red
Methyl Red, Pure
Cerven methylova
METHYL RED ETHANOL
METHYL RED, NEUTRAL
MethylRed(AcidRed2)
Methyl red,CI 13020
Methyl Red Solution
Methyl red chloride
METHYL RED FREE ACID
MethylRedIndicatorGr
MethylRedIndicatorPa
METHYL RED INDICATOR
METHYL RED SOLUTION R
Methyl red, Certified
Methyl Red, ACS reagent
Acid red 2 (C.I. 13020)
Methyl Red Free Acid ACS
METHYL RED PI MARKER 3.8
Methyl Red (CI x 13020)
Methyl Red,pure,indicator
METHYL RED, WATER SOLUBLE
METHYL RED MIXED SOLUTION
METHYL RED, SPIRIT SOLUBLE
METHYL RED MIXED SOLUTION R
METHYL RED (C.I. no 13020 )
Methyl Red, indicator, pure
Methyl Red, Neutral, Reagent
BROMOCRESOL GREEN-METHYL RED
METHYL RED-BROMOCRESOL GREEN
Methyl Red, For analysis ACS
Methyl red, For ACS analysis
METHYLRED,NEUTRAL,REAGENT,ACS
METHYL RED SOLUTION I08 100 ML
MethylRedWaterSolubleC.I.13020
Methyl Red,pure,conform to ACS
Methyl Red free acidACS reagent
Methyl Red Solution [for Spray]
Methyl Red TS, USP Test Solution
Methyl Red, indicator, pure 25GR
Methyl Red, conform to ACS, pure
METHYL RED CRYSTALS A.C.S. REAGENT
METHYL RED INDICATOR, REAG. PH. EUR.
BROMOCRESOL GREEN-METHYL RED ETHANOL
4-dimethylamino-2’-carboxylazobenzene
4-Dimethylamino-2'-carboxylazobenzene
METHYL RED (C.I. 13020) INDICATOR ACS
2-Carboxy-4'-(dimethylamino)azobenzene
2-carboxy-4’-(dimethylamino)azobenzene
(0.04% in Water) [for pH DeterMination]
O-(P-DIMETHYLAMINOPHENYLAZO)BENZOIC ACID
dimethylaminoazobenzene-2-carboxylicacid
METHYL RED SOLUTION, ACID-BASE INDICATOR
2-((4-dimethylamino)phenylazo)-benzoicaci
2-[4-(DIMETHYLAMINO)PHENYLAZO]BENZOIC ACID
4-(2-Carboxyphenylazo)-N,N-dimethylaniline
Benzoic acid, 2-4-(dimethylamino)phenylazo-
2-((4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)azo)-benzoicaci
P-DIMETHYLAMINOAZOBENZENE-O-CARBOXYLIC ACID
4-DIMETHYLAMINOAZOBENZENE-2-CARBOXYLIC ACID
2-[[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]azo]-benzoicaci
4-DIMETHYLAMINOAZOBENZENE-2'-CARBOXYLIC ACID
2-[(p-dimethylamino)-phenyl]azobenzoic acid
BROMOCRESOL GREEN/METHYL RED, MIXED INDICATOR
Benzoic acid, o-((p-(dimethylamino)phenyl)azo)-
P-(dimethylamino)-azobenzene-o-carboxylic Bacid
4′-(dimethylamino)- Aazobenzene-2-carboxylic acid
Methyl Red (0.04% in Water) [for pH Determination]
Methyl Red (0.1% in ca. 95% Ethanol) [for Titration]
2-((E)-[4-(Dimethylamino)phenyl]diazenyl)benzoic acid
Benzoicacid, 2-[2-[4-(diMethylaMino)phenyl]diazenyl]-
4-Dimethylaminoazobenzene-2'-carboxylic Acid
Acid Red 2
BROMOCRESOL GREEN/METHYL RED, MIX INDICATOR FOR ALKALINITY
Bromocresol Green/Methyl Red, mixed indicator solution
2-(4-Dimethylaminophenylazo)benzoic acid, 4-Dimethylaminoazobenzene-2μ-carboxylic acid, Acid Red2 | [EINECS(EC#)]
207-776-1 | [Molecular Formula]
C15H15N3O2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00002425 | [MOL File]
493-52-7.mol | [Molecular Weight]
269.3 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
dark red crystalline powder | [Melting point ]
178-182°C | [Boiling point ]
412.44°C (rough estimate) | [bulk density]
300-500kg/m3 | [density ]
0.839 g/mL at 25 °C | [vapor density ]
9.3 (vs air)
| [refractive index ]
1.5930 (estimate) | [Fp ]
11 °C | [storage temp. ]
−20°C | [solubility ]
ethanol: soluble1mg/mL | [Colour Index ]
13020 | [form ]
Solid | [pka]
4.95(at 25℃) | [color ]
Reddish-violet | [Odor]
Odorless | [PH Range]
4.4(red)-6.3(yellow) | [Stability:]
Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. | [Water Solubility ]
Practically insoluble in water. Soluble in alcohol, acetic acidSoluble in ethanol. Insoluble in water. | [ε(extinction coefficient)]
≥10000 at 282-288nm in methanol
≥20000 at 509-519nm in methanol
≥7000 at 329-335nm in methanol | [λmax]
410nm, 530nm, 427nm, 519nm | [Merck ]
14,6119 | [BRN ]
750102 | [Major Application]
Waveguides, LED sensors, photoresists, liquid crystals, sol-gel matrix, optical sensors, paints, toys, detection of thiols, food freshness sensors, dental product, saliva sampling method, detecting lactic acid, carbohydrates | [InChIKey]
