| Identification | More | [Name]
Sodium dodecylbenzenesulphonate | [CAS]
25155-30-0 | [Synonyms]
ALKYLARYL SULFONATE
ALKYLBENZENESULFONIC ACID SODIUM SALT
ARYLSULFONAT
DDBS
DODECENE-1 LAS
DODECYLBENZENE SODIUM SULFONATE
DODECYLBENZENESULFONIC ACID SODIUM SALT
DODECYLBENZENESULPHONIC ACID SODIUM SALT
LAS-C12
LAURYLBENZENESULFONIC ACID SODIUM SALT
LINEAR-DODECYLBENZENESULFONIC ACID SODIUM SALT
NACCONAL
P-N-DODECYLBENZENESULFONIC ACID SODIUM SALT
SODIUM ALKYLARYLSULFONATE
SODIUM ALKYLARYLSULFONATE BRANCHED
SODIUM ALKYLBENZENESULFONATE
Sodium dodecyl-benzenesuffonate
SODIUM DODECYLBENZENESULFONATE
SODIUM LAURYLBENZENESULFONATE
SODIUM LINEAR-ALKYLBENZENESULFONATE | [EINECS(EC#)]
246-680-4 | [Molecular Formula]
C18H29NaO3S | [MDL Number]
MFCD00011508 | [Molecular Weight]
348.48 | [MOL File]
25155-30-0.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white or light yellow flakes | [Melting point ]
>300 °C | [Boiling point ]
660.62℃[at 101 325 Pa] | [density ]
1.02 g/cm3 | [vapor pressure ]
0Pa at 25℃ | [refractive index ]
1.359 | [storage temp. ]
2-30°C | [form ]
powder
| [pka]
0.7[at 20 ℃] | [color ]
light yellow
| [Odor]
Slight, characteristic odor | [Stability:]
Stable. | [Water Solubility ]
800mg/L at 25℃ | [Merck ]
8612 | [BRN ]
4171051 | [InChIKey]
JHJUUEHSAZXEEO-UHFFFAOYSA-M | [LogP]
1.96 at 25℃ | [CAS DataBase Reference]
25155-30-0(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
25155-30-0(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xn | [Risk Statements ]
R22:Harmful if swallowed.
R37/38:Irritating to respiratory system and skin .
R41:Risk of serious damage to eyes. | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S27:Take off immediately all contaminated clothing .
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection . | [RIDADR ]
3077 | [WGK Germany ]
2
| [RTECS ]
DB6825000
| [HazardClass ]
9 | [PackingGroup ]
III | [HS Code ]
29041000 | [Safety Profile]
Poison by intravenous
route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A skin and
severe eye irritant. When heated to decomposiuon
it emits tomc fumes of NazO. See also
SULFONATES | [Hazardous Substances Data]
25155-30-0(Hazardous Substances Data) | [Toxicity]
LD50 in mice: 2 g/kg orally; 105 mg/kg i.v. (Hopper) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [General Description]
Sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate is a white to light yellow flakes, granules or powder. SODIUM DODECYLBENZENESULFONATE (BRANCHED CHAIN)(25155-30-0) is soluble in water. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. SODIUM DODECYLBENZENESULFONATE (BRANCHED CHAIN)(25155-30-0) is used as a synthetic detergent. | [Reactivity Profile]
SODIUM DODECYLBENZENESULFONATE is incompatible with strong oxidizers. | [Air & Water Reactions]
SODIUM DODECYLBENZENESULFONATE (BRANCHED CHAIN) is soluble in water. | [Health Hazard]
Minor skin and eye irritant. INGESTION: May cause vomiting, diarrhea, and intestinal distension. | [Description]
Sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate is a series of organic compounds with the formula C12H25C6H4SO3Na. It is a colourless salt with useful properties as a surfactant. It is usually produced as a mixture of related sulfonates. It is a major component of laundry detergent. | [Chemical Properties]
white or light yellow flakes | [Uses]
A surfactant used in proteomics research. | [Uses]
Anionic detergent. | [Flammability and Explosibility]
Nonflammable | [Industrial uses]
These frothers are mixtures of alcohols containing 6–8 carbon atoms. They were at one
time marketed by DuPont and they are tailored frothers for specific ore types. The bestknown
frother from this group is methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC) and 2-ethyl hexanol.