CEQFOVLGLXCDCX-MSUUIHNZSA-N | [CAS DataBase Reference]
493-52-7 | [IARC]
3 (Vol. 8, Sup 7) 1987 | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
Benzoic acid, 2-[[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]azo]-(493-52-7) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
Benzoic acid, 2-[[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl] azo]-(493-52-7) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
dark red crystalline powder | [Uses]
Used as pH indicator. | [Definition]
ChEBI: An azo dye consisting of benzoic acid substituted at position 2 by a 4-[(dimethylamino)phenyl]diazenyl group. | [Uses]
As indicator in 0.1% alcoholic solution; pH: 4.4 red, 6.2 yellow. Used for titrating NH3, weak organic bases, e.g., alkaloids; not suitable for organic acids, except oxalic and picric acid. Methyl red is easily reduced, thereby losing its color, and readings should be made promptly. It is gradually being replaced by sulfonphthalein indicators, such as bromcresol green, which are more stable and exhibit a sharper change in color. | [Hazard]
Questionable carcinogen. | [Preparation]
2-Aminobenzoic acid?diazo, and N,N-dimethylaniline coupling. | [General Description]
Methyl red solution is an azo dye which turns to red when pH is below 4.4 (yellow pH < 6.2, orange pH 4.4-6.2). Some bacteria utilize glucose to form large amounts of acid with the result that the pH value of the medium falls distinct. Other species produce no or less free acid. This difference can be visualized by using methyl red. This test is used to differentiate enteric bacteria. | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
Methyl Red is a maroon red crystal azo dye. Methyl Red is a pH indicator and changes color at a pH of 5.5. Methyl Red is widely used in saliva sampling method. In addition, it is also employed in carbohydrate and lactic acid detection. Methyl Red has been effectively used for intrageneric differentiation of Enterobacteriaceae. | [Properties and Applications]
moderate soluble in ethanol, insoluble in water. Alcohol solution to join hydrochloric acid for purple; Add sodium hydroxide to dim yellow. | [Purification Methods]
The acid is extracted with boiling toluene using a Soxhlet apparatus. The crystals which separate on slow cooling to room temperature are filtered off, washed with a little toluene and recrystallised from glacial acetic acid, *benzene or toluene followed by pyridine/water. Alternatively, dissolve it in aqueous 5% NaHCO3 solution, and precipitate it from a hot solution by dropwise addition of aqueous HCl. Repeat this until the extinction coefficients do not increase. [Beilstein 16 IV 504.] |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Description]
Methyl red is a commonly used indicator for acid-base titrations. This chemical is usually yellow but turns red below pH 4.0. Bacteria exhibiting mixed acids fermentation will accumulate acids in the medium, resulting in a color change. Approximately five drops of methyl red reagent are added to an overnight culture grown in MRVP broth to determine the test result.
Different bacteria convert dextrose and glucose to pyruvate using different metabolic pathways. Some of these pathways produce unstable acidic products which quickly convert to neutral compounds. Some organisms use the butylene glycol pathway, which produces neutral end products, including acetoin and 2,3-butanediol. Other organisms use the mixed acid pathway, which produces acidic end products such as lactic, acetic, and formic acid. These acidic end products are stable and will remain acidic.
The Methyl Red test involves adding the pH indicator methyl red to an inoculated tube of MR-VP broth. If the organism uses the mixed acid fermentation pathway and produces stable acidic end-products, the acids will overcome the buffers in the medium and produce an acidic environment in the medium. When methyl red is added, if acidic end products are present, the methyl red will stay red.
|
|
|