Aliphatic alcohol frothers are used as mixtures of different carbon lengths and as a
mixture of hydrocarbon oils.
| [Synthesis]
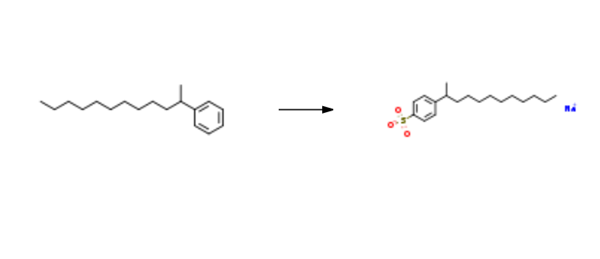
Sodium dodecylbenzenesulphonate is synthesised using 2-phenyldodecane as raw material by chemical reaction. The specific synthesis steps are as follows:
To a 5 L round bottom flask equipped with mechanical stirrer and an addition funnel was added octadecane and 2-phenyldodecane mixture ( 1.73 kg, 28%> 2-phenyldodecane). The reaction mixture was sparged with argon, warmed to 35°C and 1.25 weight % of oleum (632 g, 1.58 mol) was added dropwise, via addition funnel, to reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was stirred for 1.5 hours at room temperature. Upon completion, the reaction mixture was heated to 50°C and transferred to a separatory funnel and allowed to separate. The bottom layer was added slowly to a stirred solution of 15%> NaOH (aq) (2 L) at 10°C. Upon complete addition the resulting suspension was stirred for an additional 60 minutes. The solid was subsequently isolated by filtration and washed twice with ice-cold water. The solids were air dried for 16 hours and vacuum dried at 80°C to yield sodium, 4-(dodecan-2-yl) benzenesulfonate (555 g, 80.8% yield, 98.5% purity). lH NMR (400 MHz, (CD3)2S0/CDC13) δ 0.84 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H), 0.95- 1.38 (m, 19H), 1.51 (pquart, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 2.65 (psext, J = 7.0 Hz, 1 H), 7.1 1 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.56 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, (CD3)2S0/CDC13) δ 13.8, 22.0, 22.1 , 27.0, 28.9, 28.9, 28.9, 28.9, 31.2, 37.6, 38.8, 125.4, 125.8, 145.3, 147.7.
 | [Purification Methods]
It crystallises from propan-2-ol or H2O. [Gray et al. J Org Chem 20 515 1955, Beilstein 11 IV 514.] | [Alkyl benzene sulfonates]
Most sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonates are a member of the linear alkyl benzene sulfonates, meaning that the dodecyl group (C12H25) is un branched. This dodecyl chain is attached at the 4- position of the benzene sulfonate group. Linear dodecyl-4-benzene sulfonate anions can exist in six isomers (ignoring optical isomers), depending on the carbon of the dodecyl group that is attached to the benzene ring. The isomer shown below left is 4-(5-dodecyl ) benzene sulfonate (4 indicating the position of the benzene ring, 5 indicating the position on the dodecane chain). Branched isomers, e.g. those derived from tetramerized propylene, are also known (below right) but are not as widely used because they biodegrade too slowly.
Production
Trillions of kilograms are produced annually. Given the large scale of the application, the alkyl benzene sulfonates have been prepared by many methods. In the most common route, benzene is alkylated by long chain mono alkenes (e.g. dodecene) using hydrogen fluoride as a catalyst. The purified dodecyl benzenes (and related derivatives) are then sulfonated with sulfur trioxide to give the sulfonic acid. The sulfonic acid is subsequently neutralized with sodium hydroxide. | [Environmental considerations]
Biodegradability has been well studied , and is affected by the isomerization (branching). The salt has an LD50 of 2.3 mg / liter for fish , about 4x more toxic than the branched tetra propylene benzene sulfonate. It is however biodegraded more rapidly. Oxidative degradation initiates at the alkyl chain. |
|
|